Asp.Net Web API 导航
Asp.Net Web API第一课:入门http://www.cnblogs.com/aehyok/p/3432158.html
前言
CRUD代表着 Create、Read、Update、Delete,这是四个基本的数据库操作。许多HTTP服务模型也通过Rest或者Rest-like APIs实现CRUD操作。
在本教程中,我将建立一个非常简单的Web API来管理一个产品列表,和第一课中的Model是一样的,同样每个产品包括名称、价格和类别(如玩具或硬盘),在加上一个产品的ID。
本次教程的开发工具使用的仍然是VS2013。
这个产品的API将包含如下几个方法。
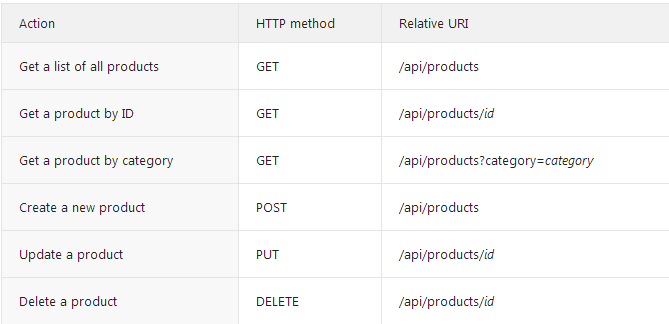
请注意某些Uri路径中包含产品ID。例如,为得到ID为28的这个产品,客户端将发送一个Get请求:http://hostname/api/products/28。
这个产品的API定义了两个资源类型的Uri
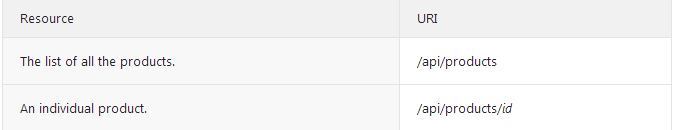
这四个主要的 HTTP 方法(GET、PUT、POST 和 DELETE)可以映射到以下的 CRUD 操作:
请注意:其中的PUT方法将替换掉产品的整个实体。也就是说,客户端被期望发送一个完整的被更新产品实体信息。如果你想支持部分更新,这个PATCH方法可以被选择。在本教程中,PATCH方法将不会得到支持。
在这个教程当中我将会使用VS2013来创建一个简单的示例。提供本文项目示例下载链接http://pan.baidu.com/s/1ePYLw
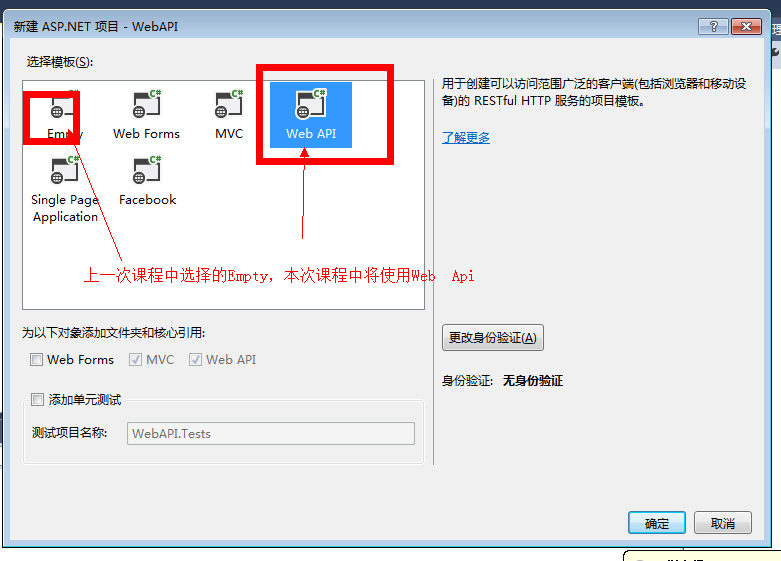
创建一个新的 Web API项目
关于创建项目,如果您不太清楚,可以查看第一课中相关内容介绍,当然本教程创建的项目和上一课中的又有所区别。
添加一个Model
这个模型和上一次课程中的也是保持一致。
直接上代码
namespace WebAPI.Models { public class Product { public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } public decimal Price { get; set; } } }
添加一个Repository
首先我们需要存储产品的集合。分开收集我们的服务实现是一个好的主意。这种方式,我们可以改变后备存储,而不用修改服务类的实现。这种模式的设计叫做仓储模式。首先建立一个接口。
namespace WebAPI.Models { interface IProductRepository { IEnumerable<Product> GetAll(); Product Get(int id); Product Add(Product item); void Remove(int id); bool Update(Product item); } }
暂时我们把接口和实体类放在了一个文件夹下。现在在Models文件夹下添加另外一个类,这个类将集成IProductRepository接口。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Web; namespace WebAPI.Models { public class ProductRepository { private List<Product> products = new List<Product>(); private int _nextId = 1; public ProductRepository() { Add(new Product { Name = "Tomato soup", Category = "Groceries", Price = 1.39M }); Add(new Product { Name = "Yo-yo", Category = "Toys", Price = 3.75M }); Add(new Product { Name = "Hammer", Category = "Hardware", Price = 16.99M }); } public IEnumerable<Product> GetAll() { return products; } public Product Get(int id) { return products.Find(p => p.Id == id); } public Product Add(Product item) { if (item == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("item"); } item.Id = _nextId++; products.Add(item); return item; } public void Remove(int id) { products.RemoveAll(p => p.Id == id); } public bool Update(Product item) { if (item == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("item"); } int index = products.FindIndex(p => p.Id == item.Id); if (index == -1) { return false; } products.RemoveAt(index); products.Add(item); return true; } } }
添加一个Web API控制器
如果你已经使用过Asp.Net MVC,那么你已经很熟悉控制器了。在Asp.Net Web API,一个控制器就是一个处理来自客户端的HTTP请求的一个class。
有关如何添加控制器的也可以参见第一课中的内容,在这里就不进行过多的介绍了。直接添加一个ProductsController。
添加一个包含IProductRepository实例的字段。
public class ProductsController : ApiController { static readonly IProductRepository repository = new ProductRepository(); }
在控制器中调用new ProductRepository不是最好的设计,因为它关系到特定的实现的IProductRepository控制器。更好的方法,请参阅之后有关依赖注入的文章介绍。
下面进行一一列举每个HTTP方法。
第一个:为了得到所有的产品信息列表,在控制器中添加的方法如下:
public IEnumerable<Product> GetAllProducts() { return repository.GetAll(); }
这个方法的名称是以Get开头,所以通过约定它映射为Get请求。此外,因为不包含参数,它映射到一个不包含在路径中的id线段的URI。
第二个:通过产品ID获取一个产品信息,在控制器中添加的方法如下:
public Product GetProduct(int id) { Product item = repository.Get(id); if (item == null) { throw new HttpResponseException(HttpStatusCode.NotFound); } return item; }
这个方法的名称是以Get开头,但是这个方法有一个名字为id的参数。这个参数被映射到URI路径中的id一段。这个Asp.Net Web API框架自动把ID参数转换为正确的int数据类型。
如果id无效,那么就会抛出一个HttpReponseException的异常。此异常将由框架转换成一个404错误。
第三个:按照类别查找产品信息,在控制器中添加的方法如下:
public IEnumerable<Product> GetProductsByCategory(string category) { return repository.GetAll().Where( p => string.Equals(p.Category, category, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase)); }
如果请求的URI中包含查询字符串,这个WebApi试图在控制器方法的参数中来匹配查询字符串。因此,窗体中的“api/products?category=category”的URI将映射到此方法。
第四个:添加一个新的产品,在控制器中添加的方法如下:
public Product PostProduct(Product item) { item = repository.Add(item); return item; }
请注意这个方法的两个事情:
此实现会工作,但它还很不完整。理想情况下,我们希望的 HTTP 响应,包括以下内容:
Asp.Net Web API使它容易操作HTTP响应消息。这是改善后的代码:
public HttpResponseMessage PostProduct(Product item) { item = repository.Add(item); var response = Request.CreateResponse<Product>(HttpStatusCode.Created, item); string uri = Url.Link("DefaultApi", new { id = item.Id }); response.Headers.Location = new Uri(uri); return response; }
请注意:此方法返回类型现在是HttpResponseMessage。通过返回HttpResponseMessage而不是产品,我们可以控制的 HTTP 响应消息,包括状态代码和位置标头的详细信息。
CreateResponse 方法将会创建 HttpResponseMessage,并自动将 Product 对象的序列化表示形式写入到响应消息的正文中。
此示例不会验证该
Product。模型验证有关的信息,请参见Asp.Net Web API 模型验证。(暂未实现)
第四个:通过PUT更新产品,在控制器添加的代码如下:
public void PutProduct(int id, Product product) { product.Id = id; if (!repository.Update(product)) { throw new HttpResponseException(HttpStatusCode.NotFound); } }
方法名称以Put开头,这样 Web API 就能够将其与 PUT 请求相匹配。这个方法有两个参数,一个是产品ID和更新的产品。ID参数是从URI中获得的,product参数是从请求正文反序列化得来的。默认情况下,ASP.NET Web API 框架从路由获取简单的参数类型,从请求正文获取复杂的类型。
第五个:删除产品,在控制器添加的代码如下:
public void DeleteProduct(int id) { Product item = repository.Get(id); if (item == null) { throw new HttpResponseException(HttpStatusCode.NotFound); } repository.Remove(id); }
如果删除请求成功,它可以返回状态 200 (OK) 与实体的描述该状态 ;如果删除仍然挂起,则返回状态 202 (已接受);或状态与没有实体正文 204 (无内容)。在这种情况下, DeleteProduct方法具有void返回类型,因此 ASP.NET Web API 自动转换此状态代码 204 (无内容)。
总结
在本次教程中,主要来探讨Wep API中的CRUD操作,针对前台的如何调用,这个在第一课中也有简单的使用。
本次教程参考的主要文章链接为:http://www.asp.net/web-api/overview/creating-web-apis/creating-a-web-api-that-supports-crud-operations