上次我们学习了Vue.js的基础,并且通过综合的小实例进一步的熟悉了Vue.js的基础应用。今天我们就继续讲讲Vue.js的组件,更加深入的了解Vue,js的使用。首先我们先了解一下什么是Vue.js的组件,组件其实就是页面组成的一部分,它是一个具有独立的逻辑和功能或页面,组件可以扩展 HTML 元素,封装可重用的代码。组件系统让我们可以用独立可复用的小组件来构建大型应用,几乎任意类型的应用的界面都可以抽象为一个组件树,如下图:

接下来我们就仔细讲讲组件的使用吧。
1 全局组件
以下就是我们注册的第一个简单的全局组件my-Com。所有实例都能用全局组件,组件在注册之后,便可以作为自定义元素class="Apple-converted-space"> <my-Com></my-Com> 在一个实例的模板中使用。但是要注意全局组件必须写在vue实例之前,才会在跟元素 下面生效,模板里面第一级只能有一个标签,不能并行。
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title></title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <div id="app"> 9 <my-Com></my-Com> 10 </div> 11 </body> 12 <script type="text/javascript" src="js/vue.js" ></script> 13 <script type="text/javascript"> 14 // 注册 15 Vue.component('myCom', { 16 template: '<h1>自定义组件!</h1>' 17 }) 18 // 创建根实例 19 new Vue({ 20 el: '#app' 21 }) 22 </script> 23 </html>

2 局部组件
以下就是我们注册的第一个简单的局部组件。其实可以不必把每个组件都注册到全局的,局部组件可以直接在vue实例里,使用components注册,这种封装也适用于其它可注册的 Vue 功能,比如指令。我们建议将模板定义在全局变量。
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title></title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <div id="app"> 9 <mycom></mycom> 10 </div> 11 </body> 12 <script type="text/javascript" src="js/vue.js" ></script> 13 <script type="text/javascript"> 14 var Child = { 15 template: '<h1>自定义组件!</h1>' 16 } 17 18 // 创建根实例 19 new Vue({ 20 el: '#app', 21 components: { 22 // mycom 将只在父模板可用 23 'mycom': Child 24 } 25 }) 26 </script> 27 </html>

3 使用Prop传递数据
组件设计初衷就是要配合使用的,最常见的就是形成父子组件的关系:组件 A 在它的模板中使用了组件 B。在 Vue 中,父子组件的关系可以总结为 prop 向下传递,事件向上传递。父组件通过 prop 给子组件下发数据,子组件通过事件给父组件发送消息。组件实例的作用域是孤立的。这意味着不可以 在子组件的模板内直接引用父组件的数据。prop 是父组件用来传递数据的一个自定义属性。父组件的数据需要通过 props 把数据传给子组件,子组件需要显式地用 props 选项声明 "prop"。
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title></title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <div id="app"> 9 <com message="hello!"></com> 10 </div> 11 </body> 12 <script type="text/javascript" src="js/vue.js" ></script> 13 <script type="text/javascript"> 14 // 注册 15 Vue.component('com', { 16 // 声明 props 17 props: ['message'], 18 template: '<span>{{ message }}</span>' 19 }) 20 // 创建根实例 21 new Vue({ 22 el: '#app' 23 }) 24 </script> 25 </html>
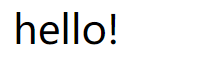
4 动态Prop
动态Prop 类似于用 v-bind 绑定 HTML 特性到一个表达式,也可以用 v-bind 动态绑定 props 的值到父组件的数据中。每当父组件的数据变化时,该变化也会传导给子组件。
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title></title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <div id="app"> 9 <div> 10 <input v-model="parent"> 11 <br> 12 <child v-bind:message="parent"></child> 13 </div> 14 </div> 15 </body> 16 <script type="text/javascript" src="js/vue.js" ></script> 17 <script type="text/javascript"> 18 // 注册 19 Vue.component('child', { 20 // 声明 props 21 props: ['message'], 22 template: '<span>{{ message }}</span>' 23 }) 24 // 创建根实例 25 new Vue({ 26 el: '#app', 27 data: { 28 parent: '父组件内容' 29 } 30 }) 31 </script> 32 </html>

当然我们也能可以使用 v-bind 的缩写语法:
1 <child :my-message="parentMsg"></child>
以下实例中将 v-bind 指令将com传到每一个重复的组件中。
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title></title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <div id="app"> 9 <ol> 10 <item v-for="item in sites" v-bind:com="item"></item> 11 </ol> 12 </div> 13 </body> 14 <script type="text/javascript" src="js/vue.js" ></script> 15 <script type="text/javascript"> 16 Vue.component('item', { 17 props: ['com'], 18 template: '<li>{{ com.text }}</li>' 19 }) 20 new Vue({ 21 el: '#app', 22 data: { 23 sites: [ 24 { text: 'Vue.js' }, 25 { text: 'BootStrap' }, 26 { text: 'JQuery' } 27 ] 28 } 29 }) 30 </script> 31 </html>

注意: prop 是单向绑定的:当父组件的属性变化时,将传导给子组件,但是不会反过来。这是为了防止子组件无意间修改了父组件的状态,来避免应用的数据流变得难以理解。但是,每次父组件更新时,子组件的所有 prop 都会更新为最新值。这意味着不可以在子组件内部改变 prop。如果这么做了的话,Vue 会在控制台出现警告。
5 使用 v-on 绑定自定义事件
父组件是使用 props 传递数据给子组件,但如果子组件要把数据传递回去,就需要使用自定义事件,父组件可以在使用子组件的地方直接用 v-on 来监听子组件触发的事件。
我们可以使用 v-on 绑定自定义事件, 每个 Vue 实例都实现了事件接口,即:
$on(eventName) 监听事件$emit(eventName) 触发事件1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title></title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <div id="app"> 9 <div id="example"> 10 <p>{{ num }}</p> 11 <button-counter v-on:vue="com"></button-counter> 12 </div> 13 </div> 14 </body> 15 <script type="text/javascript" src="js/vue.js" ></script> 16 <script type="text/javascript"> 17 Vue.component('button-counter', { 18 template: '<button v-on:click="vue">{{ counter }}</button>', 19 data: function () { 20 return { 21 counter: 0 22 } 23 }, 24 methods: { 25 vue: function () { 26 this.counter += 1 27 this.$emit('vue') 28 } 29 }, 30 }) 31 new Vue({ 32 el: '#example', 33 data: { 34 num: 0 35 }, 36 methods: { 37 com: function () { 38 this.num += 1 39 } 40 } 41 }) 42 </script> 43 </html>

6 给组件绑定原生事件
如果想在某个组件的根元素上监听一个原生事件。可以使用 v-on 的修饰符 .native。
1 <comv-on:click.native="something"></com>
7 自定义指令
默认情况下,一个组件的 v-model 会使用 value prop 和 input 事件。Vue 也允许注册自定义指令。
以下例子就是我们注册的一个全局指令 v-focus, 该指令的功能就是在页面加载时,元素会自动获得焦点。
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title></title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <div id="app"> 9 <p>页面载入时,input 元素会自动获取焦点:</p> 10 <input v-focus> 11 </div> 12 </body> 13 <script type="text/javascript" src="js/vue.js" ></script> 14 <script type="text/javascript"> 15 Vue.directive('focus', { 16 inserted: function (el) { 17 // 聚焦元素 18 el.focus() 19 } 20 }) 21 // 创建根实例 22 new Vue({ 23 el: '#app' 24 }) 25 </script> 26 </html>
8 Vue 路由实例应用
Vue框架的兼容性非常好,可以很好的跟其他第三方的路由框架进行结合。Vue官方给出了路由的方案 --- vue-router。下面我们就使用Vue的路由实现简单的单页应用。
1 <script type="text/javascript" src="js/vue.js" ></script> 2 <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue-router/dist/vue-router.js"></script>
使用 router-link 组件来导航.,通过传入 `to` 属性指定链接,<router-link> 默认会被渲染成一个 `<a>` 标签。
1 <router-link to="/Vue">路由</router-link> 2 <router-link to="/BootStrap">栅格</router-link>
定义(路由)组件,可以从其他文件 import 进来。
1 const Foo = { 2 template: '<div>Vue</div>' 3 } 4 const Bar = { 5 template: '<div>BootStrap</div>' 6 }
定义路由,每个路由应该映射一个组件。 其中"component" 可以是通过 Vue.extend() 创建的组件构造器,或者只是一个组件配置对象。
1 const routes = [{ 2 path: '/Vue', 3 component: Foo 4 }, 5 { 6 path: '/BootStrap', 7 component: Bar 8 } 9 ]
1 const router = new VueRouter({ 2 routes 3 })
要通过 router 配置参数注入路由,从而让整个应用都有路由功能。
1 const app = new Vue({ 2 router 3 }).$mount('#app')
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title></title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <div id="app"> 9 <h1>Vue 路由实例</h1> 10 11 <p> 12 <router-link to="/Vue">路由</router-link> 13 <router-link to="/BootStrap">栅格</router-link> 14 </p> 15 <!-- 路由出口 --> 16 <!-- 路由匹配到的组件将渲染在这里 --> 17 <router-view></router-view> 18 </div> 19 </body> 20 <script type="text/javascript" src="js/vue.js" ></script> 21 <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue-router/dist/vue-router.js"></script> 22 <script type="text/javascript"> 23 24 const Foo = { 25 template: '<div>Vue</div>' 26 } 27 const Bar = { 28 template: '<div>BootStrap</div>' 29 } 30 31 const routes = [{ 32 path: '/Vue', 33 component: Foo 34 }, 35 { 36 path: '/BootStrap', 37 component: Bar 38 } 39 ] 40 41 const router = new VueRouter({ 42 routes 43 }) 44 45 const app = new Vue({ 46 router 47 }).$mount('#app') 48 49 50 </script> 51 </html>

9 综合实例应用
上边已经了解了Vue路由,下边就是一个小小的综合实例,通过点击按钮,在当前页面切换不同的组件。
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 4 <head> 5 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 6 <title>综合实例</title> 7 <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> 8 <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue-router/dist/vue-router.js"></script> 9 <style> 10 ul, 11 li { 12 list-style: none; 13 } 14 15 ul { 16 overflow: hidden; 17 } 18 19 li { 20 float: left; 21 width: 100px; 22 } 23 24 h1 { 25 background-color: #98D361; 26 } 27 28 h2 { 29 background-color: #FF9209; 30 } 31 32 h3 { 33 background-color: #D84C29; 34 } 35 </style> 36 </head> 37 38 <body> 39 <div id="app"> 40 <bar> </bar> 41 <hr> 42 <p>buttons: {{ buttons }}</p> 43 <router-view class="items"></router-view> 44 <footer-bar></footer-bar> 45 </div> 46 <script> 47 var topbarTemp = ` 48 <nav> 49 <ul> 50 <li v-for="item in list"> 51 <router-link :to="item.url">{{ item.name }}</router-link> 52 </li> 53 </ul> 54 </nav> 55 `; 56 // 定义组件:topbar 57 Vue.component('bar', { 58 template: topbarTemp, 59 data: function() { 60 return { 61 list: [{ 62 name: '小说', 63 url: '/story' 64 }, 65 { 66 name: '动漫', 67 url: '/carton' 68 }, 69 { 70 name: '绘画', 71 url: '/draw' 72 }, 73 ] 74 } 75 } 76 }); 77 78 Vue.component('footer-bar', { 79 template: ` 80 <footer> 81 <p>Vue 路由<p> 82 </footer> 83 ` 84 }); 85 86 var story = { 87 template: `<div> <h1>{{ msg }}<h1></div>`, 88 data: function() { 89 return { 90 msg: 'Vue 基础' 91 } 92 } 93 }; 94 95 var carton = { 96 template: `<div> <h2>{{ msg }}<h2></div>`, 97 data: function() { 98 return { 99 msg: 'Vue 组件' 100 } 101 } 102 } 103 104 var draw = { 105 template: `<div> <h3>{{ msg }}<h3></div>`, 106 data: function() { 107 return { 108 msg: 'Vue 路由实例' 109 } 110 } 111 } 112 113 // 定义路由对象 114 var router = new VueRouter({ 115 routes: [{ 116 path: '/story', 117 component: story 118 }, 119 { 120 path: '/carton', 121 component: carton 122 }, 123 { 124 path: '/draw', 125 component: draw 126 } 127 ] 128 }); 129 130 // 初始化一个Vue实例 131 var app = new Vue({ 132 el: '#app', 133 data: { 134 buttons: '点击按钮,切换不同组件' 135 }, 136 router: router 137 }); 138 </script> 139 </body> 140 141 </html>

Vue知识还有很多,希望通过对Vue一些基础知识的学习,对于正在学习前端的知识的你可以有所帮助。