上一篇为大家分享了关于AsyncTask的使用,本篇结合AsyncTask为大家介绍一个我们经常看到的一个效果,就是当我们点击登录后,会弹出一个请等待的小窗体,这个效果是如何实现的呢?本篇我就带大家简单实现一下。
首先请看效果图:
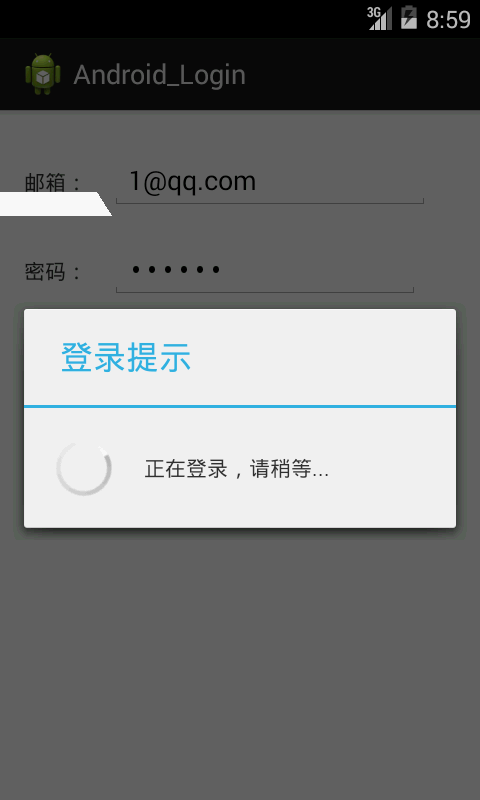
就是当我们填写好个人信息后,点击登录,然后就进入了这个界面,好了,下面我们一起来实现一下。
第一步:布局文件:activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <TextView android:id="@+id/textView1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_marginTop="22dp" android:text="邮箱:" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/editText1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignBaseline="@+id/textView1" android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/textView1" android:layout_marginLeft="15dp" android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/textView1" android:ems="10" android:inputType="textEmailAddress" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/editText1" android:layout_marginTop="40dp" android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/editText1" android:text="密码:" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/editText2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignBaseline="@+id/textView2" android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/textView2" android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/editText1" android:ems="10" android:inputType="textPassword" /> <Button android:id="@+id/button1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/editText2" android:layout_marginTop="43dp" android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/textView2" android:text="登录" /> <Button android:id="@+id/button2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignBaseline="@+id/button1" android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/button1" android:layout_marginLeft="34dp" android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/button1" android:text="注册" /> </RelativeLayout>
第二步:主Activity:
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener{ private EditText mEditText1; private EditText mEditText2; private Button mButton1; private Button mButton2; private String email; private String password; private myAsyncTast tast; private ProgressDialog dialog = null; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); init();//对控件进行初始化 } private void init() { mEditText1 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText1); mEditText2 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText2); mButton1 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1); mButton2 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button2); mButton1.setOnClickListener(this); mButton2.setOnClickListener(this); } @Override public void onClick(View arg0) { switch (arg0.getId()) { case R.id.button1: getEditTextValue();//获得用户的输入 tast = new myAsyncTast();//创建AsyncTask tast.execute();//启动AsyncTask break; case R.id.button2: Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "注册", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); break; } } private void getEditTextValue() { email = mEditText1.getText().toString(); password = mEditText2.getText().toString(); } class myAsyncTast extends AsyncTask<Void, Integer, Void>{ @Override protected void onPreExecute() { super.onPreExecute(); dialog = ProgressDialog.show(MainActivity.this, "登录提示", "正在登录,请稍等...", false);//创建ProgressDialog } @Override protected Void doInBackground(Void... arg0) { Http http = new Http(); int n = http.send(email, password);//发送给服务器 publishProgress(n); return null; } @Override protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... values) { super.onProgressUpdate(values); dialog.dismiss();//关闭ProgressDialog if(values[0]==1){ Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "登录成功", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); }else{ Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "登录失败", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } } } }
第三步:服务器端(简单起见,仅仅是模拟)
/* * 模拟服务器端 */ public class Http { private int n = 0; public int send(String email, String password){ try { Thread.sleep(5000);//模拟网络加载 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } if(email.equals("1@qq.com")&&password.equals("123456")){ n=1; } return n; } }
在这里需要说明的时,当我们真正开发时,需要向服务器发送数据时,我们需要在:AndroidManifest.xml文件中声明访问网络权限。
对于上面的内容,AsyncTask上一篇已经为大家进行了详细的介绍,如果看本篇博客你赶脚有些吃力,请仔细研究一下上一篇的博客,这里就不再赘述,对于ProgressDialog本人也是初次使用,不过可以为大家推荐一篇博客:http://blog.csdn.net/caesardadi/article/details/11982721,这里介绍的非常的详细,有兴趣的童鞋可以好好研究一下。