首先介绍一下基本类数据类型对应的包装类中Cache类(包装类中的静态内部类),例如Integer对应的Cache类为IntegerCache。下面附上Integer类中的IntegerCache源码:
private static class IntegerCache {
? ? ? ? static final int low = -128;
? ? ? ? static final int high;
? ? ? ? static final Integer cache[];
?
? ? ? ? static {
? ? ? ? ? ? // high value may be configured by property
? ? ? ? ? ? int h = 127;
? ? ? ? ? ? String integerCacheHighPropValue =
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
? ? ? ? ? ? if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? i = Math.max(i, 127);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? // Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low));
? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ? high = h;
?
? ? ? ? ? ? cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];
? ? ? ? ? ? int j = low;
? ? ? ? ? ? for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? cache[k] = new Integer(j++);
? ? ? ? }
?
? ? ? ? private IntegerCache() {}
? ? }
下面就以Integer为例简单说下自动装箱和拆箱的过程吧。
1、Integer的自动装箱
Integer a = 100;//这条语句是怎么执行的呢?
其实只是简单的调用了Integer中的静态方法:public static Integer valueOf(int i);
??看到上面的语句大家是不是豁然开朗了呢,下面让我们再看下valueOf方法为我们做了一些什么事情:
? ? public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
? ? ? ? assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;
? ? ? ? if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
? ? ? ? ? ? return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
? ? ? ? return new Integer(i);
? ? }
?从上面的IntegerCache源码中我们知道它其实是创建了一个静态的Integer数组。并对应包装了-128-127之间对应整型数值(high value may be configured by property)。这就可以解释编程中遇到的一些“奇怪”的现象了:
Integer a = 100;
Integer b = 100;
System.out.println(a == b);//true
//-----------------------------------------
Integer a = 128;
Integer b = 128;
System.out.println(a == b);//false
2、Integer的拆箱
Integer a = 100;
int b = a;
上述的b =a语句其实是调用了Integer的静态方法ntValue();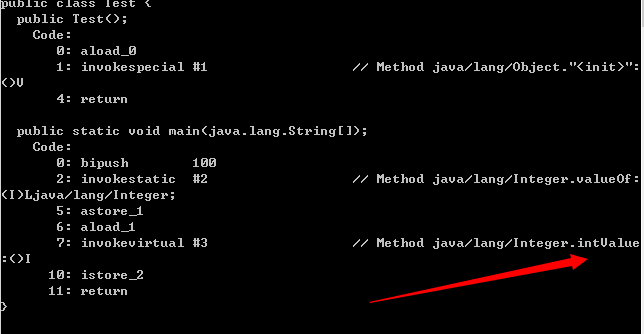
?包装类大同小异,有兴趣的java爱好者可以查看源码进行分析。
上述都是个人学习中遇到问题和解决问题过程中所学所悟,如若个人理解有偏差敬请谅解。
?
?