在常规的信息系统中, 我们有需要动态多条件查询的情况, 例如UI上有多个选择项可供用户选择多条件查询数据.
那么在.net平台Entity Framework下, 我们用Lambda表达式树如何实现, 这里我们需要一个PredicateBuilder的UML类图:
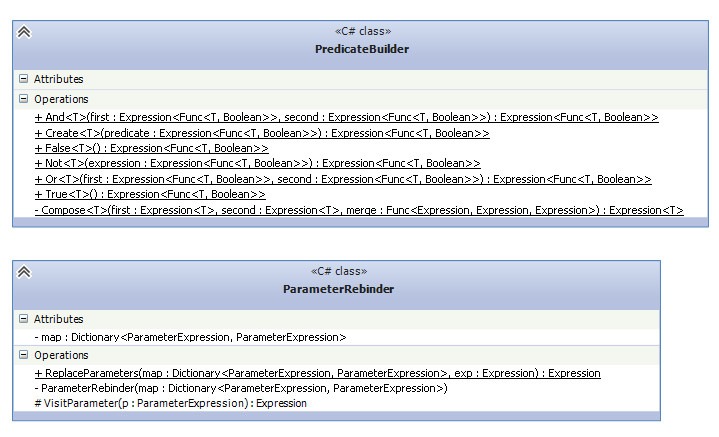
实现的代码是这样的:
class="alt"> /// <summary>
/// Enables the efficient, dynamic composition of query predicates.
/// </summary>
public static class PredicateBuilder
{
/// <summary>
/// Creates a predicate that evaluates to true.
/// </summary>
public static Expression<Func<T, bool>> True<T>() { return param => true; }
/// <summary>
/// Creates a predicate that evaluates to false.
/// </summary>
public static Expression<Func<T, bool>> False<T>() { return param => false; }
/// <summary>
/// Creates a predicate expression from the specified lambda expression.
/// </summary>
public static Expression<Func<T, bool>> Create<T>(Expression<Func<T, bool>> predicate) { return predicate; }
/// <summary>
/// Combines the first predicate with the second using the logical "and".
/// </summary>
public static Expression<Func<T, bool>> And<T>(this Expression<Func<T, bool>> first, Expression<Func<T, bool>> second)
{
return first.Compose(second, Expression.AndAlso);
}
/// <summary>
/// Combines the first predicate with the second using the logical "or".
/// </summary>
public static Expression<Func<T, bool>> Or<T>(this Expression<Func<T, bool>> first, Expression<Func<T, bool>> second)
{
return first.Compose(second, Expression.OrElse);
}
/// <summary>
/// Negates the predicate.
/// </summary>
public static Expression<Func<T, bool>> Not<T>(this Expression<Func<T, bool>> expression)
{
var negated = Expression.Not(expression.Body);
return Expression.Lambda<Func<T, bool>>(negated, expression.Parameters);
}
/// <summary>
/// Combines the first expression with the second using the specified merge function.
/// </summary>
static Expression<T> Compose<T>(this Expression<T> first, Expression<T> second, Func<Expression, Expression, Expression> merge)
{
// zip parameters (map from parameters of second to parameters of first)
var map = first.Parameters
.Select((f, i) => new { f, s = second.Parameters[i] })
.ToDictionary(p => p.s, p => p.f);
// replace parameters in the second lambda expression with the parameters in the first
var secondBody = ParameterRebinder.ReplaceParameters(map, second.Body);
// create a merged lambda expression with parameters from the first expression
return Expression.Lambda<T>(merge(first.Body, secondBody), first.Parameters);
}
/// <summary>
/// ParameterRebinder
/// </summary>
class ParameterRebinder : ExpressionVisitor
{
/// <summary>
/// The ParameterExpression map
/// </summary>
readonly Dictionary<ParameterExpression, ParameterExpression> map;
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="ParameterRebinder"/> class.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="map">The map.</param>
ParameterRebinder(Dictionary<ParameterExpression, ParameterExpression> map)
{
this.map = map ?? new Dictionary<ParameterExpression, ParameterExpression>();
}
/// <summary>
/// Replaces the parameters.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="map">The map.</param>
/// <param name="exp">The exp.</param>
/// <returns>Expression</returns>
public static Expression ReplaceParameters(Dictionary<ParameterExpression, ParameterExpression> map, Expression exp)
{
return new ParameterRebinder(map).Visit(exp);
}
/// <summary>
/// Visits the parameter.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="p">The p.</param>
/// <returns>Expression</returns>
protected override Expression VisitParameter(ParameterExpression p)
{
ParameterExpression replacement;
if (map.TryGetValue(p, out replacement))
{
p = replacement;
}
return base.VisitParameter(p);
}
}
}
UnitTest的片断代码, 一个产品查询的场景:
var myProduct=pr.Repository.Find(
BuildFindByAllQuery(productName, beignUpdateDate, endUpdateDate) ,
e => e.UpdatedTime,
pageIndex,
pageSize);
Assert.IsTrue(myProduct.Count>0);
UnitTest使用到 生成查询条件 的 私有方法:
/// <summary>
/// Builds the find by all query.
/// </summary>
private static Expression<Func<Product, bool>> BuildFindByAllQuery(string productName,DateTime? beignUpdateDate, DateTime? endUpdateDate)
{
var list = new List<Expression<Func<Product, bool>>>();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(productName)) list.Add(c => c.ProductName == productName);
if (beignUpdateDate != null) list.Add(c => c.UpdatedTime >= beignUpdateDate);
if (endUpdateDate != null) list.Add(c => c.UpdatedTime <= endUpdateDate);
//Add more condition
Expression<Func<Product, bool>> productQueryTotal = null;
foreach (var expression in list)
{
productQueryTotal = expression.And(expression);
}
return productQueryTotal;
}
上面的方法中由三个条件动态组成, 一个是匹配productName, 另两个是beginUpdateDate与endUpdateDate. 在判断它们是否为时, 构建最终查询条件集合.
最后把结果传给某个Repository类, 完成相应的数据访问.
是不是很简单, 希望对您的软件开发有帮助.
您可能感兴趣的文章:
表达式树中递归方法
IEnumerable的扩展方法
.net3.5下使用LINQ递归算法实现简洁代码
如有想了解更多软件开发资讯,请关注我的微信订阅号:

作者:Petter Liu
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/wintersun/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。
该文章也同时发布在我的独立博客中-Petter Liu Blog。