本文描述了在某种特殊场景下JDK编译器对 Java 基本类型的封包操作。
其原理非常简单,但是现象却非常 非常的迷惑人。可以让我们从另外一个角度看待jdk对基本类型的封包。
?
本文代码的原意是想找到一种当future超时后,可以尽量快的终止掉还在运行的future(事实上,future超时后(在主线程抛出超时异常后),future线程并不会停止,直到它运行结束,自然消亡。)
?
先上代码:
?
主函数:
?
class="java" name="code">package thread.InteruptTest;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* 通过线程池 开启一个线程去处理
* 模拟请求来时,开启一个线程处理请求的场景
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* User: liukunyang
* Date: 13-12-13
* Time: 上午9:51
* To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ThreadPoolExecutor exec = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, 10,
5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
TestThread tt = new TestThread();
exec.submit( tt );
//保持主线程存货, console端观察结果
System.in.read();
}
}
?
再看TestThread类:
?
package thread.InteruptTest;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
*
*
* 再启动一个线程池去提交 future 任务,该线程会在等待5秒后尝试获取future结果
* 并捕获future的超时异常。 最后设置future的 cancel 标志位,如果运行future的线程检查到标志位
* 改变就可以停止掉自己。
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* User: liukunyang
* Date: 13-12-13
* Time: 上午9:55
* To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
*/
public class TestThread extends Thread {
private ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor =
new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, 10, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
;
@Override
public void run() {
ThreadLocal th = new ThreadLocal();
DivideFuture df = new DivideFuture();
final Future future = threadPoolExecutor.submit(df);
try {
//5秒后在超时,
//给子线程5秒的时间打印 变量isC1,isC2,isC3的值
System.out.println( "1"+future.get(5,TimeUnit.SECONDS) );
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); //To change body of catch statement use File | Settings | File Templates.
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); //To change body of catch statement use File | Settings | File Templates.
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
System.out.println("超时拉");
}finally {
df.cancel();
future.cancel(true);
}
}
}
?
?
DivideFuture 类:
?
package thread.InteruptTest;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
/**
* 使用了三种不同类型的标志位,用来更好的说明 jdk对基本类型的封包操作
* 使用threadlocal的原因是 如果call 方法再调用了其他bean 的其他方法 仍然可以通过threadlocal 获取到cancel的标志位 这里为了简单没有增加调用其他方法的代码
* 但是不影响说明原理
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* User: liukunyang
* Date: 13-12-13
* Time: 上午11:05
* To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
*/
public class DivideFuture implements Callable {
private ThreadLocal thISC1 = new ThreadLocal();
private ThreadLocal<Boolean> thISC2 = new ThreadLocal<Boolean>();
private ThreadLocal thISC3 = new ThreadLocal();
private boolean isC1;
private Boolean isC2;
private RichBoolean isC3;
/**
* 修改isC1,isC2,isC3的标志位
*/
public void cancel(){
isC1 = true;
isC2 = true;
isC3.setValue(true);
}
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
//在线程调用时,再将isC初始化,
//是的threadLocal取到的线程是执行该方法的线程
isC1 = false;
isC2 = false;
isC3 = new RichBoolean(false);
thISC1.set(isC1);
thISC2.set(isC2);
thISC3.set(isC3);
// 每隔一秒获取一下标志位的值
for(int i=0; i<10 ; i++){
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch(Exception e){
}
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println( "变量 isC1 的值:" + isC1 );
System.out.println( "变量 isC1 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:" + thISC1.get() );
System.out.println( "变量 isC2 的值:" + isC2 );
System.out.println( "变量 isC2 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:" + thISC2.get() );
System.out.println( "变量 isC3 的值:" + isC3 );
System.out.println( "变量 isC3 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:" + thISC3.get() );
}
return "this is callable";
}
}
?
最后是辅助bean:
?
package thread.InteruptTest;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* User: liukunyang
* Date: 13-12-13
* Time: 下午2:03
* To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
*/
public class RichBoolean {
private boolean value;
public RichBoolean(boolean value) {
this.value = value;
}
public void setValue(boolean value) {
this.value = value;
}
public boolean isValue() {
return value;
}
}
?
?
猜猜打印的结果是啥?
?
注意红色和蓝色部分。
?
0
变量 isC1 的值:false
变量 isC1 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:false
变量 isC2 的值:false
变量 isC2 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:false
变量 isC3 的值:thread.InteruptTest.RichBoolean@5740bb
变量 isC3 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:thread.InteruptTest.RichBoolean@5740bb
1
变量 isC1 的值:false
变量 isC1 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:false
变量 isC2 的值:false
变量 isC2 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:false
变量 isC3 的值:thread.InteruptTest.RichBoolean@5740bb
变量 isC3 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:thread.InteruptTest.RichBoolean@5740bb
2
变量 isC1 的值:false
变量 isC1 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:false
变量 isC2 的值:false
变量 isC2 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:false
变量 isC3 的值:thread.InteruptTest.RichBoolean@5740bb
变量 isC3 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:thread.InteruptTest.RichBoolean@5740bb
3
变量 isC1 的值:false
变量 isC1 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:false
变量 isC2 的值:false
变量 isC2 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:false
变量 isC3 的值:thread.InteruptTest.RichBoolean@5740bb
变量 isC3 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:thread.InteruptTest.RichBoolean@5740bb
4
变量 isC1 的值:false
变量 isC1 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:false
变量 isC2 的值:false
变量 isC2 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:false
超时拉 变量 isC3 的值:thread.InteruptTest.RichBoolean@5740bb
变量 isC3 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:thread.InteruptTest.RichBoolean@5740bb
5变量 isC1 的值:true变量 isC1 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:false变量 isC2 的值:true变量 isC2 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:false变量 isC3 的值:thread.InteruptTest.RichBoolean@5740bb变量 isC3 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:thread.InteruptTest.RichBoolean@5740bb6变量 isC1 的值:true变量 isC1 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:false变量 isC2 的值:true变量 isC2 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:false变量 isC3 的值:thread.InteruptTest.RichBoolean@5740bb变量 isC3 通过ThreadLocal获取的值:thread.InteruptTest.RichBoolean@5740bb
?
?
想想为什么isC1,isC2中,future自身的变量变为了true 而他们对应的threadlocal中的值却还是false???????
难道是线程之间不能使用这种方式访问同一个变量?
那为什么isC3又是和我们想想的一样的?
?
其实仔细推导后发现原理非常简单
?
看看DivideFuture.class
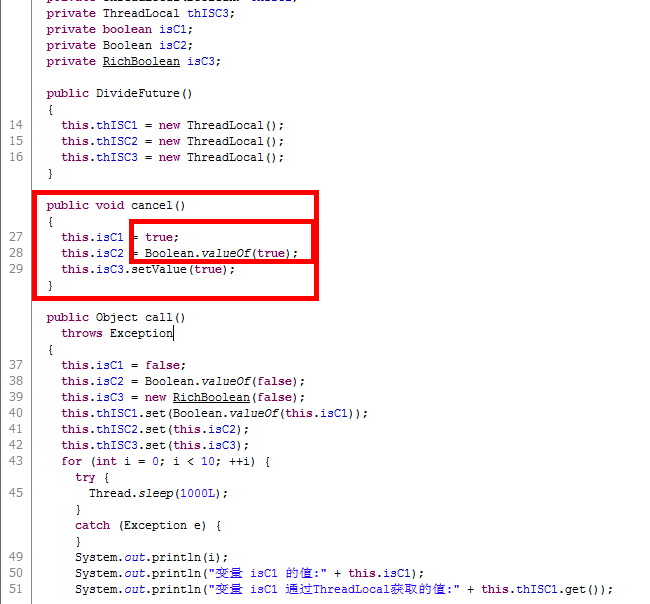
内层的红色框中说明,我们cancel时是将isC2的变量重新赋值了,也就是说isC2指向了一个新的对象 而thISC2 里面还是老的值,所以他们打印出来的结果不同。
?
同理,isC1 = true 这句话因为jdk 封包操作的原因类似isC2也是重新new了一个对象,isC1指向了新对象,而thISC1中还是老对象。所以导致了上述的结果。
?
也算是对jdk封包,解包操作的一个新
理解吧。
?
?
- 大小: 29.7 KB
 内层的红色框中说明,我们cancel时是将isC2的变量重新赋值了,也就是说isC2指向了一个新的对象 而thISC2 里面还是老的值,所以他们打印出来的结果不同。
?
同理,isC1 = true 这句话因为jdk 封包操作的原因类似isC2也是重新new了一个对象,isC1指向了新对象,而thISC1中还是老对象。所以导致了上述的结果。
?
也算是对jdk封包,解包操作的一个新理解吧。
?
内层的红色框中说明,我们cancel时是将isC2的变量重新赋值了,也就是说isC2指向了一个新的对象 而thISC2 里面还是老的值,所以他们打印出来的结果不同。
?
同理,isC1 = true 这句话因为jdk 封包操作的原因类似isC2也是重新new了一个对象,isC1指向了新对象,而thISC1中还是老对象。所以导致了上述的结果。
?
也算是对jdk封包,解包操作的一个新理解吧。
?