2.工程中添加libicucore.dylib frameworks。
友情提醒:一般人导入RegexKitLite编译报错,正是因为没有导入这个类库,加上这个就OK了
3.现在所有的nsstring对象就可以调用RegexKitLite中的方法了。
NSString *email = @”kkk@aaa.com”;
[email isMatchedByRegex:@"\\b([a-zA-Z0-9%_.+\\-]+)@([a-zA-Z0-9.\\-]+?\\.[a-zA-Z]{2,6})\\b”];
返回YES,证明是email格式,需要注意的是RegexKitLite用到的正则表达式和wiki上的略有区别。
searchString = @”http://www.example.com:8080/index.html”;
regexString = @”\\bhttps?://[a-zA-Z0-9\\-.]+(?::(\\d+))?(?:(?:/[a-zA-Z0-9\\-._?,'+\\&%$=~*!():@\\\\]*)+)?”;
NSInteger portInteger = [[searchString stringByMatching:regexString capture:1L] integerValue];
NSLog(@”portInteger: ‘%ld’”, (long)portInteger);
// 2008-10-15 08:52:52.500 host_port[8021:807] portInteger: ‘8080′
取string中http的例子。
下面给出常用的一些正则表达式(其实就是RegexKitLite官网上的,怕同鞋偷情不看)
CharacterDescription \aMatch a BELL, \u0007 \AMatch at the beginning of the input. Differs from ^ in that \A will not match after a new-line within the input. \b, outside of a [Set]Match if the current position is a word boundary. Boundaries occur at the transitions between word \w and non-word \W characters, with combining marks ignored. See also: RKLUnicodeWordBoundaries \b, within a [Set]Match a BACKSPACE, \u0008. \BMatch if the current position is not a word boundary. \cxMatch a Control-x character. \dMatch any character with the Unicode General Category of Nd (Number, Decimal Digit). \DMatch any character that is not a decimal digit. \eMatch an ESCAPE, \u001B. \ETerminates a \Q…\E quoted sequence. \fMatch a FORM FEED, \u000C. \GMatch if the current position is at the end of the previous match. \nMatch a LINE FEED, \u000A. \N{Unicode Character Name}Match the named Unicode Character. \p{Unicode Property Name}Match any character with the specified Unicode Property. \P{Unicode Property Name}Match any character not having the specified Unicode Property. \QQuotes all following characters until \E. \rMatch a CARRIAGE RETURN, \u000D. \sMatch a white space character. White space is defined as [\t\n\f\r\p{Z}]. \SMatch a non-white space character. \tMatch a HORIZONTAL TABULATION, \u0009. \uhhhhMatch the character with the hex value hhhh. \UhhhhhhhhMatch the character with the hex value hhhhhhhh. Exactly eight hex digits must be provided, even though the largest Unicode code point is \U0010ffff. \wMatch a word character. Word characters are [\p{Ll}\p{Lu}\p{Lt}\p{Lo}\p{Nd}]. \WMatch a non-word character. \x{h…}Match the character with hex value hhhh. From one to six hex digits may be supplied. \xhhMatch the character with two digit hex value hh. \XMatch a Grapheme Cluster. \ZMatch if the current position is at the end of input, but before the final line terminator, if one exists. \zMatch if the current position is at the end of input. \nBack Reference. Match whatever the nth capturing group matched. n must be a number ≥ 1 and ≤ total number of capture groups in the pattern.Note:Octal escapes, such as \012, are not supported. [pattern]Match any one character from the set. See ICU Regular Expression Character Classes for a full description of what may appear in the pattern. .Match any character. ^Match at the beginning of a line. $Match at the end of a line. \Quotes the following character. Characters that must be quoted to be treated as literals are * ? + [ ( ) { } ^ $ | \ . / OperatorsOperatorDescription |Alternation. A|B matches either A or B. *Match zero or more times. Match as many times as possible. +Match one or more times. Match as many times as possible. ?Match zero or one times. Prefer one. {n}Match exactly n times. {n,}Match at least n times. Match as many times as possible. {n,m}Match between n and m times. Match as many times as possible, but not more than m. *?Match zero or more times. Match as few times as possible. +?Match one or more times. Match as few times as possible. ??Match zero or one times. Prefer zero. {n}?Match exactly n times. {n,}?Match at least n times, but no more than required for an overall pattern match. {n,m}?Match between n and m times. Match as few times as possible, but not less than n. *+Match zero or more times. Match as many times as possible when first encountered, do not retry with fewer even if overall match fails. Possessive match. ++Match one or more times. Possessive match. ?+Match zero or one times. Possessive match. {n}+Match exactly n times. Possessive match. {n,}+Match at least n times. Possessive match. {n,m}+Match between n and m times. Possessive match. (…)Capturing parentheses. Range of input that matched the parenthesized subexpression is available after the match. (?:…)Non-capturing parentheses. Groups the included pattern, but does not provide capturing of matching text. Somewhat more efficient than capturing parentheses. (?>…)Atomic-match parentheses. First match of the parenthesized subexpression is the only one tried; if it does not lead to an overall pattern match, back up the search for a match to a position before the (?> . (?#…)Free-format comment (?#comment). (?=…)Look-ahead assertion. True if the parenthesized pattern matches at the current input position, but does not advance the input position. (?!…)Negative look-ahead assertion. True if the parenthesized pattern does not match at the current input position. Does not advance the input position. (?<=…)Look-behind assertion. True if the parenthesized pattern matches text preceding the current input position, with the last character of the match being the input character just before the current position. Does not alter the input position. The length of possible strings matched by the look-behind pattern must not be unbounded (no * or + operators). (?<!…)Negative Look-behind assertion. True if the parenthesized pattern does not match text preceding the current input position, with the last character of the match being the input character just before the current position. Does not alter the input position. The length of possible strings matched by the look-behind pattern must not be unbounded (no * or + operators). (?ismwx-ismwx:…)Flag settings. Evaluate the parenthesized expression with the specified flags enabled or -disabled. (?ismwx-ismwx)Flag settings. Change the flag settings. Changes apply to the portion of the pattern following the setting. For example, (?i) changes to a case insensitive match. See also: Regular Expression Options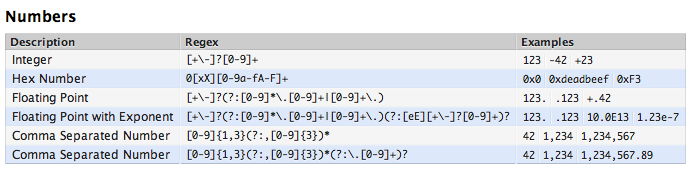

![]()
![]()

同时需要注意的是转义字符哦~~在safari上复制会直接转换(网站蛮人性化的)
同时也提供了转换工具,safari测试支持,可能下载的时候有点慢,耐心等待,链接
