?
?
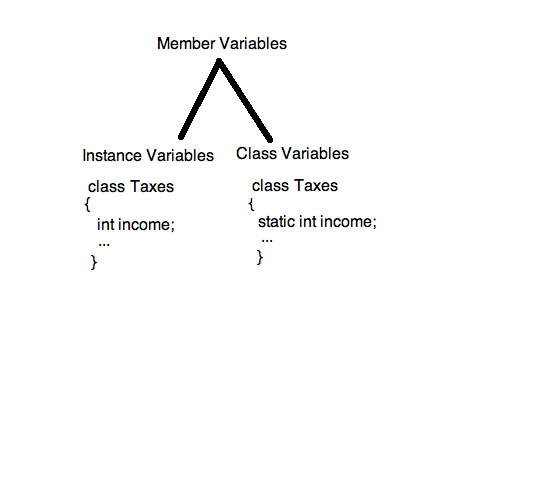
Knowing the terminology is important. Instance variables and class variables are both member variables. They are both member variables because they are both associated with aspecificclass. But, there are differences between instance variables and class variables.
Instance variables belong to an instance of a class. Another way of saying that is instance variables belong to an object, since an object is an instance of a class. Every object has it’s own copy of the instance variables. Here is what a declaration of an instance variable would look like:
class Taxes
{
int count;
/*...*/
}
Class variables, however, only haveonecopy of the variable(s) shared with all instances of the class. It’s important to remember thatclass variables are also known as static member variablesin C++, Java, and C#. Each object of the class does not have its own copy of a class variable. Instead, every object shares theone and onlycopy of that class variable – and any changes made to that copy are seen by all of the objects of that class. Here is what a class variable – or a static member variable – would look like in C++:
class Taxes
{
static int count;
/*...*/
}
Now, it should be clear what the difference between instance and class variables is. Class variables only have one copy that is shared by all the different objects of a class, whereas every object has it’s own personal copy of an instance variable. So, instance variables across different objects can have different values whereas class variables across different objects can have only one value.
Here’s a little diagram to help you remember the differences between instance and class variables: