接上文 多线程编程学习笔记——任务并行库(一)
三、 组合任务
本示例是学习如何设置相互依赖的任务。我们学习如何创建一个任务的子任务,这个子任务必须在父任务执行结束之后,再执行。
1,示例代码如下:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ThreadTPLDemo { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Task 组合操作 ————"); Task<string> task1 =CreateTask("Task1",3); Task<string> task2 = CreateTask("Task2", 2); //给task1创建一个延续操作(子操作) task1.ContinueWith(t => Console.WriteLine("task1子操作:{0},线程ID:{1},是不是线程池中的线程:{2}",
t.Result, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread),TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnRanToCompletion); task1.Start(); task2.Start(); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(4)); Task task3=task2.ContinueWith(t => Console.WriteLine("task2子操作:{0},线程ID:{1},是不是线程池中的线程:{2}",
t.Result, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread),
TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnRanToCompletion|TaskContinuationOptions.ExecuteSynchronously); task3.GetAwaiter().OnCompleted(() => Console.WriteLine("task3异步操作完成,线程ID:{0},是不是线程池中的线程:{1}",
Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread)); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); Console.WriteLine("--------------父子任务--------------"); var task5= new Task<string>(() => { var task6 = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => TaskOper("子任务Task6", 5), TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent); task6.ContinueWith(t=>TaskOper("延时操作 task7",2),TaskContinuationOptions.AttachedToParent); return TaskOper("task5", 2); }); task5.Start(); while (!task5.IsCompleted) { Console.WriteLine(" task5状态——{0}", task5.Status); Thread.Sleep(500); } Console.WriteLine(" ——task5状态—{0}", task5.Status); string result = task5.Result; Console.WriteLine(" task5运行结果——{0}", result); Console.ReadKey(); } private static string TaskOper(string name,int seconds) { Console.WriteLine("Task 线程 ID:{0} 上,是不是线程池中的线程:{1},名称: {2}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId,Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread, name); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(seconds)); return string.Format("线程ID:{0},名称:{1}:秒:{2}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId,name,seconds); } static Task<string> CreateTask(string name,int seconds) { return new Task<string>(() => TaskOper(name,seconds)); } } }
2.程序运行结果如下图。

如结果所示,程序在启动时创建了两个任务task1与task2,并为第一个任务创建了一个子操作。启动这两个任务,然后等待4秒,然后给第task2运行子操作,并通过TaskContinuationOptions. OnlyOnRanToCompletion的选项尝试同步执行这个子操作。如果子操作的运行时间非常短,则以上方式非常有用,因为放在主线程中运行比放在线程池运行要快。
如果我们注释掉那等待4秒的代码(蓝色字体),task2这个操作就会被放到线程池中,如下图。
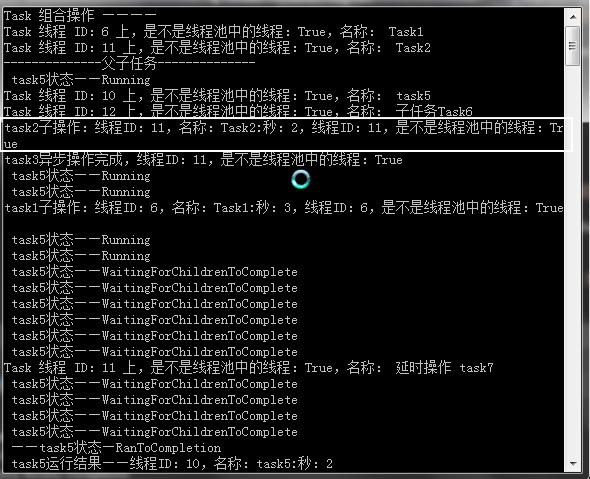
接着,我们对task2任务的子操作定义了一个子操作task3,对task3使用新的GetAwaiter和Oncompleted方法,来执行一个后续操作。
最后我们创建了一个新的任务task5,通过TaskContinuationOptions. AttachedToParent选项来运行一个子任务task6与后续操作task7。
四、 将APM模式转为任务
本示例,将上一篇(多线程编程学习笔记——线程池(一))中的(示例一线程池中调用委托)转为任务。将APM转换为TPL的关键是Task<T>.Factory.FromAsync()方法
1.代码如下:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ThreadTPLDemo { public delegate string AsyncTaskRun(string name); public delegate string IncompAsyncTaskRun(out int threadId); class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine(" 将APM模式转为Task。。。"); int threadId = 0; AsyncTaskRun tkDele = RunTask; IncompAsyncTaskRun taskDele = RunTask; Console.WriteLine(" --------1------------"); Task<string> task1=Task<string>.Factory.FromAsync( tkDele.BeginInvoke("task1", Callback, "Task异步调用回调函数"),tkDele.EndInvoke); task1.ContinueWith(t => Console.WriteLine("task1回调函数执行结束,执行后续子操作:{0}", t.Result)); while (!task1.IsCompleted) { Console.WriteLine(" task1状态——{0}", task1.Status); Thread.Sleep(500); } Console.WriteLine(" ——task1状态—{0}", task1.Status); Thread.Sleep(2000); Console.WriteLine(); Console.WriteLine(" ---------------2-----------——"); Task<string> task2 = Task<string>.Factory.FromAsync(tkDele.BeginInvoke,tkDele.EndInvoke, "task2", "Task异步调用回调函数"); task2.ContinueWith(t => Console.WriteLine("task2 回调函数执行结束,执行后续子操作:{0}", t.Result)); while (!task2.IsCompleted) { Console.WriteLine(" task2状态——{0}", task2.Status); Thread.Sleep(500); } Console.WriteLine(" ——task2状态—{0}", task2.Status); Thread.Sleep(2000); Console.WriteLine(); Console.WriteLine(" ---------------3-----------——"); IAsyncResult r = taskDele.BeginInvoke(out threadId, Callback, "在线程池中异步调用回调函数"); Task<string> task3 = Task<string>.Factory.FromAsync(r,_=> taskDele.EndInvoke(out threadId,r)); task2.ContinueWith(t => Console.WriteLine("task3 回调函数执行结束,执行后续子操作:{0},线程ID:{1}", t.Result,threadId)); while (!task2.IsCompleted) { Console.WriteLine(" task3状态——{0}", task2.Status); Thread.Sleep(500); } Console.WriteLine(" ——task3状态—{0}", task2.Status); Thread.Sleep(2000); Console.WriteLine(" --------------------------——"); Thread.Sleep(2000); Console.Read(); } private static void Callback(IAsyncResult r) { Console.WriteLine("开始调用回调函数。。。"); Console.WriteLine("回调函数此时的状态 :{0}", r.AsyncState); Console.WriteLine("调用此回调函数的线程是否在线程池 :{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); Console.WriteLine("调用此回调函数的线程在线程池在的ID :{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); } private static string RunTask(string name) { Console.WriteLine("开始工作。。。"); Console.WriteLine("调用此回调函数的线程是否在线程池 :{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); Thread.CurrentThread.Name = name; int threadId = Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId; return string.Format("此线程的ID :{0},名称{1}", threadId, Thread.CurrentThread.Name); } private static string RunTask(out int threadId) { Console.WriteLine("开始工作。。。"); Console.WriteLine("调用此回调函数的线程是否在线程池 :{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); threadId = Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId; return string.Format("此线程在线程池在的ID :{0}", threadId); } } }
2.程序运行结果如下图。
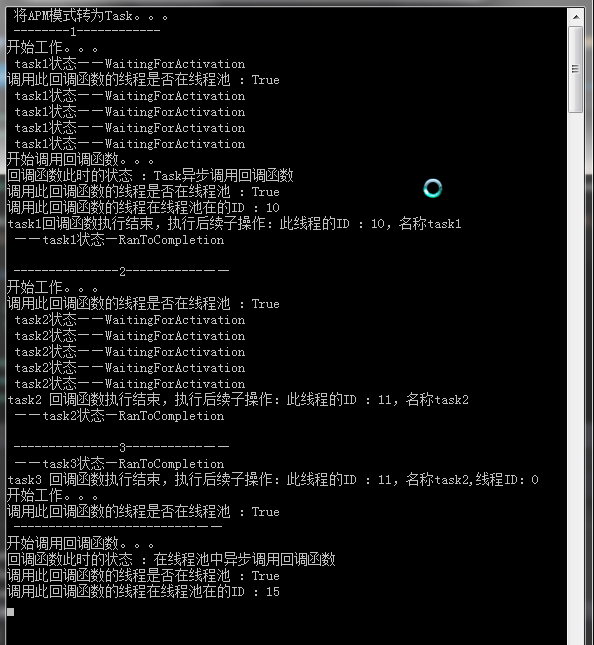
程序运行结果中可以看出来,task1中直接传入了IAsyncResult和Func< IAsyncResult,string>,task1执行委托的异步调用,正常。
Task2与task1类似,只是使用了不同的FromAsync的方法重载,这个重载不允许指定一个将会在异步调用完成之后被调用的回调函数。我们在示例中使用后续操作代替了回调函数。如果必须使用回调函数,可以使用类似task1的调用方式。
Task3我们通过一个技巧实现了调用与FromAsync不兼容的委托。我们通过将EndInvoke封装到一个lambda表达式中,从而适应FromAsync方法。
五、 将EAP模式转换为任务
本示例,将上一篇(多线程编程学习笔记——线程池(三))中的(使用BackgroundWorker组件示例)转为任务。
本示例是学习如何基于事件的异步转换为TASK来运行。本示例的关键是使用TaskCompletionSource<T>,T是异步操作结果的类型。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ThreadPoolDemo { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine(" 将EAP模式转为Task。。。"); var tcs = new TaskCompletionSource<int>(); var worker = new BackgroundWorker(); worker.DoWork += (sender, eventArgs) => { eventArgs.Result = RunTask("后台线程 1 ", 5); }; worker.RunWorkerCompleted += (sender, eventArgs) => { if (eventArgs.Error!=null) { Console.WriteLine(" ——出错—{0}", eventArgs.Error); tcs.SetException(eventArgs.Error); } else if (eventArgs.Cancelled) { Console.WriteLine(" ——取消—"); tcs.SetCanceled();//取消 } else { Console.WriteLine(" ——设置结果值—{0}", eventArgs.Result); tcs.SetResult((int)eventArgs.Result); } }; worker.RunWorkerAsync(); int result = tcs.Task.Result; Console.WriteLine(" ——任务Task运行结果—{0}", result); Thread.Sleep(2000); Console.Read(); } private static int RunTask(string name,int seconds) { Console.WriteLine("Task {0} 运行在线程={1}中,是否在线程池 :{2}",name, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId,
Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(seconds)); return 42 * seconds; } } }
2.程序运行结果如下图。
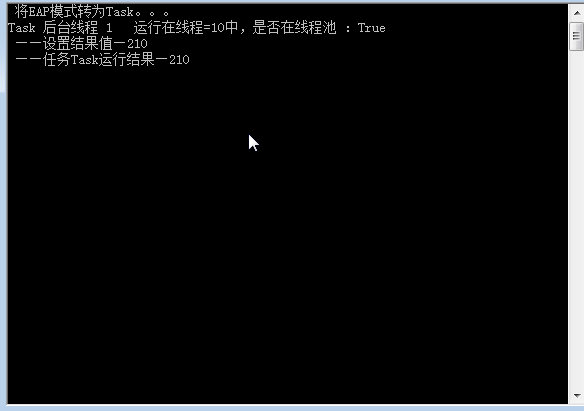
注:tcs.SetResult要封闭在try-catch中,以方便获取异常。或者可以使用tcs.TrySetResult。