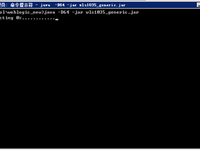
这里的例子是启动weblogic
class="java" name="code">import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Time {
public static void Test() {
//1. excutePath 为bat或者cmd所在的路径,例如:
String excutePath = "E:\\weblogic\\user_projects\\domains\\cluster_domain\\cluster01.cmd";
Process process;
try {
// 执行CMD代码,返回一个Process
process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(excutePath);
InputStream is = process.getInputStream();
// 得到相应的控制台输出信息
InputStreamReader bi = new InputStreamReader(is);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(bi);
String message;
message = br.readLine();
while (message != null && !"".equals(message)) {
// 将信息输出
System.out.println(message);
message = br.readLine();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
}
启动weblogic子节点
/**
* 启动weblogic子节点服务的方法
* */
public static void startserver() throws InterruptedException {
// Runtime.getRuntime()返回当前应用程序的Runtime对象
Runtime nRuntime = Runtime.getRuntime();
// Process可以控制该子进程的执行或获取该子进程的信息。
Process nProcess = null;
String nStartApp = "E:\\weblogic\\user_projects\\domains\\cluster_domain\\cluster01.cmd";
String nLine = null;
try {
nProcess = nRuntime.exec(nStartApp);
// 读取正确执行的返回流
BufferedReader nInfo = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
nProcess.getInputStream()));
nLine = nInfo.readLine();
while ((nLine = nInfo.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(nLine);
}
// 读取错误执行的返回流
BufferedReader nError = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
nProcess.getErrorStream()));
nLine = nError.readLine();
while ((nLine = nError.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(nLine);
}
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
- 大小: 25.2 KB
- 大小: 43.1 KB
- 大小: 39.4 KB
- 大小: 39.6 KB
- 大小: 39.6 KB
- 大小: 59.2 KB
- 大小: 43.5 KB
- 大小: 71.3 KB
- 大小: 53.7 KB

- 大小: 50.5 KB