在iOS中,有一个概念叫做像素对齐,如果像素不对齐,那么在GPU渲染时,需要进行插值计算,这个插值计算的过程会有性能损耗。
在模拟器上,有一个选项可以把像素不对齐的部分显示出来。
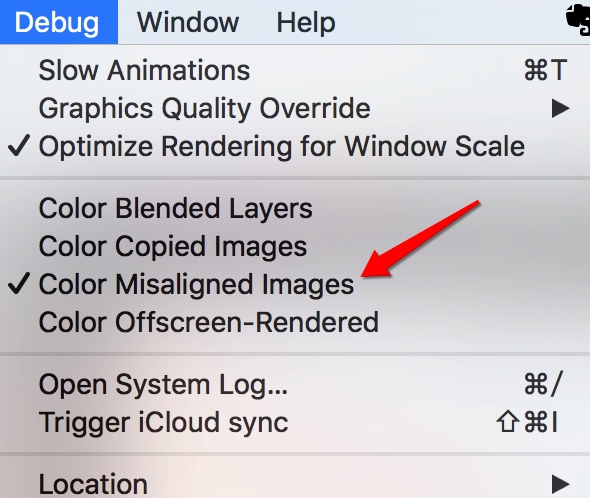 ?
?
在iOS设备上,有point(逻辑像素)的概念,以及pixel(物理像素)的概念。
在编程序时,用的是point,实际渲染时用的是pixel。一个point可以对应多个pixel。
point和pixel的比例是可以通过[[UIScreen mainScreen] scale]来制定。
If you load an image from a file whose name includes the @2x modifier, the scale is set to 2.0. You can also specify an explicit scale factor when initializing an image from a Core Graphics image. All other images are assumed to have a scale factor of 1.0.
image也有size的概念。
This value reflects the logical size of the image and takes the image’s current orientation into account. Multiply the size values by the value in the scale property to get the pixel dimensions of the image.
就是说image的size和image和scale相乘,得到物理像素的大小。
那么像素不对齐指的是物理像素(pixel)和逻辑像素(point)对齐呢?
使用300*225像素的png图片。分别使用不同的方法load到内存中,得到不同的size和scale,然后放在不同size的imageview里。使用color misaligned images来判定是否像素对齐。
这里模拟器使用的iPhone 6,屏幕的 scale是2。
NSLog(@"screen scale is %f",[[UIScreen mainScreen] scale]);
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"test.png"];
NSLog(@"image size %@, scale %f ", [NSValue valueWithCGSize:image.size], image.scale);
UIImageView *imageView = [[UIImageView alloc] initWithImage:image];
// imageView.frame = CGRectMake(50, 100, imageView.bounds.size.width * 2/3, imageView.bounds.size.height * 2/3);
imageView.frame = CGRectMake(50, 100, imageView.bounds.size.width, imageView.bounds.size.height);
NSLog(@"imageView frame %@", [NSValue valueWithCGRect:imageView.frame]);
[self.view addSubview:imageView];