Compiler
1.2 the structure of a compiler
Compiler : analysis and synthesis
syntactically 语法上的
semantically 语意上的
The analysis part breaks up the source program into constituent pieces and imposes a grammatical structure on them.
The analysis part also collects information about the source program and stores it in a data structure called a symbol table, which is passed along with the intermediate representation to the synthesis part.
The synthesis part constructs the desired target program from the intermediate representstion and the information in the symbol table .
The analysis part is often called the front end of the compiler ;the synthesis part is the back end .
A typical decomposition of a compiler into phases is shown :
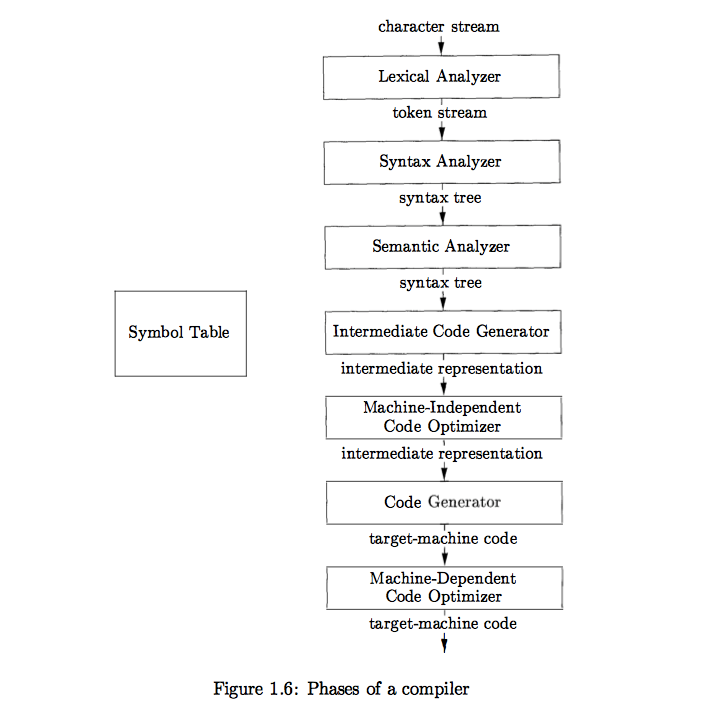
1.2.1 lexical analysis
lexemes .
<token-name, attribute-value>



1.2.2 syntax analysis
The parser uses the first components of the tokens produced by the lexical analyzer to create a tree-like intermediate representation that depicts the grammatical structure of the token steam . A typical representation is a syntax teee in which each interior node represents an operation and the children of the node represent the arguments of the operation .
1.2.3 semantic analysis
The semantic analysis uses the syntax tree and the information in the symbol table to check the source program for semantic consistency with the language definition .
Type checking :
coercions: the language specification may permit some type conversions called coercions
1.2.4 intermediate code generation
This intermediate representation should have two important properties : it should be easy to produce and it should be easy to translate into the target machine .
three-address code .
1.2.5 code optimization
The machine -independent code -optimization phase attempts to improve the intermediate code so that better target code will result .
12.6 Code generation
The code generator takes as input an intermediate representation of the source program and maps it into the target language .
A crucial aspect of code generation is the judicious assignment of registers to hold variables .
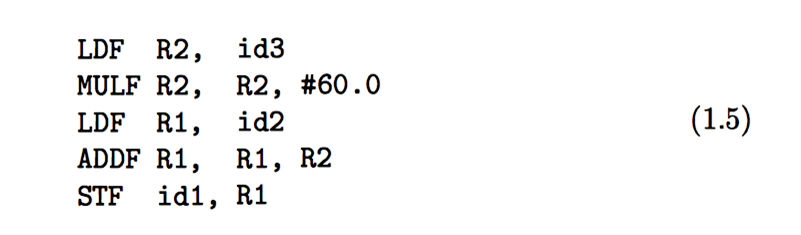
ldf :load float
mulf:multiplies float
addf : add float
stf :store float
1.2.7 symbol-table management
an essential function of a compiler is to record the variable names used in the source program and collect information about various attributes of each name .
The symbol table is a data structure containing a record for each variable name ,with fields for the attributes of the name .
1.2.8 The grouping of phases into passes
the discussion of phases deals with the logical organization of a compiler . In an implementation ,activities from several phase may be grouped together into a pass
With these collections ,we can produce compilers for different source languages for one target machine by combining different front ends with the back end for that target machine . Similarly ,we can produce compilers for different target machines ,by combining a front end with back ends for different target machines .
1.2.9 compiler-construction tools
some commonly used compiler-construction tools includes
1. parser generators that automatically produce syntax analyzers from a grammatical description of a programming language .