一.Junit
1.怎么使用
在AndroidManifest.xml文件中进行配置, 在manifest借点下配置instrumentation, 在application借点下配置uses-library
定义类继承AndroidTestCast
定义测试方法, Run As JunitTest
如果需要判断测试结果, 可以使用Assert.assertEquals()方法.
下面是利用独立的测试工程JunitTest来测试工程Junit:

package com.shellway.junit; public class Service { public int divide(int a,int b){ return a/b; } }Service.java
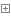
package com.shellway.junit; import junit.framework.Assert; import android.test.AndroidTestCase; public class TestT extends AndroidTestCase { public void test1(){ Service service = new Service(); System.out.println(service.divide(10, 2)); } public void test2(){ Service service = new Service(); System.out.println(service.divide(10, 0)); } public void test3(){ Service service = new Service(); Assert.assertEquals(2.5, service.divide(10, 4)); } }TestT.java

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.shellway.junit"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="16"
android:targetSdkVersion="21" />
<instrumentation
android:targetPackage="com.shellway.junit"
android:name="android.test.InstrumentationTestRunner" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<uses-library android:name="android.test.runner" />
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
AndroidManifest.xml
JunitTest工程中的:

package com.shellway.junit.test; import junit.framework.Assert; import com.shellway.junit.Service; import android.test.AndroidTestCase; public class MyTest extends AndroidTestCase { public void test1(){ Service service = new Service(); System.out.println(service.divide(10,2)); } public void test2(){ Service service = new Service(); System.out.println(service.divide(10, 0)); } public void test3(){ Service service = new Service(); Assert.assertEquals(2.5, service.divide(10, 4)); } }MyTest.java

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.shellway.junit.test"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="16" />
<instrumentation
android:name="android.test.InstrumentationTestRunner"
android:targetPackage="com.shellway.junit" />
<application
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<uses-library android:name="android.test.runner" />
</application>
</manifest>
AndroidManifest.xml
二.日志
1.怎么使用
Log.v(), d(), i(), w(), e()
可以按级别输出日子信息, 可以指定Tag

package com.example.logcat; import android.test.AndroidTestCase; import android.util.Log; public class LogTest extends AndroidTestCase { public void test1(){ System.out.println("System.out"); System.err.println("System.out"); } public void test2(){ Log.v("LogTest", "verbose"); Log.d("LogTest", "debug"); Log.i("LogTest", "info"); Log.w("LogTest", "warning"); Log.e("LogTest", "error"); } }LogTest.java

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.logcat" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0" > <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" android:targetSdkVersion="21" /> <instrumentation android:targetPackage="com.example.logcat" android:name="android.test.InstrumentationTestRunner" /> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <uses-library android:name="android.test.runner" /> <activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>AndroidManifest.xml
三.读写文件
1.读写SD卡
获取SD卡路径要使用Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory()
最好在使用SD卡之前判断状态, Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)
写入SD卡需要权限, android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE
2.读写手机
可以使用Context.openFileOutput(String, int)方法打开输出流
指定文件名后会自动在当前应用所在文件夹下生成files文件夹, 在其中创建文件
int参数是文件权限, 可以是使用Context下的常量进行设置
四.SharedPreferences
1.什么是SharedPreferences
是一个键值对结构的容器, 类似于Map(Properties), 可以向其中存储键值对, 根据键查找值, 存储在容器中的数据会以xml文件形式保存.
2.怎么使用
使用Context.getSharedPreferences(String, int)获取对象, 指定文件名和文件模式
使用SharedPreferences.edit()方法获取编辑器Editor
使用Editor.putString(), putInt()等方法存储数据
使用Editor.commit()方法提交修改(类似事务)
获取的时候直接使用 SharedPreferences.getString(), getInt()等方法获取数据
五.XML
1.解析
获取解析器: Xml.newPullParser()
设置输入流: parser.setInput(InputStream, String)
获取当前事件类型: parser.getEventType(), 共5种
获取下一个事件类型: parser.next()
获取标签名: parser.getName()
获取属性值: parser.getAttributeValue(int)
获取下一个文本: parser.nextText()
2.生成
获取解析器:
设置输出流:
开始文档:
结束文档:
开启标签:
结束标签:
设置属性:
设置文本:
六.SQLite数据库
1.SQLite数据库的特点
手机自带的数据库, 不区分数据类型(除了主键), 语法和MySQL相同, 每个库是一个文件
2.创建库
定义类继承SQLiteOpenHelper, 定义构造函数, 显式调用父类构造函数, 传入4个参数
重写onCreate()和onUpgrade()方法
调用getWritableDatabase()或者getReadableDatabase()方法都可以创建数据库
数据库文件不存在时, 会创建数据库文件, 并且执行onCreate()方法
数据库文件存在, 并且版本没有改变时, 不执行任何方法
数据库文件存在, 版本提升, 执行onUpgrade()方法
3.增删改查
增删改都可以使用SQLiteDatabase.execSQL()方法执行SQL语句完成
查询方法需要使用SQLiteDatabase.rawQuery()方法进行查询, 得到一个Cursor, 再调用moveToNext()和getString()getInt()等方法获取数据