AOP的底层已经封装好了以后,我们就要开始针对应用层写具体的业务逻辑了。
也就是说我们需要有个类继承于AopProxyBase,并且重写其After,Bofore以达到我们的拦截记录的功能。代码如下:
public class TransactionProxy : AopProxyBase { public TransactionProxy(MarshalByRefObject obj, Type type) : base(obj, type) { } public override void Before(System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging.IMessage requestMsg, AopMethodAttribute[] attrs) { } public override void After(System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging.IMessage requestMsg, System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging.IMessage Respond, AopMethodAttribute[] attrs) { foreach (var attr in attrs) { if (attr is LogicRollBackTransAttribute) { return; } } var args = requestMsg.Properties["__Args"] as object[]; string methodName = requestMsg.Properties["__MethodName"] as string; CustomTransaction customTrans = null; List<object> list = new List<object>(); customTrans = CallContext.GetData(TransKey.CustomTransKey) as CustomTransaction; if (customTrans != null) { list.AddRange(args); TransactionUnit unit = AppTransactionManage.Instance.GetRollBackInfo(methodName); if (unit != null) { unit.Argments = list; } customTrans.Compensation.Add(unit); CallContext.SetData(TransKey.CustomTransKey, customTrans); var outArgs = Respond.Properties["__OutArgs"] as object[]; IDbTransaction dbTrans; foreach (var attr in attrs) { if (attr is DbTransAttribute || attr is LogicTransAttribute) { if (outArgs != null) { foreach (var arg in outArgs) { if (arg is IDbTransaction) { dbTrans = arg as IDbTransaction; if (customTrans != null) { customTrans.AddDbTransaction(dbTrans); } } } } } } } } }View Code
在After的地方,我们可以看到,我们做了一次LogicRollBackTransAttribute的判定,避免在回调的时候,又再走一次拦截和记录的流程。
同时做了DbTransAttribute和LogicTransAttribute的判定。因为我把事务分为两类,一类是db本身自己控制的,可以直接rollback的,一类是logic的,需要我们去手动通过逻辑回滚的。代码如下:
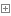
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method)] public class LogicTransAttribute : AopMethodAttribute { public string MethodName { get; set; } public LogicTransAttribute() { } public LogicTransAttribute(string name) { this.MethodName = name; } } [AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method)] public class DbTransAttribute : AopMethodAttribute { }View Code
同时可以看到,我把每一个函数的调用作为一个单元,用TransactionUnit类来保存,代码如下:

public class TransactionUnit { public object InstanceObject; /// <summary> /// 执行的方法 /// </summary> public MethodInfo Forward; /// <summary> /// 失败回滚的方法 /// </summary> public MethodInfo Rollback; /// <summary> /// 参数 /// </summary> public IList<object> Argments; }View Code
因为,一个事务里面,可能包含了多次操作redis,或者多次操作db,为了保证线程安全,同时又需要避开锁,我用了CallContext将一个线程里面的一段事务,保存在其线程上下文中。在保存一个完整的TransactionUnit的时候,不可能每一次都去通过反射去取MethodInfo,所以又增加了一段初始化和字典来保存其MethodInfo。代码如下:

public class AppTransactionManage { private Dictionary<string, TransactionUnit> _transMaps; static AppTransactionManage() { } private AppTransactionManage() { if (this._transMaps == null) { this._transMaps = new Dictionary<string, TransactionUnit>(); } } private static AppTransactionManage _instance; public static AppTransactionManage Instance { get { if (_instance == null) { _instance = new AppTransactionManage(); } return _instance; } } public TransactionUnit GetRollBackInfo(string methodName) { if (this._transMaps == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("not init"); if (this._transMaps.ContainsKey(methodName)) { return this._transMaps[methodName]; } return null; } public void Init(params string[] assembly) { if (assembly != null) { foreach (string s in assembly) { var ass = Assembly.Load(s); if (ass != null) { var types = ass.GetTypes(); foreach (var type in types) { var transAttr = type.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(TransactionAttribute), false) as TransactionAttribute; if (transAttr != null) { var methods = type.GetMethods(); foreach (var method in methods) { var forwardTrans = method.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(LogicTransAttribute), false) as LogicTransAttribute; var rollbackTrans = method.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(LogicRollBackTransAttribute), false) as LogicRollBackTransAttribute; TransactionUnit unit; if (forwardTrans != null) { if (!this._transMaps.TryGetValue(forwardTrans.MethodName, out unit)) { unit = new TransactionUnit(); } unit.Forward = method; unit.InstanceObject = Activator.CreateInstance(type); this._transMaps[forwardTrans.MethodName] = unit; } if (rollbackTrans != null) { if (!this._transMaps.TryGetValue(rollbackTrans.MethodName, out unit)) { unit = new TransactionUnit(); } unit.Rollback = method; unit.InstanceObject = Activator.CreateInstance(type); this._transMaps[rollbackTrans.MethodName] = unit; } } } } } } } } }View Code
为了友好开发者的调用,可以让其像使用SqlTransaction一样来使用,我又对外公开了一个CustomTranstion,将调用方式封装在这个类里面,代码如下:

public class CustomTransaction : IDisposable { private List<IDbTransaction> _dbTransactions; private bool _isRollBack = true; /// <summary> /// 补偿机制 /// </summary> public List<TransactionUnit> Compensation; public void Commit() { if (this._dbTransactions != null) { this._dbTransactions.ForEach((t) => t.Commit()); } this._isRollBack = false; } public void RollBack() { if (this.Compensation != null) { this.Compensation.ForEach((t) => { object[] paramsArray = t.Argments == null ? null : t.Argments.ToArray(); t.Rollback.Invoke(t.InstanceObject, paramsArray); }); } if (this._dbTransactions != null) { this._dbTransactions.ForEach((t) => t.Rollback()); } } private bool _isRetry = true; public CustomTransaction(bool isRetry = true) { this._isRetry = isRetry; if (this._dbTransactions == null) { this._dbTransactions = new List<IDbTransaction>(); } if (this.Compensation == null) { this.Compensation = new List<TransactionUnit>(); } CallContext.SetData(TransKey.CustomTransKey, this); } public void AddDbTransaction(IDbTransaction transaction) { this._dbTransactions.Add(transaction); } public void Dispose() { if (this._isRollBack) { this.RollBack(); } CallContext.FreeNamedDataSlot(TransKey.CustomTransKey); } }View Code
这个时候,你就可以像是用SqlTransaction一样去Using(var trans = new CustomTranstion()){}然后在using里面去写trans.Commit();来提交所有的事务操作,如果不做Commit操作的话,在CustomTranstion里面,会自动去调用其rollback()操作。
但是这并没有完,所有的只是记录下来了,但是并没有保存到DB去做持久化。这个时候就需要增加一个队列,来不断的去将TransactionUnit来保存到db,同时又需要把队列去做持久化,避免一些意外原因,导致队列数据丢失,而缺失了这部分的日志记录(虽然我个人认为这一部分可以省略)。代码如下:

[Serializable] public class TransQueue : IDisposable { public Queue<Action> _transQueue; private Thread _thread; private bool _isDispose; public delegate void PersistenceHandler(Action[] actions); PersistenceHandler persistenceHandler; private readonly object _syncObject = new object(); public TransQueue() { if (_transQueue == null) { _transQueue = new Queue<Action>(); } if (persistenceHandler == null) { persistenceHandler = PersistenceToDisk; } if (_thread == null) { _thread = new Thread(Thread_Work) { IsBackground = true }; } _thread.Start(); } public void Push(Action action) { if (_transQueue == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("transQueue is not init"); lock (_syncObject) { _transQueue.Enqueue(action); } } public void Thread_Work() { while (!_isDispose) { Action[] items = null; if (_transQueue != null && _transQueue.Count > 0) { lock (_syncObject) { items = new Action[_transQueue.Count]; _transQueue.CopyTo(items, 0); } } if (items != null && items.Length > 0) { persistenceHandler.BeginInvoke(items, PersistenceHandlerCallBack, persistenceHandler); foreach (var item in items) { item.Invoke(); } } } } public void PersistenceHandlerCallBack(IAsyncResult result) { try { (result.AsyncState as PersistenceHandler).EndInvoke(result); } catch (Exception e) { } } public void PersistenceToDisk(Action[] items) { BinaryHelper.SaveToFile(items); } public void Dispose() { _isDispose = true; _thread.Join(); } } public class TransQueueManage { private int _threadNumber = 2; private TransQueue[] _transQueue; Random random = new Random(); private TransQueueManage() { if(_transQueue == null) { _transQueue = new TransQueue[_threadNumber]; for (var i = 0; i < _threadNumber; i++) { _transQueue[i] = new TransQueue(); } } } static TransQueueManage() { } private static readonly object _syncObject = new object(); private static TransQueueManage _instance; public static TransQueueManage Instance { get { if (_instance == null) { lock (_syncObject) { if (_instance == null) { _instance = new TransQueueManage(); } } } return _instance; } } public void Push(Action action) { var index = GetRandomThreadIndex(); _transQueue[index].Push(action); } public int GetRandomThreadIndex() { return random.Next(0, _threadNumber); } }View Code