本篇中会为大家介绍在ASP.NET Web API中ModelBinder的绑定原理以及涉及到的一些对象模型,还有简单的Model绑定示例,在前面的篇幅中讲解了Model元数据、ValueProvider的模块,然后还有本篇的Model绑定的模块这些会结合到后面篇幅中的ParameterBinder模块中来使用,也就是说在ASP.NET Web API框架中绑定的方式有两种实现,都是通过ParameterBinder来对参数进行绑定,而在ParameterBinder中的实现则会有两种方式,今天就给大家单独的说明一下Model绑定,把它看成一个单独的功能模块就行了。
不瞎扯了,直接进入主题,首先我们来看IModelBinder接口类型的定义,所有的ModelBinder功能模块都实现了IModelBinder接口,如示例代码1-1
示例代码1-1
IModelBinder
namespace System.Web.Http.ModelBinding { public interface IModelBinder { bool BindModel(HttpActionContext actionContext, ModelBindingContext bindingContext); } }
在代码1-1中我们可以看到BindModel()方法中定义了两个参数而且都是上下文类型的参数,第一个上下文参数表示操作上下文,它是在控制器方法被执行之前就被创建并且其中封装了一些后续操作必要的信息以及存储请求、响应和参数绑定的结果值,这个稍后会跟大家讲解,它起到一个很重要的作用。
第二个上下文参数是绑定上下文参数,这个容易理解,意思就是对象里封装着本次要绑定对象的信息也就是Model元数据、ValueProvider之类的信息,现在不理解也没关系慢慢往后看看完就会明白的。
HttpActionContext
代码1-2
namespace System.Web.Http.Controllers { public class HttpActionContext { public HttpActionContext(); public HttpActionContext(HttpControllerContext controllerContext, HttpActionDescriptor actionDescriptor); public Dictionary<string, object> ActionArguments { get; } public HttpActionDescriptor ActionDescriptor { get; set; } public HttpControllerContext ControllerContext { get; set; } public ModelStateDictionary ModelState { get; } public HttpRequestMessage Request { get; } public HttpResponseMessage Response { get; set; } }
}
代码1-2就是HttpActionContext类型的定义了,下面简单的描述一下几个属性所表示的含义,ActionArguments属性中的值是对应着控制器方法的参数列表,其中Key值就是参数名称,Value值就是参数的实际数据值了,因为Model绑定是一个递归的过程在复杂类型的子项绑定完毕后并不会对这个属性进行赋值,而是等这一个参数项全部绑定完成了才会进行赋值。
HttpActionDescriptor类型的ActionDescriptor属性,这个是HttpControllerDescriptor类型之后所见的第二个这种描述类型,后面还会有HttpParameterDescriptor类型,在这里ActionDescriptor属性中就是封装着当前所要请求的控制器方法信息,类似封装着方法的元数据信息。
ControllerContext属性就不用多说了想必大家也都知道它的作用,ModelStateDictionary类型的ModelState属性则是在Model绑定之后才会对其操作,是把参数绑定验证后的值存在这个属性当中。
HttpActionContextExtensions
代码1-3
namespace System.Web.Http.Controllers { // 摘要: // 包含 System.Web.Http.Controllers.HttpActionContext 的扩展方法。 [EditorBrowsable(EditorBrowsableState.Never)] public static class HttpActionContextExtensions { public static bool Bind(this HttpActionContext actionContext, ModelBindingContext bindingContext); public static bool Bind(this HttpActionContext actionContext, ModelBindingContext bindingContext, IEnumerable<IModelBinder> binders); //…… } }
代码1-3的所示的是包含HttpActionContext类型的扩展方法类型HttpActionContextExtensions,我们在这之中可以看到两个Bind()方法,这两个Bind()也是Model绑定至关重要的地方,因为Model绑定的递归就是在这里实现的,至于怎么实现的稍后会说。
这里的第一个Bind()方法其实就是调用第二个Bind()方法来执行的。而第二Bind()方法中IEnumerable<IModelBinder>参数则是从HttpActionContext类型中获取到当前的HttpControllerContext并且再从其中获取到当前请求的配置对象HttpConfiguration对象,最后从配置对象中的容器属性中获取ModelBinder的提供程序集合,然后根据当前ModelBindingContext中的ModelType类型使用提供程序集合来判断后获取适合类型的IModelBinder集合,从而调用第二个Bind()方法。
这样看可能还是不太理解递归的情况,大家稍安勿躁,后面慢慢讲解。
ModelBindingContext
代码1-4
namespace System.Web.Http.ModelBinding { // 摘要: // 提供运行模型联编程序的上下文。 public class ModelBindingContext { // 摘要: // 初始化 System.Web.Http.ModelBinding.ModelBindingContext 类的新实例。 public ModelBindingContext(); public ModelBindingContext(ModelBindingContext bindingContext); public bool FallbackToEmptyPrefix { get; set; } public object Model { get; set; } public ModelMetadata ModelMetadata { get; set; } public string ModelName { get; set; } public ModelStateDictionary ModelState { get; set; } public Type ModelType { get; } public IDictionary<string, ModelMetadata> PropertyMetadata { get; } public ModelValidationNode ValidationNode { get; set; } public IValueProvider ValueProvider { get; set; } } }
代码1-4中所示的就是绑定上下文对象,首先我们看到它的重载构造函数中有个ModelBindingContext类型的参数用以表示嵌套,内部的实现是用以传递ModelState属性的状态值和ValueProvider值提供程序,至于为什么是这种结构?这个跟绑定复杂类型的时候有关,构造就如同ModelState属性对象的ModelStateDictionary类型一样,这种结构稍后会讲解。
当中的Model属性表示当前ModelBindingContext中绑定过后的Model值,然后ModelMetadata、ModelName、ModelType、PropertyMetadata这些属性都是表示当前ModelBindingContext中Model的对应值。这个”当前”可能是string类型,也可能是复杂类型。(复杂类型在绑定的时候会被ASP.NET Web API框架封装起来有个特定的类型,这个稍后讲解)
简单类型绑定器- TypeConverterModelBinder
代码1-5
public sealed class TypeConverterModelBinder : IModelBinder { // Methods public bool BindModel(HttpActionContext actionContext, ModelBindingContext bindingContext) { object obj2; ModelBindingHelper.ValidateBindingContext(bindingContext); ValueProviderResult result = bindingContext.ValueProvider.GetValue(bindingContext.ModelName); if (result == null) { return false; } bindingContext.ModelState.SetModelValue(bindingContext.ModelName, result); try { obj2 = result.ConvertTo(bindingContext.ModelType); } catch (Exception exception) { if (IsFormatException(exception)) { string errorMessage = ModelBinderConfig.TypeConversionErrorMessageProvider(actionContext, bindingContext.ModelMetadata, result.AttemptedValue); if (errorMessage != null) { bindingContext.ModelState.AddModelError(bindingContext.ModelName, errorMessage); } } else { bindingContext.ModelState.AddModelError(bindingContext.ModelName, exception); } return false; } ModelBindingHelper.ReplaceEmptyStringWithNull(bindingContext.ModelMetadata, ref obj2); bindingContext.Model = obj2; return true; } }
在代码1-5中,我们看到TypeConverterModelBinder类型实现了IModelBinder接口,并且在BindModel()方法中直接就是使用绑定上下文中的ValueProvider根据绑定上下文中的ModelName属性,ModelName就是我们前面ValueProvider篇幅中讲解到的前缀值和属性值的合并。而后会将获取到的结果值进行类型判断,如果不能正确的转换成string类型则会提示各种异常,当然了这种异常不会报出来,只是添加到了当前绑定上下文的ModelState属性中,如果可以转换成功则会对当前绑定上下文的Model值进行赋值。
简单类型绑定器提供程序- TypeConverterModelBinderProvider
代码1-6
public sealed class TypeConverterModelBinderProvider : ModelBinderProvider { // Methods public override IModelBinder GetBinder(HttpConfiguration configuration, Type modelType) { if (modelType == null) { throw Error.ArgumentNull("modelType"); } if (!TypeHelper.HasStringConverter(modelType)) { return null; } return new TypeConverterModelBinder(); } }
代码1-6中所示TypeConverterModelBinderProvider类型则为简单类型绑定器的提供程序,并且继承自ModelBinderProvider类型,讲到这里了我才发现我把这个类型忘记说明了,不过没关系,大家自行看一下就好了,ModelBinderProvider就是一个抽象类,然后定义了一个抽象的行为。
在TypeConverterModelBinderProvider类型的实现中,我们可以清楚的看到如果参数modelType可以成功的转换成string类型则会返回TypeConverterModelBinder类型的实例,不然则返回null。
复杂类型封装对象-ComplexModelDto
代码1-7
namespace System.Web.Http.ModelBinding.Binders { // 摘要: // 表示一个复杂模型的数据传输对象 (DTO)。 public class ComplexModelDto { public ComplexModelDto(ModelMetadata modelMetadata, IEnumerable<ModelMetadata> propertyMetadata); public ModelMetadata ModelMetadata { get; } public Collection<ModelMetadata> PropertyMetadata { get; } public IDictionary<ModelMetadata, ComplexModelDtoResult> Results { get; } } }
大家也看到了代码1-7中的注释部分,表示一个复杂模型(Model)的数据传输对象,实际就是对复杂类型的重新封装,封装的方式大家也看到了都是以Model元数据的方式,这个类型我就不多说了。对于Model元数据不太清楚的朋友建议去把前面的篇幅看一下。
复杂类型封装器-MutableObjectModelBinder
对于MutableObjectModelBinder类型中的实现代码我就不贴了太多了,在这些理论基础都讲完之后后面的篇幅中会有代码示例的。
这里我就用文字来描述一下MutableObjectModelBinder类型所要实现的功能,为什么叫MutableObjectModelBinder为复杂类型封装器呢?因为MutableObjectModelBinder类型它不干绑定的事情,在它执行的时候就一定可以判定当前绑定上下文的Model是一个复杂类型,这个时候MutableObjectModelBinder会根据当前绑定上下文中的Metadata下的Properties属性获取到当前Model下属性的Model元数据列表,并且根据每一项的Model元数据进行筛选,筛选的条件依赖于应用在Model属性上的特性,也就是HttpBindingBehaviorAttribute类型,对于这个类型看完这些之后自己去琢磨吧。
在获取到Model下对应属性的Model元数据集合后,然后创建ComplexModelDto对象实例,并且新建一个绑定上下文把新建的ComplexModelDto对象实例作为Model、ModelType这些相关属性,然后最后会调用actionContext.Bind(context);,也就是代码1-3中的HttpActionContext扩展方法进入Model绑定中的递归。
复杂类型封装器提供程序- MutableObjectModelBinderProvider
代码1-8
public sealed class MutableObjectModelBinderProvider : ModelBinderProvider { // Methods public override IModelBinder GetBinder(HttpConfiguration configuration, Type modelType) { if (!MutableObjectModelBinder.CanBindType(modelType)) { return null; } return new MutableObjectModelBinder(); } }
代码1-8中可以看到在根据类型判断的时候是调用的MutableObjectModelBinder中的静态方法CanBindType(),在CanBindType()方法实现中判断类型不能为ComplexModelDto类型和string类型的,string类型的好理解,因为是属于TypeConverterModelBinder类型来绑定的,ComplexModelDto类型是为了防止框架的处理进入一个死循环,这个看到最后大家就会明白的。
复杂类型绑定器- ComplexModelDtoModelBinder
代码1-9
public sealed class ComplexModelDtoModelBinder : IModelBinder { // Methods public bool BindModel(HttpActionContext actionContext, ModelBindingContext bindingContext) { ModelBindingHelper.ValidateBindingContext(bindingContext, typeof(ComplexModelDto), false); ComplexModelDto model = (ComplexModelDto)bindingContext.Model; foreach (ModelMetadata metadata in model.PropertyMetadata) { ModelBindingContext context = new ModelBindingContext(bindingContext) { ModelMetadata = metadata, ModelName = ModelBindingHelper.CreatePropertyModelName(bindingContext.ModelName, metadata.PropertyName) }; if (actionContext.Bind(context)) { model.Results[metadata] = new ComplexModelDtoResult(context.Model, context.ValidationNode); } } return true; } }
看这代码1-9中所示类型的名字不用说也是用来对ComplexModelDto对象进行处理的,可以在代码实现中看出来,先把绑定上下文中的Model获取出来转换成ComplexModelDto实例对象,然后遍历其属性PropertyMetadata,根据其每一项的Model元数据创建一个绑定上下文,然后调用actionContext.Bind(context)方法,这也是Model绑定递归的过程之一。这种情况会出现在初始Model类型是复杂类型并且其属性中也有复杂类型。
复杂类型绑定器提供程序- ComplexModelDtoModelBinderProvider
代码1-10
public override IModelBinder GetBinder(HttpConfiguration configuration, Type modelType) { if (modelType == null) { throw Error.ArgumentNull("modelType"); } if (!(modelType == this.ModelType)) { return null; } if (this.SuppressPrefixCheck) { return this._modelBinderFactory(); } return new SimpleModelBinder(this); }
代码1-10并不是ComplexModelDtoModelBinderProvider类型中本身的实现,而是其本质的实现是SimpleModelBinderProvider类型来完成的,分为检查Model的前缀和不检查两种。这个自行看一下就知道了。
我们看下整体的结构图。
图1
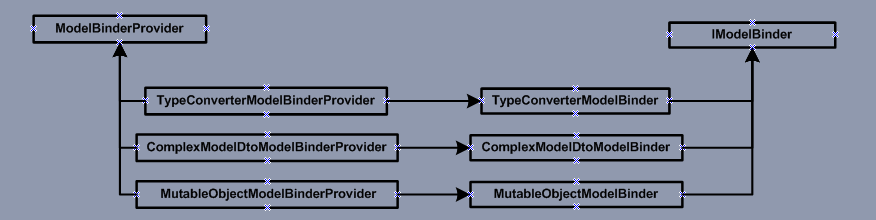
当然了还有其他的ModelBinder类型这里就不一一讲解了。最后我们看一下模拟复杂绑定的示意图。
图2

这里的Product是一个复杂类型,其中有三个string类型的属性,执行的顺序为红、蓝、黄。这里要说明的就是除了红色部分进入HttpActionContextExtensions之后不会再次递归,其他蓝色和黄色部分均有可能,只要碰到有复杂类型。
大概的说明一下流程代码部分在示例篇章会贴出来,首先在Product类型进行绑定的时候会先获取到Product的类型,然后根据当前框架中注册的一系列ModelBinder提供程序进行筛选获取到可以对复杂类型进行绑定的ModelBinder对象,在上图中也就是MutableObjectModelBinder类型,在MutableObjectModelBinder类型处理中会将Product类型的所有属性Model元数据进行封装,封装为ComplexModelDto对象实例,然后MutableObjectModelBinder类型会生成一个ModelBindingContext1对象实例,调用HttpActionContext类型的扩展方法类型HttpActionContextExtensions中的方法Bind()进行Model绑定,在Bind()方法中会重复红色线条流程部分,意思就是说会根据ModelBindingContext1对象实例中的Metadata属性获取到Model类型,刚才我们也说过了Model类型被封装为ComplexModelDto类型了,而后根据这个类型进行筛选获取到ComplexModelDtoModelBinderProvider提供程序,随之生成ComplexModelDtoModelBinder实例,在ComplexModelDtoModelBinder执行Model绑定的处理过程中,会遍历ComplexModelDto类型实例中的每一项属性元数据并且生成对应的ModelBindingContext,在上图也就是ModelBindingContext2以及在ModelBindingContext2执行绑定操作后的ModelBindingContext3。在ModelBindingContext2生成完毕之后会再次的调用HttpActionContext类型的扩展方法类型HttpActionContextExtensions中的方法Bind()进行Model绑定,因为Product中的属性都是string类型所以不存在复杂类型,按照上图中的顺序大家可以看出,如果是复杂类型则会重新执行到红色线条的起始部分。因为这个时候是string类型所以筛选出的提供程序类型为TypeConverterModelBinderProvider,从而生成TypeConverterModelBinder实例为之绑定。
作者:金源
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/jin-yuan/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面