Hashtable与ConcurrentHashMap区别
相同点: Hashtable 和 ConcurrentHashMap都是线程安全的,可以在多线程环境中运行; key跟value都不能是null
区别: 两者主要是性能上的差异,Hashtable的所有操作都会锁住整个对象,虽然能够保证线程安全,但是性能较差; ConcurrentHashMap内部使用Segment数组,每个Segment类似于Hashtable,在“写”线程或者部分特殊的“读”线程中锁住的是某个Segment对象,其它的线程能够并发执行其它的Segment对象。
?
下面从下面两个问题来具体了解下Hashtable和ConcurrentHashMap
1, Hashtable怎样实现线程安全?
2,ConcurrentHashMap怎样实现线程安全?为什么性能会比Hashtable好?
?
先来看第一个问题: Hashtable怎样实现线程安全?
下面是Hashtable的get和put方法
class="java" name="code"> /**
* The hash table data.
*/
//Hashtable使用Entry数组来保存数据
private transient Entry[] table;
public synchronized V get(Object key) {
Entry tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
//通过求模运算得到下标的索引值,保证下标在 【0,tab.length)
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return e.value;
}
}
return null;
}
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
V old = e.value;
e.value = value;
return old;
}
}
modCount++;
//元素数量超过阀值,需要增大散列表的大小
if (count >= threshold) {
// Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded
rehash();
tab = table;
index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
}
// Creates the new entry.
Entry<K,V> e = tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
return null;
}
?可以看到,Hashtable的方法都是声明为synchronized的,这样就能够保证Hashtable是线程安全的。 Hashtable的内部结构如下图所示:
?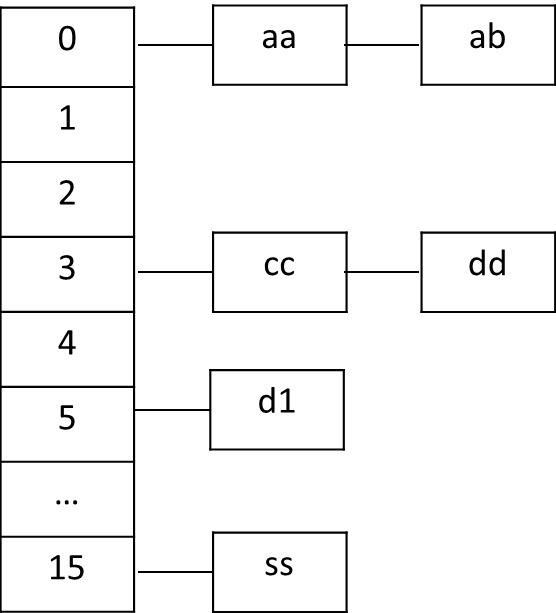
Hashtable在put元素时,会根据定义的方法计算hash值,如果这个位置没有元素,直接添加,如d1,如果已经有元素,会按照链表的方式将元素插在链表的头部,如aa。
?
?
再来看第二个问题: ConcurrentHashMap怎样实现线程安全?为什么性能会比Hashtable好?
1,下面是ConcurrentHashMap的put方法
// ConcurrentHashMap的key 跟 value都不能是null
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
return segmentFor(hash).put(key, hash, value, false);
}
?好的hash算法很重要(对于Hashtable,HashMap等也同样),如果冲突的概率大,会严重影响性能,下面是ConcurrentHashMap的hash算法,不过为什么会冲突较小就不明白了 ,望高手解决
,望高手解决
?
private static int hash(int h) {
// Spread bits to regularize both segment and index locations,
// using variant of single-word Wang/Jenkins hash.
h += (h << 15) ^ 0xffffcd7d;
h ^= (h >>> 10);
h += (h << 3);
h ^= (h >>> 6);
h += (h << 2) + (h << 14);
return h ^ (h >>> 16);
}
/**
* Returns the segment that should be used for key with given hash
* @param hash the hash code for the key
* @return the segment
*/
final Segment<K,V> segmentFor(int hash) {
return segments[(hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask];
}
?在segmentFor的方法中,变量segmentShift和segmentMask在创建ConcurrentHashMap的时候初始化, 如下所示
?
?
//initialCapacity: 初始容量大小,默认为16 //loadFactor: 跟threshold的值相关,控制是否需要扩容的阀门值,默认为0.75f //concurrencyLevel: the estimated number of concurrently updating threads, 跟Segment数组大小相关,默认为16 public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) { if (!(loadFactor > 0) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); if (concurrencyLevel > MAX_SEGMENTS) concurrencyLevel = MAX_SEGMENTS; // Find power-of-two sizes best matching arguments int sshift = 0; int ssize = 1; while (ssize < concurrencyLevel) { ++sshift; ssize <<= 1; //获取不小于concurrencyLevel的最小的2的幂,跟segmentFor计算相关 } segmentShift = 32 - sshift; segmentMask = ssize - 1; //二进制的低位都为1,在segmentFor方法中,保证(hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask结果在0~ssize-1之间(很好的算法,比求模的运算效率高) this.segments = Segment.newArray(ssize); if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; int c = initialCapacity / ssize; if (c * ssize < initialCapacity) ++c; int cap = 1; while (cap < c) cap <<= 1; for (int i = 0; i < this.segments.length; ++i) this.segments[i] = new Segment<K,V>(cap, loadFactor); }
?如果使用默认的参数构造ConcurrentHashMap,即initialCapacity=16,loadFactor=0.75f,concurrencyLevel=16, 得到的ssize=16,sshift=4, segmentMask=15, Segment数组长度为16。在表达式(hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask中,segmentMask的二进制为 00000000? 00000000? 00000000? 00001111,通过位与运算得到的结果范围为0~15,相比Hashtable的模运算,效率更高。 但是可能会有疑问,为何需要保证ssize为2的幂?如果ssize不是2的幂,得到的segmentMask低位不是全部为1,比如ssize=14,segmentMask=13,二进制为00000000? 00000000? 00000000? 00001101,此时位与运算肯定无法得到索引为 00000000? 00000000? 00000000? 0000**1*的数值,比如2、3、6、7、10、11、14,会导致Segment数组的利用率低,产生较大的hash冲突。
?
再来看下Segment的put方法
?
V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
lock();
try {
int c = count;
// 判断是否需要扩容
if (c++ > threshold) // ensure capacity
rehash();
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table;
int index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
HashEntry<K,V> first = tab[index];
HashEntry<K,V> e = first;
while (e != null && (e.hash != hash || !key.equals(e.key)))
e = e.next;
V oldValue;
if (e != null) {
oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.value = value;
}
else {
oldValue = null;
++modCount;
tab[index] = new HashEntry<K,V>(key, hash, first, value);
count = c; // write-volatile
}
return oldValue;
} finally {
unlock();
}
}
?在put方法中,使用ReentrantLock的 lock()和unlock()方法控制同步,Segment的定义如下
/**
* Segments are specialized versions of hash tables. This
* subclasses from ReentrantLock opportunistically, just to
* simplify some locking and avoid separate construction.
*/
static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable
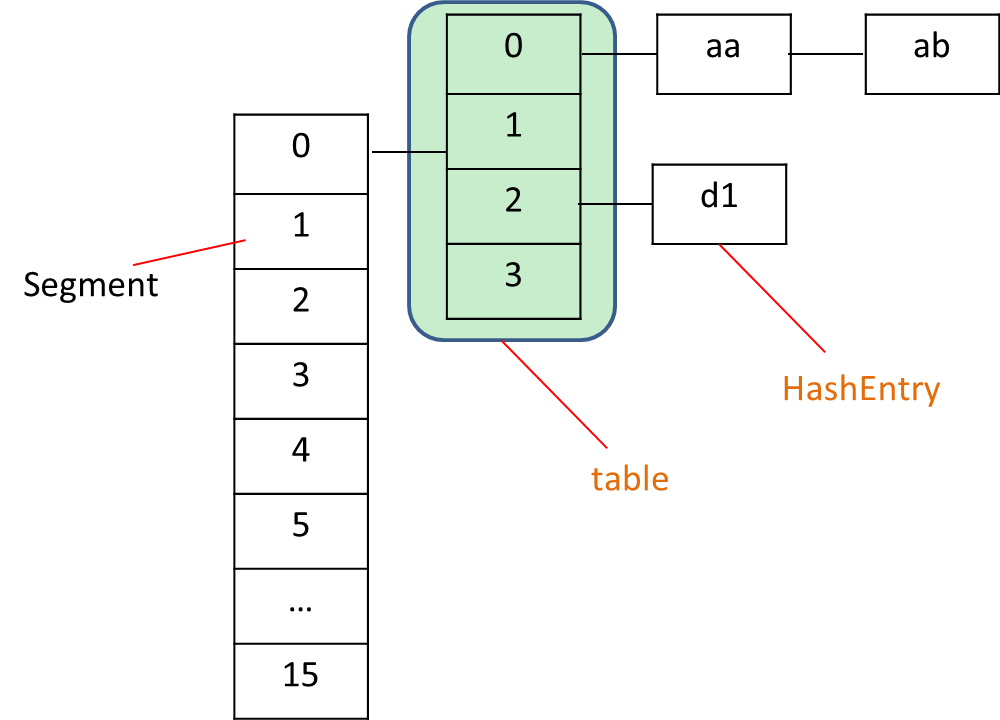
?从上面代码可知,ConcurrentHashMap在并发修改时,锁住的是当前Segment的对象,其它Segment中的并发操作可以同时执行,性能会比使用Hashtable好。 ConcurrentHashMap的结构如下所示:
?
?
?
?
?看到 kidneyball 分析的一段话,写得很好,哈哈,就搬过来了(勿怪)。
?
Q:? Hashtable,ConcurrentHashMap 有什么区别,这两个都是hash表,都是同步的
A:? Hashtable的任何操作都会把整个表锁住,是阻塞的。好处是总能获取最实时的更新,比如说线程A调用putAll写入大量数据,期间线程B调用get,线程B就会被阻塞,直到线程A完成putAll,因此线程B肯定能获取到线程A写入的完整数据。坏处是所有调用都要排队,效率较低。
???? ConcurrentHashMap 是设计为非阻塞的。在更新时会局部锁住某部分数据,但不会把整个表都锁住。同步读取操作则是完全非阻塞的。好处是在保证合理的同步前提下,效率很高。坏处 是严格来说读取操作不能保证反映最近的更新。例如线程A调用putAll写入大量数据,期间线程B调用get,则只能get到目前为止已经顺利插入的部分 数据。此外,使用默认构造器创建的ConcurrentHashMap比较占内存,如果程序需要创建巨量ConcurrentHashMap,应该在构造 时指定concurrencyLevel (详情参考 http://ria101.wordpress.com/2011/12/12/concurrenthashmap-avoid-a-common-misuse/ )。
?
转自:http://www.myexception.cn/program/1514881.html