Android手机一般以客户端的角色主动连接SPP协议设备(接上蓝牙模块的数字传感器),连接流程是:
1.使用registerReceiver注册BroadcastReceiver来获取蓝牙状态、搜索设备等消息;
2.使用BlueAdatper的搜索;
3.在BroadcastReceiver的onReceive()里取得搜索所得的蓝牙设备信息(如名称,MAC,RSSI);
4.通过设备的MAC地址来建立一个BluetoothDevice对象;
5.由BluetoothDevice衍生出BluetoothSocket,准备SOCKET来读写设备;
6.通过BluetoothSocket的createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord()方法来选择连接的协议/服务,这里用的是SPP(UUID:00001101-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FB);
7.Connect之后(如果还没配对则系统自动提示),使用BluetoothSocket的getInputStream()和getOutputStream()来读写蓝牙设备。
先来看看本文程序运行的效果图,所选的SPP协议设备是一款单导联心电采集表:
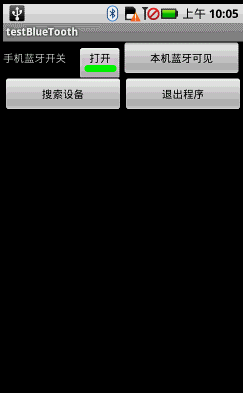
本 文程序包含两个Activity(testBlueTooth和WaveDiagram),testBlueTooth是搜索建立蓝牙连接。 BluetoothAdapter、BluetoothDevice和BluetoothSocket的使用很简单,除了前三者提供的功能外,还可以通过 给系统发送消息来控制、获取蓝牙信息,例如:
注册BroadcastReceiver:
IntentFilter intent = new IntentFilter(); intent.addAction(BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND);// 用BroadcastReceiver来取得搜索结果 intent.addAction(BluetoothDevice.ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED); intent.addAction(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_SCAN_MODE_CHANGED); intent.addAction(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_STATE_CHANGED); registerReceiver(searchDevices, intent);
在BroadcastReceiver的onReceive()枚举所有消息的内容:
String action = intent.getAction();
Bundle b = intent.getExtras();
Object[] lstName = b.keySet().toArray();
// 显示所有收到的消息及其细节
for (int i = 0; i < lstName.length; i++) {
String keyName = lstName[i].toString();
Log.e(keyName, String.valueOf(b.get(keyName)));
}
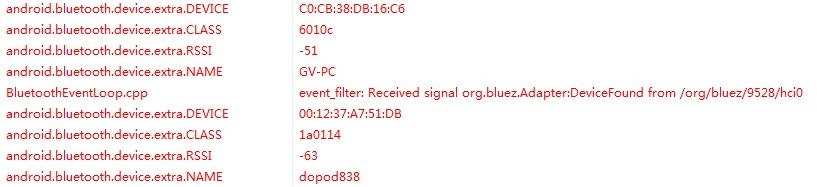
在DDMS里面可以看到BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND返回的消息:
程序另外一个Activity~~~WaveDiagram用于读取蓝牙数据并绘制波形图,这里要注意一下JAVA的byte的取值范围是跟C/C++不一样的,Android接收到的byte数据要做"& 0xFF"处理,转为C/C++等值的数据。