背景
ViewPager。它是google SDk中自带的一个附加包的一个类,可以用来实现屏幕间的切换。这个附加包是android-support-v4.jar。
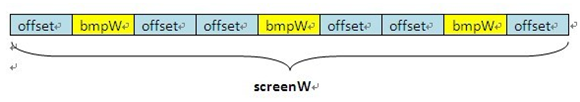
根据屏幕的分辨率和图片的宽度计算动画移动的偏移量
代码
viewpager.xml
界面设计很简单,第一行三个头标,第二行动画图片,第三行页卡内容展示。界面设计很简单,第一行三个头标,第二行动画图片,第三行页卡内容展示。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <LinearLayout android:id="@+id/linearLayout1" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="100.0dip" android:background="#FFFFFF" > <TextView android:id="@+id/text1" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_weight="1.0" android:gravity="center" android:text="页卡1" android:textColor="#000000" android:textSize="22.0dip" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/text2" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_weight="1.0" android:gravity="center" android:text="页卡2" android:textColor="#000000" android:textSize="22.0dip" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/text3" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_weight="1.0" android:gravity="center" android:text="页卡3" android:textColor="#000000" android:textSize="22.0dip" /> </LinearLayout> <ImageView android:id="@+id/cursor" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:scaleType="matrix" android:src="@drawable/a" /> <android.support.v4.view.ViewPager android:id="@+id/vPager" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center" android:layout_weight="1.0" android:background="#000000" android:flipInterval="30" android:persistentDrawingCache="animation" /> </LinearLayout>
我们要展示三个页卡,所以还需要三个页卡内容的界面设计,这里我们只设置了背景颜色,能起到区别作用即可。3个lay.xml,设置颜色不同。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:orientation="vertical" android:background="#1586FF" > </LinearLayout>
初始化头标
/** * 初始化头标 */ private void InitTextView() { t1 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text1); t2 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text2); t3 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text3); t1.setOnClickListener(new MyOnClickListener(0)); t2.setOnClickListener(new MyOnClickListener(1)); t3.setOnClickListener(new MyOnClickListener(2)); }
头标点击监听
/** * 头标点击监听 * */ public class MyOnClickListener implements View.OnClickListener { private int index = 0; public MyOnClickListener(int i) { index = i; } @Override public void onClick(View v) { mPager.setCurrentItem(index); } };
以上功能就是点击第几个,就展示第几个页卡内容。
初始化ViewPager
/** * 初始化ViewPager */ private void InitViewPager() { mPager = (ViewPager) findViewById(R.id.vPager); listViews = new ArrayList<View>(); LayoutInflater mInflater = getLayoutInflater(); listViews.add(mInflater.inflate(R.layout.lay1, null)); listViews.add(mInflater.inflate(R.layout.lay2, null)); listViews.add(mInflater.inflate(R.layout.lay3, null)); mPager.setAdapter(new MyPagerAdapter(listViews)); mPager.setCurrentItem(0); mPager.setOnPageChangeListener(new MyOnPageChangeListener()); }
我们将三个页卡界面装入其中,默认显示第一个页卡。这里我们还需要实现一个适配器。
ViewPager适配器
/** * ViewPager适配器 */ public class MyPagerAdapter extends PagerAdapter { public List<View> mListViews; public MyPagerAdapter(List<View> mListViews) { this.mListViews = mListViews; } @Override public void destroyItem(View arg0, int arg1, Object arg2) { ((ViewPager) arg0).removeView(mListViews.get(arg1)); } @Override public void finishUpdate(View arg0) { } @Override public int getCount() { return mListViews.size(); } @Override public Object instantiateItem(View arg0, int arg1) { ((ViewPager) arg0).addView(mListViews.get(arg1), 0); return mListViews.get(arg1); } @Override public boolean isViewFromObject(View arg0, Object arg1) { return arg0 == (arg1); } @Override public void restoreState(Parcelable arg0, ClassLoader arg1) { } @Override public Parcelable saveState() { return null; } @Override public void startUpdate(View arg0) { } }
这里我们实现了各页卡的装入和卸载。
页卡切换监听
/** * 页卡切换监听 */ public class MyOnPageChangeListener implements OnPageChangeListener { int one = offset * 2 + bmpW;// 页卡1 -> 页卡2 偏移量 int two = one * 2;// 页卡1 -> 页卡3 偏移量 @Override public void onPageSelected(int arg0) { Animation animation = null; switch (arg0) { case 0: if (currIndex == 1) { animation = new TranslateAnimation(one, 0, 0, 0); } else if (currIndex == 2) { animation = new TranslateAnimation(two, 0, 0, 0); } break; case 1: if (currIndex == 0) { animation = new TranslateAnimation(offset, one, 0, 0); } else if (currIndex == 2) { animation = new TranslateAnimation(two, one, 0, 0); } break; case 2: if (currIndex == 0) { animation = new TranslateAnimation(offset, two, 0, 0); } else if (currIndex == 1) { animation = new TranslateAnimation(one, two, 0, 0); } break; } currIndex = arg0; animation.setFillAfter(true);// True:图片停在动画结束位置
animation.setDuration(300); cursor.startAnimation(animation); } @Override public void onPageScrolled(int arg0, float arg1, int arg2) { } @Override public void onPageScrollStateChanged(int arg0) { } }
初始化动画
private void InitImageView() { cursor = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.cursor); bmpW = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.a).getWidth(); DisplayMetrics dm = new DisplayMetrics(); getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(dm); int screenW = dm.widthPixels;// 获取屏幕分辨率宽度 offset = (screenW / 3 - bmpW) / 2; // 计算偏移量:屏幕宽度/3,平分为3分,如果是3个view的话,再减去图片宽度,因为图片居中,所以要得到两变剩下的空隙需要再除以2 Matrix matrix = new Matrix(); matrix.postTranslate(offset, 0); // 初始化位置,在中间 cursor.setImageMatrix(matrix); // 设置动画初始位置 }
根据屏幕的分辨率和图片的宽度计算动画移动的偏移量。
OnCreate函数
private ViewPager mPager;//页卡内容 private List<View> listViews; // Tab页面列表 private ImageView cursor;// 动画图片 private TextView t1, t2, t3;//页卡头标 private int offset = 0;//动画图片偏移量 private int currIndex = 0;//当前页卡编号 private int bmpW;//动画图片宽度 @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.viewpager); InitImageView(); InitTextView(); InitViewPager(); }
简短不割
TranslateAnimation是移动的动画效果。它有三个构造函数,分别是:
public TranslateAnimation(Context context,AttributeSet attrs)
略过
public TranslateAnimation(float fromXDelta, float toXDelta, float fromYDelta, float toYDelta)
这个是我们最常用的一个构造方法,
float fromXDelta:这个参数表示动画开始的点离当前View X坐标上的差值;
float toXDelta, 这个参数表示动画结束的点离当前View X坐标上的差值;
float fromYDelta, 这个参数表示动画开始的点离当前View Y坐标上的差值;
float toYDelta,这个参数表示动画开始的点离当前View Y坐标上的差值;
如果view在A(x,y)点 那么动画就是从B点(x+fromXDelta, y+fromYDelta)点移动到C 点(x+toXDelta,y+toYDelta)点.
public TranslateAnimation (int fromXType, float fromXValue, int toXType, float toXValue, int fromYType, float fromYValue, int toYType, float toYValue)
fromXType:第一个参数是x轴方向的值的参照(Animation.ABSOLUTE, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,or Animation.RELATIVE_TO_PARENT);
fromXValue:第二个参数是第一个参数类型的起始值;
toXType,toXValue:第三个参数与第四个参数是x轴方向的终点参照与对应值;
后面四个参数就不用解释了。如果全部选择Animation.ABSOLUTE,其实就是第二个构造函数。
以x轴为例介绍参照与对应值的关系:
如果选择参照为Animation.ABSOLUTE,那么对应的值应该是具体的坐标值,比如100到300,指绝对的屏幕像素单位。
如果选择参照为Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF或者 Animation.RELATIVE_TO_PARENT指的是相对于自身或父控件,对应值应该理解为相对于自身或者父控件的几倍或百分之多少。多试参数就明白了。
android允许我们在对话框中显示指定的xml文件,从而实现自定义对话框的效果。自定义的登录对话框。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:id="@+id/loginForm" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <TableRow> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="用户名:" android:textSize="10pt" /> <!-- 输入用户名的文本框 --> <EditText android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="请填写登录帐号" android:selectAllOnFocus="true" /> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="密码:" android:textSize="10pt" /> <!-- 输入密码的文本框 --> <EditText android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:password="true" /> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="电话号码:" android:textSize="10pt" /> <!-- 输入电话号码的文本框 --> <EditText android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="请填写您的电话号码" android:phoneNumber="true" android:selectAllOnFocus="true" /> </TableRow> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="注册" /> </TableLayout>
Java
bn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View source) { // 设置对话框的图标 builder.setIcon(R.drawable.tools); // 设置对话框的标题 builder.setTitle("自定义普通对话框"); //装载/res/layout/login.xml界面布局 TableLayout loginForm = (TableLayout)getLayoutInflater().inflate( R.layout.login, null); // 设置对话框显示的View对象 builder.setView(loginForm); // 为对话框设置一个“确定”按钮 builder.setPositiveButton("登录" , new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { } }); // 为对话框设置一个“取消”按钮 builder.setNegativeButton("取消" ,new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { } }); //创建、并显示对话框 builder.create().show(); } }
 参考:http://blog.csdn.net/lizhenmingdirk/article/details/7345851
参考:http://blog.csdn.net/lizhenmingdirk/article/details/7345851
作用:
1、对于一个没有被载入或者想要动态载入的界面,都需要使用inflate来载入。
2、对于一个已经载入的Activity,就可以使用实现了这个Activiyt的的findViewById方法来获得其中的界面元素。
方法:
Android里面想要创建一个画面的时候, 初学一般都是新建一个类, 继承Activity基类, 然后在onCreate里面使用setContentView方法来载入一个在xml里定义好的界面.
其实在Activity里面就使用了LayoutInflater来载入界面, 通过getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE)方法可以获得一个 LayoutInflater, 也可以通过LayoutInflater inflater = getLayoutInflater();来获得.然后使用inflate方法来载入layout的xml,
@Override public void onClick(View v) { showCustomDialog(); } public void showCustomDialog() { AlertDialog.Builder builder; AlertDialog alertDialog; Context mContext = MainActivity.this; LayoutInflater inflater = (LayoutInflater) mContext.getSystemService(LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE); View layout = inflater.inflate(R.layout.custom_dialog, null); TextView text = (TextView) layout.findViewById(R.id.text); text.setText("Hello, Welcome to Mr Wei's blog!"); ImageView image = (ImageView) layout.findViewById(R.id.image); image.setImageResource(R.drawable.icon); builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(mContext); builder.setView(layout); alertDialog = builder.create(); alertDialog.show(); }
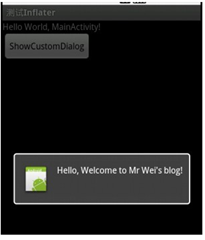 参考:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_629b701e0100rg4d.html
参考:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_629b701e0100rg4d.html
艹奥,还有几个忘记是哪参考来的了,不好意思没有写出来哈。
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/yydcdut/p/3697233.html