一、首先,让我们确认下什么是service?
service就是android系统中的服务,它有这么几个特点:它无法与用户直接进行交互、它必须由用户或者其他程序显式的启动、它的优先级比较高,它比处于前台的应用优先级低,但是比后台的其他应用优先级高,这就决定了当系统因为缺少内存而销毁某些没被利用的资源时,它被销毁的概率很小哦。
二、那么,什么时候,我们需要使用service呢?
我们知道,service是运行在后台的应用,对于用户来说失去了被关注的焦点。这就跟我们打开了音乐播放之后,便想去看看图片,这时候我们还不想音乐停止,这里就会用到service;又例如,我们打开了一个下载链接之后,我们肯定不想瞪着眼睛等他下载完再去做别的事情,对吧?这时候如果我们想手机一边在后台下载,一边可以让我去看看新闻啥的,就要用到service。
三、service分类:
一般我们认为service分为两类,本地service和远程service。
本地service顾名思义,那就是和当前应用在同一个进程中的service,彼此之间拥有共同的内存区域,所以对于某些数据的共享特别的方便和简单;
远程service:主要牵扯到不同进程间的service访问。因为android的系统安全的原因导致了我们在不同的进程间无法使用一般的方式共享数据。在这里android为我们提供了一个AIDL工具。(android interface description language)android接口描述语言。在后边我们将会对其进行详细的介绍。
四、service生命周期:
和Activity相比,service的生命周期已经简单的不能再简单了,只有onCreate()->onStart()->onDestroy()三个方法。
Activity中和service有关的方法:
startService(Intent intent):启动一个service
stopService(Intent intent) :停止一个service
如果我们想使用service中的一些数据或者访问其中的一些方法,那么我们就要通过下面的方法:
public boolean bindService(Intent intent, ServiceConnection conn, int flags) ;
public void unbindService(ServiceConnection conn);
intent是跳转到service的intent,如 Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setClass(this,MyService.class);
conn则是一个代表与service连接状态的类,当我们连接service成功或失败时,会主动触发其内部的onServiceConnected或onServiceDisconnected方法。如果我们想要访问service中的数据,可以在onServiceConnected()方法中进行实现,
使用service的步骤:
第一步:我们要继承service类,实现自己的service。
如果想要访问service中的某些值,我们通常会提供一个继承了Binder的内部类,通过onBund()方法返回给service请求。这里实际上巧妙的利用了内部类能够访问外部类属性的特点。
第二步:在androidManifest.xml中进行注册,如:
<!-- service配置开始 -->
<service android:name="MyService"></service>
<!-- service配置结束-->
第三步:在activity中进行启动、绑定、解绑或者停止service。
(很多书上说,service与用户是不能交互的,其实这话很不正确,我们完全可以通过activity与service进行交互!我认为,确切的说法应该是service与用户不能进行直接的交互)。
-----------------------------
一、bindService简介
bindService是绑定Service服务,执行service服务中的逻辑流程。
service通过Context.startService()方法开始,通过Context.stopService()方法停止;也可以通过Service.stopSelf()方法或者Service.stopSelfResult()方法来停止自己。只要调用一次stopService()方法便可以停止服务,无论之前它被调用了多少次的启动服务方法。
客户端建立一个与Service的连接,并使用此连接与Service进行通话,通过Context.bindService()方法来绑定服务,Context.unbindService()方法来关闭服务。多个客户端可以绑定同一个服务,如果Service还未被启动,bindService()方法可以启动服务。
上面startService()和bindService()两种模式是完全独立的。你可以绑定一个已经通过startService()方法启动的服务。例如:一个后台播放音乐服务可以通过startService(intend)对象来播放音乐。可能用户在播放过程中要执行一些操作比如获取歌曲的一些信息,此时activity可以通过调用bindServices()方法与Service建立连接。这种情况下,stopServices()方法实际上不会停止服务,直到最后一次绑定关闭。
如果没有程序停止它或者它自己停止,service将一直运行。在这种模式下,service开始于调用Context.startService() ,停止于Context.stopService(). service可以通过调用Android Service 生命周期() 或 Service.stopSelfResult()停止自己。不管调用多少次startService() ,只需要调用一次 stopService() 就可以停止service。
可以通过接口被外部程序调用。外部程序建立到service的连接,通过连接来操作service。建立连接调开始于Context.bindService(), 结束于Context.unbindService(). 多个客户端可以绑定到同一个service,如果service没有启动, bindService() 可以选择启动它。
这2种模式不是完全分离的。你可以可以绑定到一个通过startService()启动的服务。如一个intent想要播放音乐,通过startService() 方法启动后台播放音乐的service。然后,也许用户想要操作播放器或者获取当前正在播放的乐曲的信息,一个activity就会通过bindService()建立一个到此service的连接. 这种情况下 stopService() 在全部的连接关闭后才会真正停止service。
二、bindService启动流程
context.bindService() ——> onCreate() ——> onBind() ——> Service running ——> onUnbind() ——> onDestroy() ——> Service stop
onBind()将返回给客户端一个IBind接口实例,IBind允许客户端回调服务的方法,比如得到Service的实例、运行状态或其他操作。这个时候把调用者(Context,例如Activity)会和Service绑定在一起,Context退出了,Srevice就会调用onUnbind->onDestroy相应退出。
所以调用bindService的生命周期为:onCreate --> onBind(只一次,不可多次绑定) --> onUnbind --> onDestory。
在Service每一次的开启关闭过程中,只有onStart可被多次调用(通过多次startService调用),其他onCreate,onBind,onUnbind,onDestory在一个生命周期中只能被调用一次。
三、bindService生命周期
像一个activity那样,一个service有些可以用来改变状态的生命周期方法,但是比activity的方法少,service生命周期方法只有三个public
void onCreate()
void onStart(Intent intent)
void onDestroy()
通过实现这三个生命周期方法,你可以监听service的两个嵌套循环的生命周期:
1、整个生命周期
service的整个生命周期是在onCreate()和onDestroy()方法之间。和activity一样,在onCreate()方法里初始化,在onDestroy()方法里释放资源。例如,一个背景音乐播放服务可以在onCreate()方法里播放,在onDestroy()方法里停止。
2、活动的生命周期
service的活动生命周期是在onStart()之后,这个方法会处理通过startServices()方法传递来的Intent对象。音乐service可以通过开打intent对象来找到要播放的音乐,然后开始后台播放。注: service停止时没有相应的回调方法,即没有onStop()方法,只有onDestroy()销毁方法。
onCreate()方法和onDestroy()方法是针对所有的services,无论它们是否启动,通过Context.startService()和Context.bindService()方法都可以访问执行。然而,只有通过startService()方法启动service服务时才会调用onStart()方法。
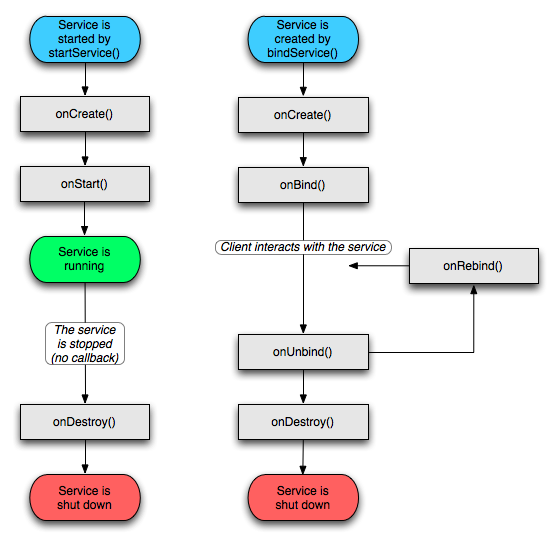
如果一个service允许别人绑定,那么需要实现以下额外的方法:
IBinder onBind(Intent intent)
boolean onUnbind(Intent intent)
void onRebind(Intent intent)
onBind()回调方法会继续传递通过bindService()传递来的intent对象
onUnbind()会处理传递给unbindService()的intent对象。如果service允许绑定,onBind()会返回客户端与服务互相联系的通信句柄(实例)。
如果建立了一个新的客户端与服务的连接,onUnbind()方法可以请求调用onRebind()方法。
记住: 任何服务无论它怎样建立,默认客户端都可以连接,所以任何service都能够接收onBind()和onUnbind()方法
四、bindService和startservice示例
(1)mainactivity
public class MainActivity extends Activity { Button startServiceButton;// 启动服务按钮 Button shutDownServiceButton;// 关闭服务按钮 Button startBindServiceButton;// 启动绑定服务按钮 @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); getWidget(); regiestListener(); } /** 获得组件 */ public void getWidget() { startServiceButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.startServerButton); startBindServiceButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.startBindServerButton); shutDownServiceButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.sutdownServerButton); } /** 为按钮添加监听 */ public void regiestListener() { startServiceButton.setOnClickListener(startService); shutDownServiceButton.setOnClickListener(shutdownService); startBindServiceButton.setOnClickListener(startBinderService); } /** 启动服务的事件监听 */ public Button.OnClickListener startService = new Button.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(View view) { /** 单击按钮时启动服务 */ Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, CountService.class); startService(intent); Log.v("MainStadyServics", "start Service"); } }; /** 关闭服务 */ public Button.OnClickListener shutdownService = new Button.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(View view) { /** 单击按钮时启动服务 */ Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, CountService.class); /** 退出Activity是,停止服务 */ stopService(intent); Log.v("MainStadyServics", "shutDown serveice"); } }; /** 打开绑定服务的Activity */ public Button.OnClickListener startBinderService = new Button.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(View view) { /** 单击按钮时启动服务 */ Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, UseBrider.class); startActivity(intent); Log.v("MainStadyServics", "start Binder Service"); } }; @Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { // Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present. getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu); return true; }
(2)service
package com.example.testservice; /**引入包*/ import android.app.Service;// 服务的类 import android.os.IBinder; import android.os.Binder; import android.content.Intent; import android.util.Log; /** 计数的服务 */ public class CountService extends Service { /** 创建参数 */ boolean threadDisable; int count; public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { return null; } public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); /** 创建一个线程,每秒计数器加一,并在控制台进行Log输出 */ new Thread(new Runnable() { public void run() { while (!threadDisable) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } count++; Log.v("CountService", "Count is" + count); } } }).start(); } public void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); /** 服务停止时,终止计数进程 */ this.threadDisable = true; } public int getConunt() { return count; } class ServiceBinder extends Binder { public CountService getService() { return CountService.this; } } }
(3)bindservice(一定要记着这个是要获得,链接的对象)
package com.example.testservice; /**引入包*/ import android.app.Activity; import android.content.ComponentName; import android.content.Context; import android.content.Intent; import android.content.ServiceConnection; import android.os.Bundle; import android.os.IBinder; import android.util.Log; /** 通过bindService和unBindSerivce的方式启动和结束服务 */ public class UseBrider extends Activity { /** 参数设置 */ CountService countService; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(new UseBriderFace(this)); Intent intent = new Intent(UseBrider.this, CountService.class); /** 进入Activity开始服务 */ bindService(intent, conn, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); } private ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection() { /** 获取服务对象时的操作 */ public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub countService = ((CountService.ServiceBinder) service).getService(); } /** 无法获取到服务对象时的操作 */ public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub countService = null; } }; protected void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); this.unbindService(conn); Log.v("MainStadyServics", "out"); } }
至于startservice和bindservice的使用场景,有网友这么说:
1.通过startservice开启的服务.一旦服务开启, 这个服务和开启他的调用者之间就没有任何的关系了.
调用者不可以访问 service里面的方法. 调用者如果被系统回收了或者调用了ondestroy方法, service还会继续存在
2.通过bindService开启的服务,服务开启之后,调用者和服务之间 还存在着联系 ,
一旦调用者挂掉了.service也会跟着挂掉 .
示例下载地址:http://pan.baidu.com/share/link?shareid=1614272126&uk=1428765741
还有一个多样化的demo学习地址:http://pan.baidu.com/share/link?shareid=1616100229&uk=1428765741
部分内容来源于互联网,感谢作者的无私提供