UICollectionView是iOS6引入的控件,而UIDynamicAnimator是iOS7上新添加的框架。本文主要涵盖3部分:
一是简单概括UICollectionView的使用;二是自定义一个UICollectionViewLayout来实现不同的Collection布局;
三是在自定义UICollectionViewLayout的基础上添加UIDynamicAnimator。
因为UICollectionView在iOS6上就引入了,所以这里就简单的介绍下。在正式使用前,我们有必要对UICollectionView认识一下。
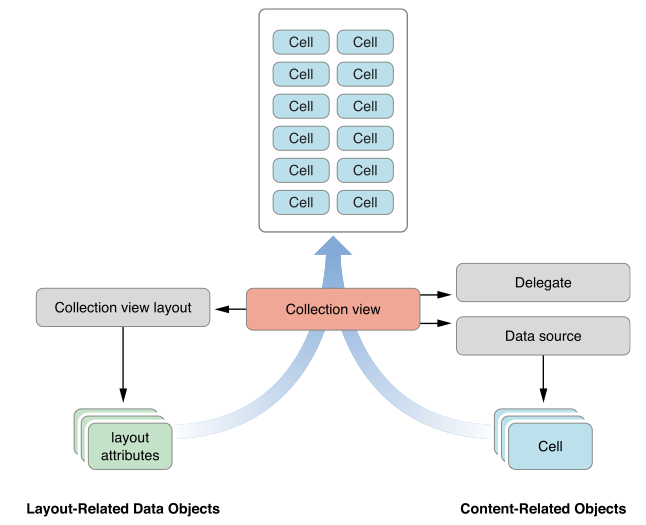
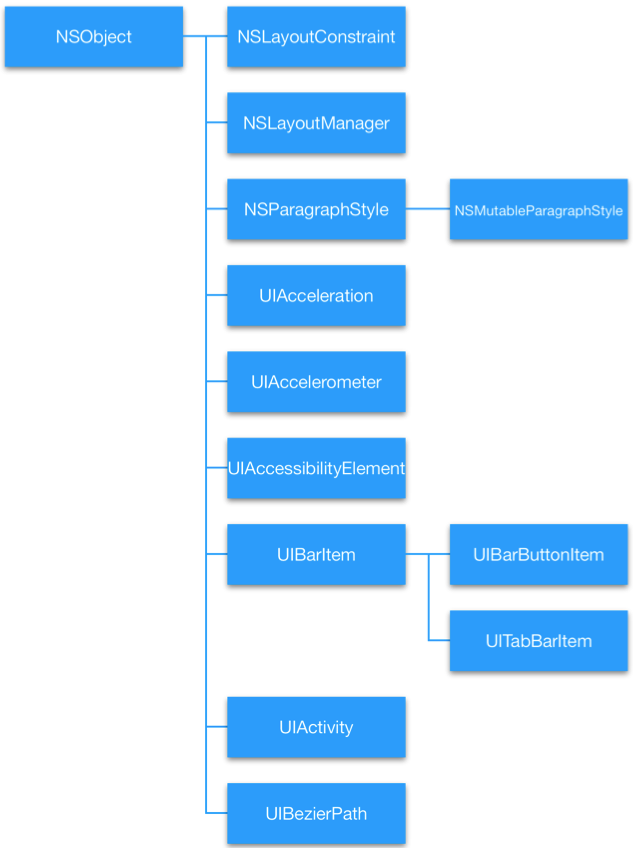
UICollectionView和UITableView有点类似,但又有不一样。从上图可以看出,组建一个UICollectionView不仅需要内容相关的对象,
如DataSource和Delegate,还需要布局相关的对象即UICollectionViewLayout。
熟悉UITableView的,对DataSource和Delegate应该比较亲切,他们的作用和在TableView里的完全一样。而UICollectionViewLayout是一个新的类,
他的作用就是控制所有view的显示。Layout会为每个view(如果需要显示),提供一个LayoutAttribute,通过LayoutAttribute,CollectionView就
知道如何去组织了。注意LayoutAttribute除了可以提供frame信息,还可以添加伪3D的信息和UIKit的动态信息。通过抽离布局信息,这样很好的维护了
模块间的独立性,而且也方便我们对layout进行重定义。理解这个框架图有助于理解CollectionView的渲染过程以及自定义Layout。
下面我们认识下COllectionView:
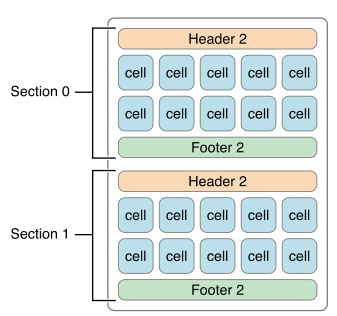
上图是UICollectionViewFlowLayout的一个布局,我们以此进行介绍:
知道了这些,我们就可以实现一个简单的CollectionView了。
在storeboard里新建一个viewController,并在view上添加一个UICollectionView,collectionview的delegate和datasource都在SB里连接好。
为了简单,我们直接使用UICollectionViewFlowLayout:

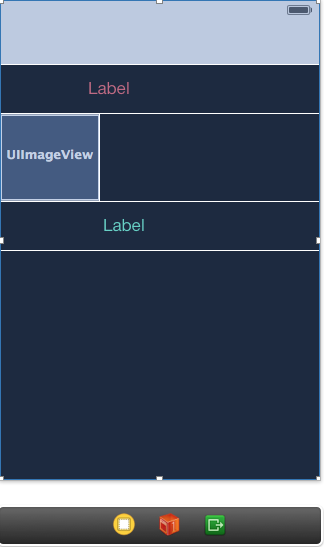
红色和绿色的label所在处就代表header和footer,他们都是用supplementary来表示,中间的Imageview所在处代表一个cell。
代码里三者都进行了简单的继承自定义,注意给他们三者设置一个identifier,这样利于重用。
然后在代码里实现dataSource方法:
class="brush:objc;gutter:true;">- (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInCollectionView:(UICollectionView *)collectionView
{
return 2;
}
- (NSInteger)collectionView:(UICollectionView *)view numberOfItemsInSection:(NSInteger)section;
{
return 20;
}
- (UICollectionViewCell *)collectionView:(UICollectionView *)collectionView cellForItemAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
ZJCell *cell = [collectionView dequeueReusableCellWithReuseIdentifier:@"ZJCell" forIndexPath:indexPath];
NSString *imgName = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%d.JPG",indexPath.row];
cell.imageView.image = [UIImage imageNamed:imgName];
return cell;
}
- (UICollectionReusableView *)collectionView:(UICollectionView *)collectionView viewForSupplementaryElementOfKind:(NSString *)kind atIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
ZJSupplementaryView *supplementaryView = nil;
NSString *text = nil;
if ([kind isEqualToString:UICollectionElementKindSectionHeader])
{
supplementaryView = [collectionView dequeueReusableSupplementaryViewOfKind:kind withReuseIdentifier:@"CLHeader" forIndexPath:indexPath];
text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Header %d",indexPath.section];
supplementaryView.backgroundColor = [UIColor darkGrayColor];
}
else
{
supplementaryView = [collectionView dequeueReusableSupplementaryViewOfKind:kind withReuseIdentifier:@"CLFooter" forIndexPath:indexPath];;
text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Footer %d",indexPath.section];
supplementaryView.backgroundColor = [UIColor lightGrayColor];
}
supplementaryView.label.text = text;
return supplementaryView;
}
这样一个最简单的flow式的照片显示就实现了,成品如下:

Layout类中,有3个方法是必定会被依次调用:
prepareLayout: 准备所有view的layoutAttribute信息
collectionViewContentSize: 计算contentsize,显然这一步得在prepare之后进行
layoutAttributesForElementsInRect: 返回在可见区域的view的layoutAttribute信息
此外,还有其他方法可能会被调用:
- (UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *)layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { } - (UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *)layoutAttributesForSupplementaryViewOfKind:(NSString *)kind atIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { } - (UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *)layoutAttributesForDecorationViewOfKind:(NSString *)decorationViewKind atIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { } - (BOOL)shouldInvalidateLayoutForBoundsChange:(CGRect)newBounds { }
比如,如果没有Decoration view,那么相应的方法就可以不实现。
接下来我们要实现一个自定义的layout。官方文档CollectionViewPGforIOS中指出了需要自定义layout的情形:

简单的说,就是现有的类(UICollectionViewLayout和UICollectionViewFlowLayout)不能满足需要的情况下需要自定义。
下面我们来实现CollectionViewPGforIOS中的自定义的例子,如图:
文档中,已经详细的阐述了每一步需要做的事情,这里就不多说了。但是因为文档中对于实现细节没有涉及,因此这里主要还是围绕之前提到的3个方法来进行说明。
这里假设你已经看过文档,并且知道自定义所需要的步骤。还需要声明的是,文档中给出的图以及下文的文字说明都是竖状排列的,但是由于疏忽,实现的时候变成了横向。希望因此不会给你造成混淆。
前提还需要做的准备:
1 定义Layout的子类
@interface ZJCustomLayout : UICollectionViewLayout @property (nonatomic, weak) id<ZJCustomLayoutProtocol> customDataSource; @end
@interfaceZJCustomLayout ()
{
NSInteger numberOfColumn;//here in this Sample Column equals the section
}
@property (nonatomic) NSDictionary *layoutInformation;//存储所有view的layoutAttribute
@property (nonatomic) CGFloat maxWidth;//用于计算contentSize
@property (nonatomic) UIEdgeInsets insets;
@end
protocol是用来获取一些数据,稍后定义。在扩展中定义一些属性,用于存储信息。
2 定义LayoutAttribute的子类
@interface ZJCollectionViewLayoutAttributes : UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes<UIDynamicItem> @property (nonatomic) NSArray *children; @end @implementation ZJCollectionViewLayoutAttributes - (BOOL)isEqual:(id)object { ZJCollectionViewLayoutAttributes *attribute = (ZJCollectionViewLayoutAttributes *)object; if ([self.children isEqualToArray:attribute.children]) { return [super isEqual:object]; } return NO; } @end
ZJCollectionViewLayoutAttribute就是每一个cell的属性,children表示当前cell所拥有的子cell。而isEqual是子类必须要重载的。
我们首先看一下,cell是如何布局的:
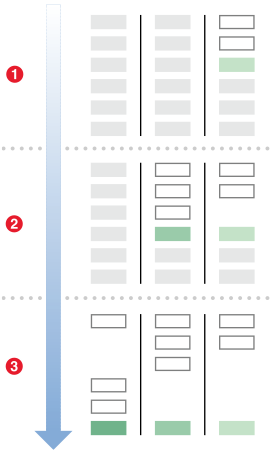
红色3是cell的最终位置。布局的时候,先把最后一列的cell依次加上,如红色1所示。
然后排前一列即第二列,先依次加上,这时最后的绿色cell有子cell,就把第三列的绿色cell位置更新。
最后排第一列,因为第一个cell有3个子cell,所以要空两个开始排列。这时最后一个绿色cell有子cell这时就又要调整第二列以及第三列的绿色cell。
这里cell调整的思路很清晰:先依次从上到下排列,然后再根据是否有子cell进行更新。
在实际实现中,我根据这样的思路,设计了类似的算法:
很显然,在初始化每个cell的layoutAttribute的时候,我们需要先知道每一个cell的子cell的情况,于是我们设计一个协议:
@protocol ZJCustomLayoutProtocol <NSObject> - (NSArray *)childrenAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath; @end
这个和CollectionView的dataSource,delegate一样,由viewController来提供。
接下来我们开始实现:
- (void)prepareLayout { if (self.layoutInformation) { return; } //whole size preparation NSMutableDictionary *layoutInformation = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary]; NSMutableDictionary *cellInformation = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary]; NSIndexPath *indexPath; NSInteger numSections = [self.collectionView numberOfSections]; numberOfColumn = numSections; //初始化attribute for(NSInteger section = 0; section < numSections; section++) { NSInteger numItems = [self.collectionView numberOfItemsInSection:section]; for(NSInteger item = 0; item < numItems; item++) { indexPath = [NSIndexPath indexPathForItem:item inSection:section]; ZJCollectionViewLayoutAttributes *attributes = [self attributesWithChildrenAtIndexPath:indexPath]; // attributes.zIndex = -(0 + 1); // attributes.transform = CGAffineTransformMakeRotation(.1); // attributes.transform3D = CATransform3DMakeRotation(.3, 0, 0, 1); [cellInformation setObject:attributes forKey:indexPath]; } } //从最后向前开始逐个调整attribute for(NSInteger section = numSections - 1; section >= 0; section--) { NSInteger numItems = [self.collectionView numberOfItemsInSection:section]; NSInteger totalHeight = 0; for(NSInteger item = 0; item < numItems; item++) { indexPath = [NSIndexPath indexPathForItem:item inSection:section]; ZJCollectionViewLayoutAttributes *attributes = [cellInformation objectForKey:indexPath];//1 attributes.frame = [self frameForCellAtIndexPath:indexPath withHeight:totalHeight]; // begin adjust the frame and its children's frame if (item) { NSIndexPath *previousIndex = [NSIndexPath indexPathForRow:item - 1 inSection:section]; ZJCollectionViewLayoutAttributes *previousAttribute = cellInformation[previousIndex]; CGRect rect = attributes.frame; CGRect previousRect = previousAttribute.frame; rect.origin.x = previousRect.origin.x + previousRect.size.width + CELL_ROW_SPACE; //前一个cell是否有孩子 if (previousAttribute.children) { ZJCollectionViewLayoutAttributes *preLastChildAttri = cellInformation[previousAttribute.children.lastObject]; CGRect preLastChildFrame = preLastChildAttri.frame; rect.origin.x = preLastChildFrame.origin.x + preLastChildFrame.size.width + CELL_ROW_SPACE; // rect.origin.x += (CELL_WIDTH + CELL_ROW_SPACE) * (previousAttribute.children.count - 1); } attributes.frame = rect; //调整自己的子cell if (attributes.children) { NSUInteger childrenCount = attributes.children.count; CGFloat baseOffset = rect.origin.x; for (NSUInteger count = 0; count < childrenCount; count ++) { NSIndexPath *childIndexpath = attributes.children[count];; ZJCollectionViewLayoutAttributes *childAttri = cellInformation[childIndexpath]; CGRect childRect = childAttri.frame; childRect.origin.x = baseOffset + count *(CELL_WIDTH + CELL_ROW_SPACE); childAttri.frame = childRect; } } } //记录最大的长度(宽度) CGFloat currentWidth = attributes.frame.origin.x + attributes.frame.size.width; if (self.maxWidth < currentWidth) { self.maxWidth = currentWidth; } cellInformation[indexPath] = attributes; // totalHeight += [self.customDataSource numRowsForClassAndChildrenAtIndexPath:indexPath];//3 } } [layoutInformation setObject:cellInformation forKey:@"MyCellKind"];//5
通过这里获得的数据我们可以返回contentSize了。虽然高度上会有调整,但是宽度上是和section绑定的。
- (CGSize)collectionViewContentSize { CGFloat width = self.maxWidth + CELL_ROW_SPACE; CGFloat height = self.collectionView.numberOfSections * (CELL_HEIGHT + CELL_SEC_SPACE) + self.insets.top + self.insets.bottom; return CGSizeMake(width, height); }
接下来就要实现layoutAttributesForElementsInRect,这个通过CGRectIntersectsRect来选择是否在当前的rect里:
- (NSArray *)layoutAttributesForElementsInRect:(CGRect)rect { NSMutableArray *myAttributes = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:self.layoutInformation.count]; for (NSString *key in self.layoutInformation) { NSDictionary *attributesDict = [self.layoutInformation objectForKey:key]; for (NSIndexPath *indexPath in attributesDict) { ZJCollectionViewLayoutAttributes *attributes = [attributesDict objectForKey:indexPath]; if (CGRectIntersectsRect(rect, attributes.frame)) { [myAttributes addObject:attributes]; } } } return myAttributes; }
然后在viewController类里实现datasource,不要忘记实现我们自定义的protocol。这样,我们就能看到所有的cell了。
接下来我们就要实现cell间的连线。连线我是作为supplementary view来处理。如果一个cell有子cell,那么就设置view,并记录点的相应位置,如图:
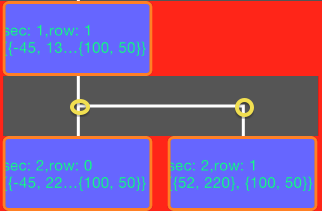
因此仿照cell的处理方式,定义了suppleLayoutAttribute,主要用于存储点:
@interface ZJCollectionSuppleLayoutAttributes : UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes @property (nonatomic) NSArray *pointArray; @end
然后继承了UICollectionReusableView用于划线:
@interface ZJClassReusableView() @property (nonatomic) NSArray *pointArray; @end @implementation ZJClassReusableView - (id)initWithFrame:(CGRect)frame { self = [super initWithFrame:frame]; if (self) { // Initialization code self.backgroundColor = [UIColor darkGrayColor]; } return self; } // Only override drawRect: if you perform custom drawing. // An empty implementation adversely affects performance during animation. - (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect { [super drawRect:rect]; // Drawing code CGRect frame = self.frame; CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(); CGContextSetStrokeColorWithColor(context, [UIColor whiteColor].CGColor); CGContextSetLineWidth(context, 2); NSUInteger count = self.pointArray.count; for (NSUInteger num = 0; num < count; num ++) { CGPoint point = [[self.pointArray objectAtIndex:num] CGPointValue]; CGFloat xPosition = point.x - frame.origin.x; if (num == 0) { CGContextMoveToPoint(context, xPosition, 0); CGContextAddLineToPoint(context, xPosition, rect.size.height); } else { CGContextMoveToPoint(context, xPosition, frame.size.height/2); CGContextAddLineToPoint(context, xPosition, rect.size.height); } } if (count > 1) { CGPoint first = [[self.pointArray objectAtIndex:0] CGPointValue]; CGPoint last = [[self.pointArray lastObject] CGPointValue]; CGContextMoveToPoint(context, first.x - frame.origin.x, frame.size.height/2); CGContextAddLineToPoint(context, last.x - frame.origin.x + 1, frame.size.height/2); } CGContextStrokePath(context); } - (void)applyLayoutAttributes:(UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *)layoutAttributes { [super applyLayoutAttributes:layoutAttributes]; self.pointArray = ((ZJCollectionSuppleLayoutAttributes *)layoutAttributes).pointArray; } @end
而在customLayout中,需要添加:
//frame for supplement view NSMutableDictionary *suppleDict = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary]; for(NSInteger section = 0; section < numSections; section++) { NSInteger numItems = [self.collectionView numberOfItemsInSection:section]; for(NSInteger item = 0; item < numItems; item++) { indexPath = [NSIndexPath indexPathForItem:item inSection:section]; ZJCollectionSuppleLayoutAttributes *suppleAttri = [ZJCollectionSuppleLayoutAttributes layoutAttributesForSupplementaryViewOfKind:ZJSupplementKindDiagram withIndexPath:indexPath]; ZJCollectionViewLayoutAttributes *cellAttribute = cellInformation[indexPath]; NSArray *cellChildren = cellAttribute.children; if (cellChildren) { NSUInteger childrenCount = cellChildren.count; //calculate the frame CGRect cellFrame = cellAttribute.frame; CGRect suppleFrame = cellFrame; suppleFrame.origin.y = cellFrame.origin.y + cellFrame.size.height; suppleFrame.size.height = CELL_SEC_SPACE; NSMutableArray *mPointArray = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:childrenCount]; for (NSUInteger childNum = 0; childNum < childrenCount; childNum ++) { NSIndexPath *firstIndexPath = [cellChildren objectAtIndex:childNum]; ZJCollectionViewLayoutAttributes *firstChildAttri = cellInformation[firstIndexPath]; CGRect firstChildFrame = firstChildAttri.frame; CGPoint firstPoint = CGPointMake(firstChildFrame.origin.x + firstChildFrame.size.width /2, firstChildFrame.origin.y + firstChildFrame.size.height /2); [mPointArray addObject:[NSValue valueWithCGPoint:firstPoint]]; if (childNum == childrenCount - 1) { suppleFrame.size.width = firstChildFrame.origin.x + firstChildFrame.size.width - suppleFrame.origin.x; } } suppleAttri.frame = suppleFrame; suppleAttri.pointArray = mPointArray; } [suppleDict setObject:suppleAttri forKey:indexPath]; } }
这样一个树状结构的图就完成了。
本身这段时间在学习UIDynamicAnimator,正好学到和collectionView的部分,觉得对CollectionView不太熟悉,就先温习了一遍。
所以UIDynamicanimator其实是重点。我的主要参考资料是WWDC2013 221,以及collection-views-and-uidynamics。
主要实现了Cell的动态动画,当拖动collectionView的时候,cell会晃动。
具体的添加方法我就不详细解说了,这里主要说明下自定义的layout添加UIDynamicAnimator需要注意的地方。
- (NSArray *)layoutAttributesForElementsInRect:(CGRect)rect { .... //之前的代码后要添加 NSArray *array = [self.dynamicAnimator itemsInRect:rect]; [myAttributes addObjectsFromArray:array]; }
不知道为什么一定要通过这样的方式把添加到DynamicAnimator的Cell属性取出来,否则cell就会不显示。
还有就是在shouldInvalidateLayoutForBoundsChange中动态更新DynamicItem,否则动画无从启动。
主要涉及UICollectionView的使用,简单的自定义UICollectionViewLayout,以及添加UIKitDynamic。
关于CollectionView的点击,插入,删除等操作没有涵盖。
另外,自定义Layout的时候没有考虑性能,比如cell数量大的时候,现有prepare中的方式无疑会造成程序页面变卡;
添加的动态行为没有很好的修饰,纯粹为了说明两者结合的方法。
本文使用到的图片都来自官方文档和本人demo的截图。
最后附上代码,请大家指正。
CollectionSample