本文将简单介绍用于
线程协作的Condition, 并给出一个
例子,实现一个多线程题目--有三个线程分别打印A、B、C,请用多线程编程实现,在屏幕上
循环打印10次ABCABC…
。
Condition是从JDK 1.5开始有的。API是这么描述的:

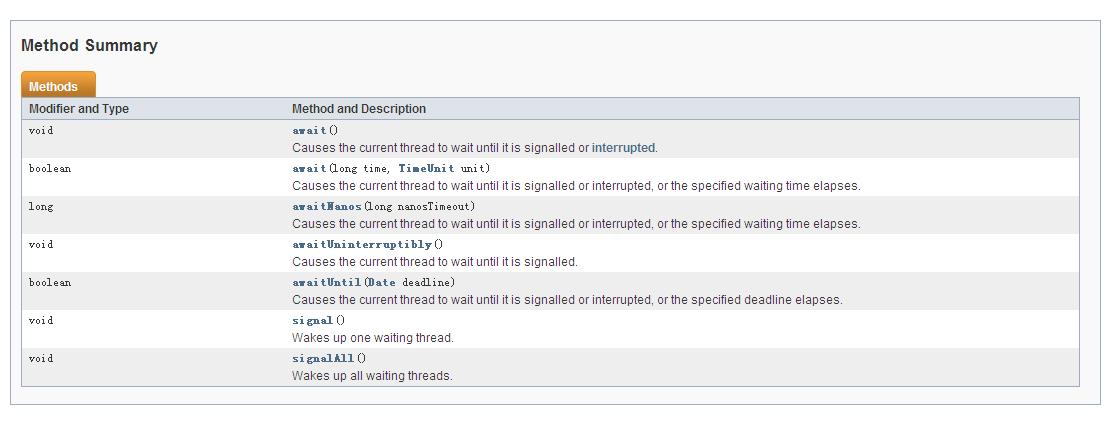
以上是Condition
接口定义的方法,
await()对应于Object#wait(),
signal()对应于Object#notify(),
signalAll()对应于Object#notifyAll()。
Condition是与Lock结合使用的,通过Lock.newCondition()方法能够创建与Lock绑定的Condition实例。
Lock和Condition的关系就如同 Object.wait(),Object.notify()方法和synchronized一样,它们都可以配合使用完成对多线程协作的控制。
JDK提供的
ArrayBlockingQueue很好地诠释了Condition的使用。
class="java" name="code">public class ArrayBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable {
/** Condition for waiting takes */
private final Condition notEmpty;
/** Condition for waiting puts */
private final Condition notFull;
/**
* Inserts element at current put position, advances, and signals.
* Call only when holding lock.
*/
private void insert(E x) {
items[putIndex] = x;
putIndex = inc(putIndex);
++count;
notEmpty.signal();
}
/**
* Extracts element at current take position, advances, and signals.
* Call only when holding lock.
*/
private E extract() {
final Object[] items = this.items;
E x = this.<E>cast(items[takeIndex]);
items[takeIndex] = null;
takeIndex = inc(takeIndex);
--count;
notFull.signal();
return x;
}
/**
* Deletes item at position i.
* Utility for remove and iterator.remove.
* Call only when holding lock.
*/
void removeAt(int i) {
final Object[] items = this.items;
// if removing front item, just advance
if (i == takeIndex) {
items[takeIndex] = null;
takeIndex = inc(takeIndex);
} else {
// slide over all others up through putIndex.
for (;;) {
int nexti = inc(i);
if (nexti != putIndex) {
items[i] = items[nexti];
i = nexti;
} else {
items[i] = null;
putIndex = i;
break;
}
}
}
--count;
notFull.signal();
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue, waiting
* for space to become available if the queue is full.
*
* @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == items.length)
notFull.await();
insert(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == 0)
notEmpty.await();
return extract();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
... ...
}
下面就使用Condition来完成一个线程面试题:有三个线程分别打印A、B、C,请用多线程编程实现,在屏幕上循环打印10次ABCABC…
程序如下:
package my.thread.test;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* 题目:有三个线程分别打印A、B、C,请用多线程编程实现,在屏幕上循环打印10次ABCABC…
*
* 本程序采用Lock和Condition来实现。
*
* @author Eric
*
*/
public class ConditionExample {
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition conditionA = lock.newCondition();
private Condition conditionB = lock.newCondition();
private Condition conditionC = lock.newCondition();
/** 当前线程的名字 */
private char currentThreadName = 'A';
private static final Logger logger = Logger
.getLogger("my.thread.test.OrderPrintTest");
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConditionExample ce = new ConditionExample();
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
service.execute(ce.new ThreadA());
service.execute(ce.new ThreadB());
service.execute(ce.new ThreadC());
service.shutdown();
}
private class ThreadA implements Runnable {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (currentThreadName != 'A') {
try {
/*
* 如果当前线程名字不是A,那么ThreadA就处理等待状态
*/
conditionA.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
logger.severe(e.getLocalizedMessage());
}
}
/*
* 打印出第几遍以及A信息
*/
System.out.println(String.format("第%d遍", i + 1));
System.out.println("A");
/*
* 将当前线程名置为B, 然后通知ThreadB执行
*/
currentThreadName = 'B';
conditionB.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
private class ThreadB implements Runnable {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (currentThreadName != 'B') {
try {
/*
* 如果当前线程名字不是B,那么ThreadB就处理等待状态
*/
conditionB.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
logger.severe(e.getLocalizedMessage());
}
}
/*
* 打印信息B
*/
System.out.println("B");
/*
* 将当前线程值置为C 并通过ThreadC来执行
*/
currentThreadName = 'C';
conditionC.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
private class ThreadC implements Runnable {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (currentThreadName != 'C') {
try {
/*
* 如果当前线程名字不是C,那么ThreadC就处理等待状态
*/
conditionC.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
logger.severe(e.getLocalizedMessage());
}
}
/*
* 打印信息C
*/
System.out.println("C");
System.out.println();
/*
* 将当前线程值置为A 并通过ThreadA来执行
*/
currentThreadName = 'A';
conditionA.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
}
程序运行结果如下:
第1遍
A
B
C
第2遍
A
B
C
第3遍
A
B
C
第4遍
A
B
C
第5遍
A
B
C
第6遍
A
B
C
第7遍
A
B
C
第8遍
A
B
C
第9遍
A
B
C
第10遍
A
B
C

- 大小: 16 KB
- 大小: 51 KB

