在之前,我们写了自己的Asp.Net框架,对整个流程有了一个大概的认识。这次我们来看一下Asp.Net整个请求处理过程是怎么样的。
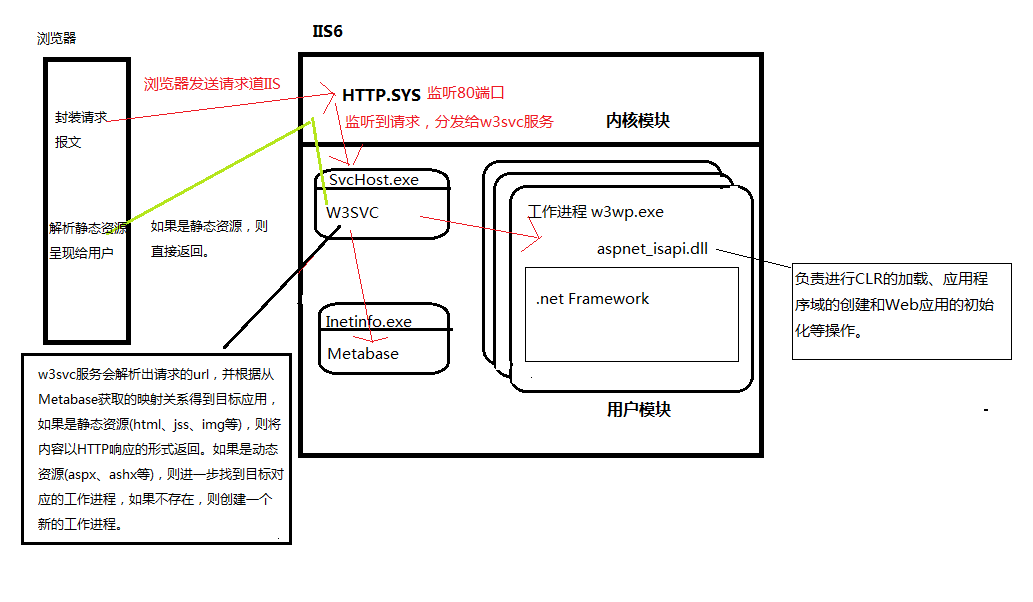
浏览器封装请求报文,发送请求到达服务器,服务器内核模块的HTTP.SYS监听到用户的HTTP请求,将其分发给W3SVC,W3SVC解析出请求的URL,并根据Metabase获取映射关系得到目标应用,如果是静态资源(HTML,jss,img等),则将内容以HTTP响应的车型是返回。如果是动态文件(aspx、ashx)等,则进一步获取到目标对应的工作进程w3wp.exe,如果不存在,则创建一个新的工作进程。工作进程w3wp.exe利用aspnet_isapi.dll创建处理当前请求的应用程序域,随后ISAPIRuntime会被加载,ISAPIRuntime会接管该HTTP请求。
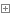
ISAPIRuntime会首先创建一个ISAPIWorkRequest对象,对请求报文进行了简单的封装,并将该ISAPIWorkRequest对象传递给HttpRuntime。
HttpRuntime会根据ISAPIWorkRequest创建用于封装Http请求上下文的对象HttpConetxt。
HttpContext主要包括HttpRequest(当前请求)和HttpResponse(服务器响应)
1 [SecurityPermission(SecurityAction.LinkDemand, Unrestricted=true)] 2 public int ProcessRequest(IntPtr ecb, int iWRType) 3 { 4 IntPtr zero = IntPtr.Zero; 5 if (iWRType == 2) 6 { 7 zero = ecb; 8 ecb = UnsafeNativeMethods.GetEcb(zero); 9 } 10 //创建了ISAPIWorkRquest空对象 11 ISAPIWorkerRequest wr = null; 12 try 13 { 14 bool useOOP = iWRType == 1; 15 //通过ecb句柄创建了ISAPIWorkRequest对象 16 wr = ISAPIWorkerRequest.CreateWorkerRequest(ecb, useOOP); 17 wr.Initialize(); 18 string appPathTranslated = wr.GetAppPathTranslated(); 19 string appDomainAppPathInternal = HttpRuntime.AppDomainAppPathInternal; 20 if ((appDomainAppPathInternal == null) || StringUtil.EqualsIgnoreCase(appPathTranslated, appDomainAppPathInternal)) 21 { 22 //IsapiRuntime把WR交给了HttpRuntime 23 HttpRuntime.ProcessRequestNoDemand(wr); 24 return 0; 25 } 26 HttpRuntime.ShutdownAppDomain(ApplicationShutdownReason.PhysicalApplicationPathChanged, SR.GetString("Hosting_Phys_Path_Changed", new object[] { appDomainAppPathInternal, appPathTranslated })); 27 return 1; 28 } 29 catch (Exception exception) 30 { 31 try 32 { 33 WebBaseEvent.RaiseRuntimeError(exception, this); 34 } 35 catch 36 { 37 } 38 if ((wr == null) || !(wr.Ecb == IntPtr.Zero)) 39 { 40 throw; 41 } 42 if (zero != IntPtr.Zero) 43 { 44 UnsafeNativeMethods.SetDoneWithSessionCalled(zero); 45 } 46 if (exception is ThreadAbortException) 47 { 48 Thread.ResetAbort(); 49 } 50 return 0; 51 } 52 } 53 54ISAPIRuntime
HttpRuntime通过HttpApplicationFactory获取一个新的或现有的HttpApplication对象。
1 private void ProcessRequestInternal(HttpWorkerRequest wr) 2 { 3 Interlocked.Increment(ref this._activeRequestCount); 4 if (this._disposingHttpRuntime) 5 { 6 try 7 { 8 wr.SendStatus(0x1f7, "Server Too Busy"); 9 wr.SendKnownResponseHeader(12, "text/html; charset=utf-8"); 10 byte[] bytes = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("<html><body>Server Too Busy</body></html>"); 11 wr.SendResponseFromMemory(bytes, bytes.Length); 12 wr.FlushResponse(true); 13 wr.EndOfRequest(); 14 } 15 finally 16 { 17 Interlocked.Decrement(ref this._activeRequestCount); 18 } 19 } 20 else 21 { 22 HttpContext context; 23 try 24 { 25 //通过wr创建了上下文对象 26 context = new HttpContext(wr, false); 27 } 28 catch 29 { 30 try 31 { 32 wr.SendStatus(400, "Bad Request"); 33 wr.SendKnownResponseHeader(12, "text/html; charset=utf-8"); 34 byte[] data = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("<html><body>Bad Request</body></html>"); 35 wr.SendResponseFromMemory(data, data.Length); 36 wr.FlushResponse(true); 37 wr.EndOfRequest(); 38 return; 39 } 40 finally 41 { 42 Interlocked.Decrement(ref this._activeRequestCount); 43 } 44 } 45 wr.SetEndOfSendNotification(this._asyncEndOfSendCallback, context); 46 HostingEnvironment.IncrementBusyCount(); 47 try 48 { 49 try 50 { 51 this.EnsureFirstRequestInit(context); 52 } 53 catch 54 { 55 if (!context.Request.IsDebuggingRequest) 56 { 57 throw; 58 } 59 } 60 context.Response.InitResponseWriter(); 61 62 //通过HttpApplicationFactory获取HttpApplication实例 63 IHttpHandler applicationInstance = HttpApplicationFactory.GetApplicationInstance(context); 64 if (applicationInstance == null) 65 { 66 throw new HttpException(SR.GetString("Unable_create_app_object")); 67 } 68 if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled(5, 1)) 69 { 70 EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_START_HANDLER, context.WorkerRequest, applicationInstance.GetType().FullName, "Start"); 71 } 72 if (applicationInstance is IHttpAsyncHandler) 73 { 74 IHttpAsyncHandler handler2 = (IHttpAsyncHandler) applicationInstance; 75 context.AsyncAppHandler = handler2; 76 77 //执行HttpApplication的BeginProcessRequest方法 78 handler2.BeginProcessRequest(context, this._handlerCompletionCallback, context); 79 } 80 else 81 { 82 applicationInstance.ProcessRequest(context); 83 this.FinishRequest(context.WorkerRequest, context, null); 84 } 85 } 86 catch (Exception exception) 87 { 88 context.Response.InitResponseWriter(); 89 this.FinishRequest(wr, context, exception); 90 } 91 } 92 }HttpRuntime
HttpApplication负责处理分发给它的请求。由于一个HttpApplication对象在同一时间只能处理一个请求,只有完成对某个请求的处理后,HttpApplication才能用于后续请求 的处理,所以Asp.Net采用对象池的获取HttpApplication对象。
当第一个请求到达时,HttpApplicationFactory会一次创建多个HttpApplication对象,并将其置于对象池中,选择其中一个对象来处理该请求。处理完毕后HttpApplication不会回收,而是释放到池中。池中空闲的HttpApplication对象用于处理后续请求,当没有空闲的时候再进行创建新的HttpApplication。
HttpApplication对象的创建时根据Global文件编译后的类型,通过反射的方式创建的,很消耗资源和时间,因此这里使用了对象池的技术
1.确保Global文件被编译,如果没有Global文件,则对所有事件提供HttpApplication的默认行为。
Global:它继承自HttpApplication类,用于维护一个HttpApplication对象池,并在需要的时候讲对象池中的对象分配给应用程序。
2.创建一个特殊的HttpApplication对象,并调用它的Application_Start方法。
3.获取一个用于处理当前请求的HttpApplication实例,进行初始化。

1 internal static IHttpHandler GetApplicationInstance(HttpContext context) 2 { 3 if (_customApplication != null) 4 { 5 return _customApplication; 6 } 7 if (context.Request.IsDebuggingRequest) 8 { 9 return new HttpDebugHandler(); 10 } 11 _theApplicationFactory.EnsureInited(); 12 _theApplicationFactory.EnsureAppStartCalled(context); 13 return _theApplicationFactory.GetNormalApplicationInstance(context); 14 }View Code
初始化:①.创建HttpModuleCollection集合——>根据配置文件,获取所有的HttpModule,并循环执行HttpModule的初始化方法。

1 private void InitModules() 2 { 3 HttpModuleCollection modules = RuntimeConfig.GetAppConfig().HttpModules.CreateModules(); 4 HttpModuleCollection other = this.CreateDynamicModules(); 5 modules.AppendCollection(other); 6 this._moduleCollection = modules; 7 this.InitModulesCommon(); 8 } 9 10 11 private void InitModulesCommon() 12 { 13 int count = this._moduleCollection.Count; 14 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) 15 { 16 this._currentModuleCollectionKey = this._moduleCollection.GetKey(i); 17 this._moduleCollection[i].Init(this); 18 } 19 this._currentModuleCollectionKey = null; 20 this.InitAppLevelCulture(); 21 }View Code
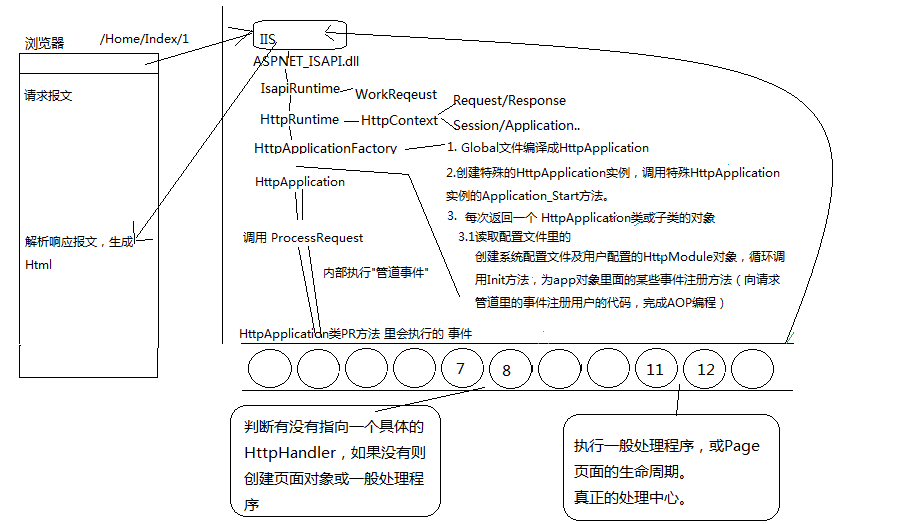
②.对HttpApplication的管道事件和HttpHandler有序绑定,主要有两处HttpHandler。
1.——>在管道第7-8个事件之间执行了MapHandlerExecutionStep事件:
判断是否指向了一个具体的HttpHandler实例,如果没有,则根据请求的url创建页面处理程序或一般处理程序。
(为什么要判断是否指向一个具体的HttpHandler呢,MVC请求到达的时候会在第七个事件中,指向一个MvcHandler,而不是创建一般处理程序)
2.——>在管道第11-12个事件之间执行了HttpHandler的ProcessRequest方法:
执行一般处理程序的ProceRequest方法,或者是Page页面的生命周期。

1 internal override void BuildSteps(WaitCallback stepCallback) 2 { 3 ArrayList steps = new ArrayList(); 4 HttpApplication app = base._application; 5 bool flag = false; 6 UrlMappingsSection urlMappings = RuntimeConfig.GetConfig().UrlMappings; 7 flag = urlMappings.IsEnabled && (urlMappings.UrlMappings.Count > 0); 8 steps.Add(new HttpApplication.ValidateRequestExecutionStep(app)); 9 steps.Add(new HttpApplication.ValidatePathExecutionStep(app)); 10 if (flag) 11 { 12 steps.Add(new HttpApplication.UrlMappingsExecutionStep(app)); 13 } 14 app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventBeginRequest, steps); 15 app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventAuthenticateRequest, steps); 16 app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventDefaultAuthentication, steps); 17 app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventPostAuthenticateRequest, steps); 18 app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventAuthorizeRequest, steps); 19 app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventPostAuthorizeRequest, steps); 20 app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventResolveRequestCache, steps); 21 app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventPostResolveRequestCache, steps); 22 23 //创建页面对象或一般处理程序 24 steps.Add(new HttpApplication.MapHandlerExecutionStep(app)); 25 app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventPostMapRequestHandler, steps); 26 app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventAcquireRequestState, steps); 27 app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventPostAcquireRequestState, steps); 28 app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventPreRequestHandlerExecute, steps); 29 steps.Add(app.CreateImplicitAsyncPreloadExecutionStep()); 30 31 //执行一般处理程序的PR方法或开始Page页面的生命周期 32 steps.Add(new HttpApplication.CallHandlerExecutionStep(app)); 33 app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventPostRequestHandlerExecute, steps); 34 app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventReleaseRequestState, steps); 35 app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventPostReleaseRequestState, steps); 36 steps.Add(new HttpApplication.CallFilterExecutionStep(app)); 37 app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventUpdateRequestCache, steps); 38 app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventPostUpdateRequestCache, steps); 39 this._endRequestStepIndex = steps.Count; 40 app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventEndRequest, steps); 41 steps.Add(new HttpApplication.NoopExecutionStep()); 42 this._execSteps = new HttpApplication.IExecutionStep[steps.Count]; 43 steps.CopyTo(this._execSteps); 44 this._resumeStepsWaitCallback = stepCallback; 45 }View Code
HttpRuntime拿到了HttpApplication对象,HttpRuntime开始触发HttpApplication的请求处理,即调用HttpApplication的BeginProcessRequest方法。

1 IAsyncResult IHttpAsyncHandler.BeginProcessRequest(HttpContext context, AsyncCallback cb, object extraData) 2 { 3 this._context = context; 4 this._context.ApplicationInstance = this; 5 this._stepManager.InitRequest(); 6 this._context.Root(); 7 HttpAsyncResult result = new HttpAsyncResult(cb, extraData); 8 this.AsyncResult = result; 9 if (this._context.TraceIsEnabled) 10 { 11 HttpRuntime.Profile.StartRequest(this._context); 12 } 13 this.ResumeSteps(null); 14 return result; 15 } 16 17View Code
ResumeSteps
其中error = application.ExecuteStep(this._execSteps[this._currentStepIndex], ref completedSynchronously);
便是通过_execSteps来依次执行事件函数的调用。
在所有事件函数被调用完成之后,HttpApplication实例会被回收,ISAPIRuntime.ProcessRequest处理完毕,结果返回给COM,并通过COM的再一次处理,返回给客户端。这样一次请求就至此结束了。

1 [DebuggerStepperBoundary] 2 internal override void ResumeSteps(Exception error) 3 { 4 bool flag = false; 5 bool completedSynchronously = true; 6 HttpApplication application = base._application; 7 CountdownTask applicationInstanceConsumersCounter = application.ApplicationInstanceConsumersCounter; 8 HttpContext context = application.Context; 9 ThreadContext context2 = null; 10 AspNetSynchronizationContextBase syncContext = context.SyncContext; 11 try 12 { 13 if (applicationInstanceConsumersCounter != null) 14 { 15 applicationInstanceConsumersCounter.MarkOperationPending(); 16 } 17 using (syncContext.AcquireThreadLock()) 18 { 19 try 20 { 21 context2 = application.OnThreadEnter(); 22 } 23 catch (Exception exception) 24 { 25 if (error == null) 26 { 27 error = exception; 28 } 29 } 30 try 31 { 32 try 33 { 34 Label_004D: 35 if (syncContext.Error != null) 36 { 37 error = syncContext.Error; 38 syncContext.ClearError(); 39 } 40 if (error != null) 41 { 42 application.RecordError(error); 43 error = null; 44 } 45 if (!syncContext.PendingCompletion(this._resumeStepsWaitCallback)) 46 { 47 if ((this._currentStepIndex < this._endRequestStepIndex) && ((context.Error != null) || base._requestCompleted)) 48 { 49 context.Response.FilterOutput(); 50 this._currentStepIndex = this._endRequestStepIndex; 51 } 52 else 53 { 54 this._currentStepIndex++; 55 } 56 if (this._currentStepIndex >= this._execSteps.Length) 57 { 58 flag = true; 59 } 60 else 61 { 62 this._numStepCalls++; 63 syncContext.Enable(); 64 error = application.ExecuteStep(this._execSteps[this._currentStepIndex], ref completedSynchronously); 65 if (completedSynchronously) 66 { 67 this._numSyncStepCalls++; 68 goto Label_004D; 69 } 70 } 71 } 72 } 73 finally 74 { 75 if (flag) 76 { 77 context.RaiseOnRequestCompleted(); 78 } 79 if (context2 != null) 80 { 81 try 82 { 83 context2.DisassociateFromCurrentThread(); 84 } 85 catch 86 { 87 } 88 } 89 } 90 } 91 catch 92 { 93 throw; 94 } 95 } 96 if (flag) 97 { 98 context.RaiseOnPipelineCompleted(); 99 context.Unroot(); 100 application.AsyncResult.Complete(this._numStepCalls == this._numSyncStepCalls, null, null); 101 application.ReleaseAppInstance(); 102 } 103 } 104 finally 105 { 106 if (applicationInstanceConsumersCounter != null) 107 { 108 applicationInstanceConsumersCounter.MarkOperationCompleted(); 109 } 110 } 111 }View Code
HttpApplication 管线会依次处理下面的请求: