1.关于编
写代码中遇到要同时调用执行几种方法的时候运用
线程。
在以前学到的知识中,,我们在一个类中调用方法只能是以串联的方式。当一个方法执行完成时才能执行下一个方法。但是运用线程就能实现并联的功能:
1.1
在线程里面写多个方法,再在run方法里面调用这些方法:
class="java"> public void run(){
if(type ==0){
a();
}
if(type ==1){
b();
}
if(type ==2){
c();
}
if(type ==3){
d();
}
}
public void a(){
int scrx = 0;
int scry = 0;
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){
System.out.println("a执行啦");
if(go){
//设置颜色
g.setColor(Color.BLUE);
g.clearRect(scrx, scry, 30, 30);
g.fillOval(i, i, 30, 30);
scrx =i;
scry =i;
//程序暂停时间
try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch(Exception ef){}
}else{try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch(Exception ef){}}
}
}
public void b(){
int scrx = 0;
int scry = 0;
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){
if(go){
System.out.println("b执行啦");
g.setColor(Color.green);
g.clearRect(scrx, scry, 30, 30);
g.fillOval(980-i, i, 30, 30);
scrx =980-i;
scry =i;
try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch(Exception ef){}
}else{try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch(Exception ef){}}
}
}
public void c(){
int scrx = 0;
int scry = 0;
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){
if(go){
System.out.println("c执行啦");
g.setColor(Color.BLUE);
g.clearRect(scrx, scry, 30, 30);
g.fillOval(i, 680-i, 30, 30);
scrx =i;
scry =680-i;
try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch(Exception ef){}
}else{try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch(Exception ef){}}
}
}
public void d(){
int scrx = 0;
int scry = 0;
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){
if(go){
System.out.println("d执行啦");
g.setColor(Color.gray);
g.clearRect(scrx, scry, 30, 30);
g.fillOval(980-i, 680-i, 30, 30);
scrx =980-i;
scry =680-i;
try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch(Exception ef){}
}else{try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch(Exception ef){}}
}
}
1.2写好线程类,即是继承于Thread,之后,在于事件
监听器中实例化线程对象,运用对象调用start()方法,这样便会执行写入run()中的方法。
PaintThread pt = new PaintThread(g,0);
pt.start();
PaintThread pt1 = new PaintThread(g,1);
pt1.start();
PaintThread pt2 = new PaintThread(g,2);
pt2.start();
PaintThread pt3 = new PaintThread(g,3);
pt3.start();
这样上面的四个方法会同时运行,得到如下效果:[img]
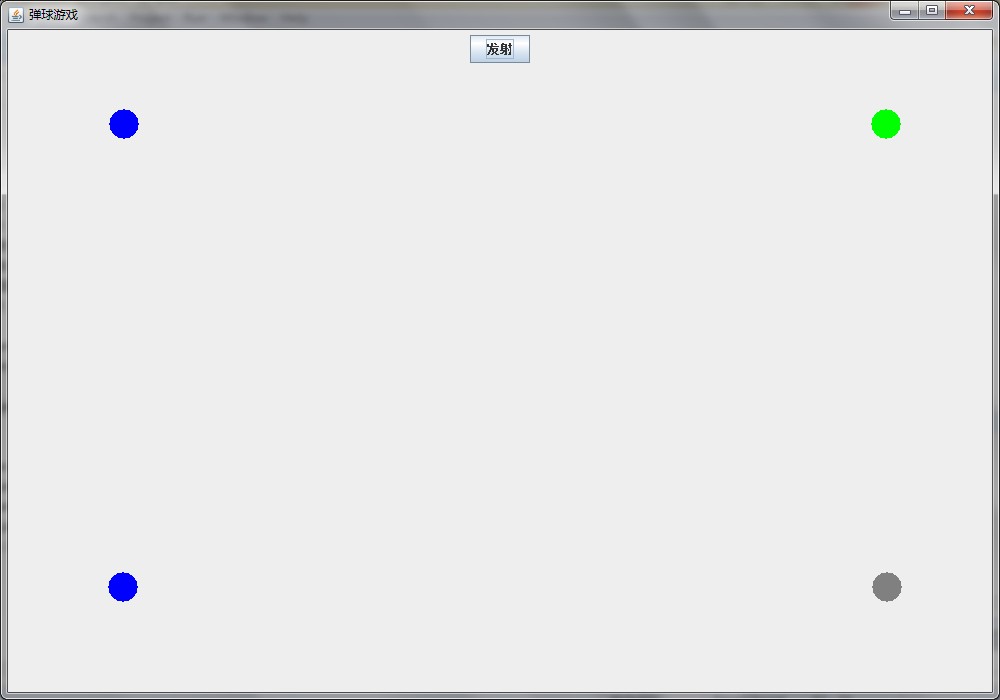
[/img]。
就是四个小球从四个方向同时走动!!!!

- 大小: 29.6 KB
