今天学习了下java的IO流,这里做个总结,方便查找。
?
InputStream/OutputSrteam
InputStream是个抽象类,表示字节输入流的所有类的超类。常见的有向文件写入数据。
OutputStream是个抽象类,表示字节输出流的所有类的超类。常见的有从文件写出数据。
继承关系:
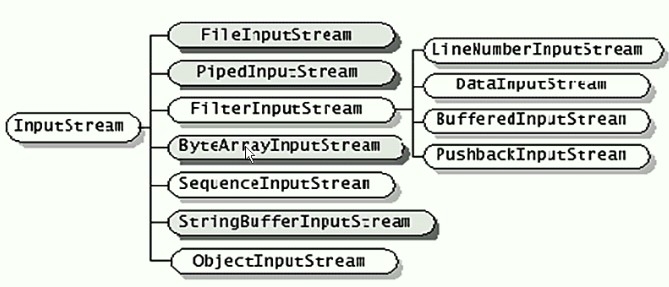

??
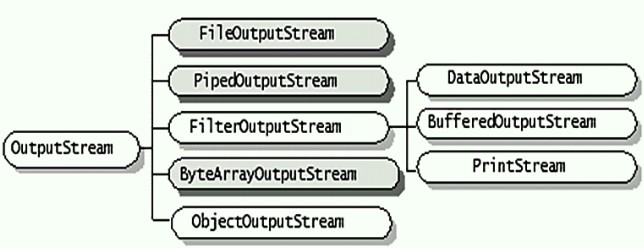

?
举例:采用FileInputStream/FileOutputStream读写文件。
?
class="java" name="code">package yingjun.io;
import java.io.*;
//读取文件
public class TestFileInputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream in = null;//定义一个输入字节流
try {
in = new FileInputStream("D:/test/newfilename.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("找不到指定文件");
System.exit(-1);
}
try {
long num = 0;
int b = 0;
while((b=in.read())!=-1){ //不等于-1就说明没有读到结尾
System.out.print((char)b); //输出字节
num++;
}
in.close();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("共读取 "+num+" 字节");
} catch (IOException e1) {
System.out.println("文件读取错误"); System.exit(-1);
}
}
}
?
?
package yingjun.io;
import java.io.*;
//读出文件并写入另一个文件
public class TestFileOutputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int b = 0;
FileInputStream in = null;//用于读文件
FileOutputStream out = null;//用于向文件写数据
try {
in = new FileInputStream("D:/test/oldfile.txt");//就像在oldfile这个文件里插入一个管道用于读取里面的内容。
out = new FileOutputStream("D:/test/newfile.txt");//就像在newfile这个文件里插入一个管道用于向里面写人内容
while((b=in.read())!=-1){
out.write(b);
}
in.close();
out.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e2) {
System.out.println("找不到指定文件"); System.exit(-1);
} catch (IOException e1) {
System.out.println("文件复制错误"); System.exit(-1);
}
System.out.println("文件已经复制");
}
}
##################################################################
Reader/Writer
?
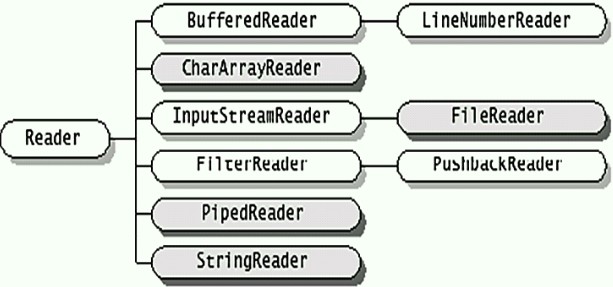
Reader用于读取字符流的抽象类子类必须实现的方法只有 read(char[], int, int) 和 close()。但是,多数子类将重写此处定义的一些方法,以提供更高的效率和/或其他功能。
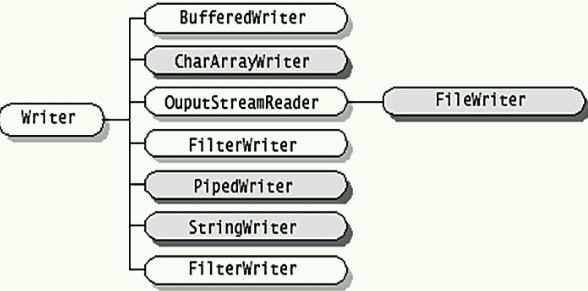
?Writer写入字符流的抽象类。子类必须实现的方法仅有 write(char[], int, int)、flush() 和 close()。但是,多数子类将重写此处定义的一些方法,以提供更高的效率和/或其他功能。
?
?
?举例:采用FileReader/FileWriter读写文件。
package yingjun.io;
import java.io.*;
//读取文件
public class TestFileReader {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader fr = null;
int c = 0;
try {
fr = new FileReader("D:/test/newfilename.txt");
while ((c = fr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)c);
}
fr.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("找不到指定文件");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("出错");
}
}
}
?
package yingjun.io;
import java.io.*;
//写入文件
public class TestFileWriter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fw = new FileWriter("D:/test/newfilename.txt");
for(int c=0;c<=50000;c++){
fw.write(c);//c表示的是unicode编码,50000基本涵盖了所有国家的文字。
}
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("出错");
System.exit(-1);
}
}
}
? ########################################################################?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ??? ??? 常见处理流
?########################################################################
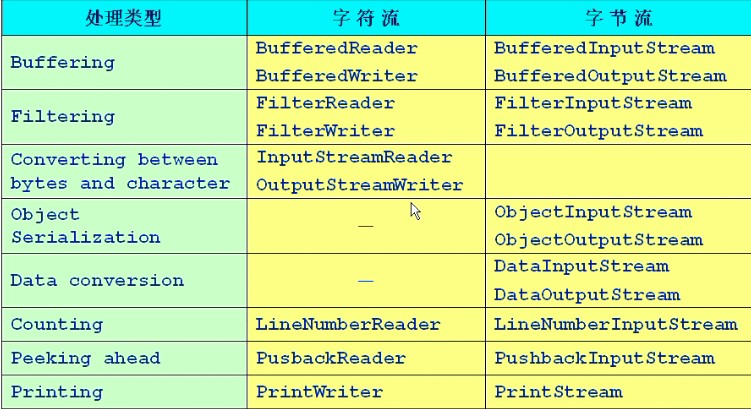
?
1:缓冲流
?
package yingjun.io;
import java.io.*;
public class TestBufferStream2 {
//向一个文件里写入数据并且从中读取出
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:/test/DateTest.java,true"));//true表示不会删除文件之前所有的内容
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader( new FileReader("D:/test/DateTest.java"));
String s = null;
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
s = String.valueOf(Math.random());
bw.write(s);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.flush();
while((s=br.readLine())!=null){ //BufferReader有缓存区的功能,可以读一行
System.out.println(s);
}
bw.close();
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
?2:转换流
?
?
package yingjun.io;
import java.io.*;
public class TestTransForm2 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);//System.in代表键盘输入流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);//在外面再套接一层
String s = null;
try {
s = br.readLine(); //等待键盘输入直到输入一行
while(s!=null){
if(s.equalsIgnoreCase("exit")) break;
System.out.println(s.toUpperCase());
s = br.readLine();
}
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
?3:数据流
?
?
package yingjun.io;
import java.io.*;
public class TestDataStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); //定义字节数组流
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(baos);//套接数据类型流
try {
dos.writeDouble(Math.random());//写入double类型数据
dos.writeBoolean(true);
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(baos.toByteArray());
System.out.println(bais.available());
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(bais);
System.out.println(dis.readDouble());//读取double类型数据
System.out.println(dis.readBoolean());
dos.close();
dis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
??4:打印流
?
?
package yingjun.io;
import java.io.*;
public class TestPrintStream1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrintStream ps = null;
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/test/DateTest.java");
ps = new PrintStream(fos);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(ps != null){
System.setOut(ps);//设定System.out输出到ps(原来是在dos)
}
for(char c = 0; c <= 60000; c++){
System.out.print(c+ " ");//print具有自动的flush功能,所有数据将被写入文件
}
}
}
?
package yingjun.io;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
//类似log功能
public class TestPrintStream3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = null;
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
try {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter ("D:/test/log.java", true);//log
PrintWriter log = new PrintWriter(fw);
while ((s = br.readLine())!=null) {
if(s.equalsIgnoreCase("exit")) break;
System.out.println(s.toUpperCase());
log.println("-----");
log.println(s.toUpperCase());
//log.flush();
}
log.println("==="+new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss").format(new Date())+"===");
log.flush();
log.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
?5:对象流
?
package yingjun.io;
import java.io.*;
public class TestObjectIO {
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
T t = new T();
t.k = 111;
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/test/DateTest.java");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
oos.writeObject(t);
oos.flush();
oos.close();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:/test/DateTest.java");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
T tReaded = (T)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(tReaded.i + " " + tReaded.j + " " + tReaded.d + " " + tReaded.k);
}
}
class T implements Serializable //可以被序列化的(可以把对象写到文件或者网络上传输)
{
int i = 10;
int j = 9;
double d = 2.3;
transient int k = 15; //transient修饰的成员变量在序列化的时候不考虑
}
?
?