Java编程语言中几种不同的引用类型是面试时经常容易被问到的问题:强引用,软引用,弱引用,虚引用。
其实除了Java之外,某些 其他编程语言也有类似概念,比如ABAP。今天我们就来比较一下。
根据ABAP帮助文档,我们可以把某个对象的引用包在一个Weak Reference的实例里。ABAP的Weak Reference实例通过类CL_ABAP_WEAK_REFERENCE实现。
看下面的例子:首先我在堆上创建了一个新的LCL_PERSON实例,然后包到一个ABAP weak reference里。
lo_person = NEW lcl_person( 'Jerry' ).
lo_weak = NEW cl_abap_weak_reference( lo_person ).
 class="content_image lazy">
class="content_image lazy">
稍后,我们想拿到被包裹的lo_person引用时,使用weak reference提供的get方法。见下图示例:
lo_person = CAST lcl_person( lo_weak->get( ) ).
引用lo_person什么时候会变成initial呢?如果当ABAP垃圾回收器(Garbage Collector)开始工作时,已经没有任何引用再指向lo_person, 则lo_person会变成initial。
看下面这个例子加深理解。
monospace; font-size: inherit; background-color: inherit;" class="language-js">REPORT ztest.
PARAMETERS: clear TYPE char1 as CHECKBOX DEFAULT abap_true,
gc TYPE char1 as CHECKBOX DEFAULT abap_true.
CLASS lcl_person DEFINITION.
PUBLIC SECTION.
DATA: mv_name TYPE string.
METHODS: constructor IMPORTING !iv_name TYPE string.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS lcl_person IMPLEMENTATION.
METHOD: constructor.
me->mv_name = iv_name.
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.
START-OF-SELECTION.
DATA: lo_person TYPE REF TO lcl_person,
lo_weak TYPE REF TO cl_abap_weak_reference.
lo_person = NEW lcl_person( 'Jerry' ).
lo_weak = NEW cl_abap_weak_reference( lo_person ).
IF clear = abap_true.
CLEAR: lo_person.
ENDIF.
IF gc = abap_true.
cl_abap_memory_utilities=>do_garbage_collection( ).
ENDIF.
lo_person = CAST lcl_person( lo_weak->get( ) ).
IF lo_person IS INITIAL.
WRITE: / 'reference not available'.
ELSE.
WRITE: / 'reference still available'.
ENDIF.
这个report有两个开关,如下图。第一个开关控制lo_person这个引用是否被关键字CLEAR显式地置为INITIAL, 第二个开关决定是否在代码中显式地调用ABAP垃圾回收器。

这两个开关的打开和关闭状态,一共有4种组合。

在第一种情况下,通过关键字CLEAR清除了lo_person的引用,从ABAP的内存检查器(事务码s_memory_inspector)能发现,lo_person现在已经不指向任何内存中的对象了。

对于其他三种情况,LCL_PERSON的实例都不会被ABAP垃圾回收器清除:
Java中的weak reference表现行为和ABAP一致。
我把上面的ABAP测试代码用Java程序重新写一遍:
import java.lang.ref.WeakReference;
class Person {
private String mName;
public Person(String name) {
this.mName = name;
}
public String getName() {
return this.mName;
}
}
public class WeakReferenceTest {
public static void check(Person person) {
if (person == null) {
System.out.println("Reference invalid");
}
else {
System.out.println("Reference still available");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person jerry = null;
WeakReference<Person> person = new WeakReference<Person>(new Person(
"Jerry"));
jerry = new Person("Ben");
// if you comment out this line, Reference will be available
System.gc();
Person restore = person.get();
check(restore);
}
}
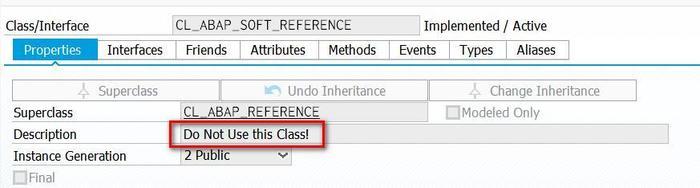
在我目前使用的ABAP Netweaver 750 SP4系统中,ABAP软应用尚未实现,

在系统里只有个空的CL_ABAP_SOFT_REFERENCE, 其描述信息写的是Do Not Use this Class!
Java和ABAP中的几种引用类型的分析和比较
那么我们就来试试Java的软应用 Soft Reference:
package reference;
import java.lang.ref.SoftReference;
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Person2 {
private String mName;
public Person2(String name) {
this.mName = name;
}
public String getName() {
return this.mName;
}
public void finalize() {
System.out.println("finalize called: " + this.mName);
}
public String toString() {
return "Hello, I am " + this.mName;
}
}
public class SoftReferenceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SoftReference<Person2> person = new SoftReference<Person2>(new Person2(
"Jerry"));
System.out.println(person.get());
ArrayList<Person2> big = new ArrayList<Person2>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
big.add(new Person2(String.valueOf(i)));
}
System.gc();
System.out.println("End: " + person.get());
}
}
控制台打印出的输出:
Hello, I am Jerry
End: Hello, I am Jerry
即便我创建了1万个Person对象的实例,确实消耗了一些内存,然后内存消耗还远远没有大到会导致包含在软应用中的Person2类的引用被JDK删除掉的程度。因此我在代码中调用Java的垃圾回收器System.gc()之后,该引用仍然存在。
在Java中,软应用通常被用来实现在内存资源很有限的环境下的缓存机制,比如Android手机开发中。
使用下面的代码测试虚引用:
package aop;
import java.lang.ref.PhantomReference;
import java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue;
public class PhantomReferenceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object phantomObj;
PhantomReference phantomRef, phantomRef2;
ReferenceQueue phantomQueue;
phantomObj = new String("Phantom Reference");
phantomQueue = new ReferenceQueue();
phantomRef = new PhantomReference(phantomObj, phantomQueue);
System.out.println("1 Phantom Reference:" + phantomRef.get());
System.out.println("2 Phantom Queued: " + phantomRef.isEnqueued());
phantomObj = null;
System.gc();
System.out.println("3 Anything in Queue? : " + phantomQueue.poll());
if (!phantomRef.isEnqueued()) {
System.out.println("4 Requestion finalization.");
System.runFinalization();
}
System.out.println("5 Anything in Queue?: " + phantomRef.isEnqueued());
phantomRef2 = (PhantomReference) phantomQueue.poll();
System.out.println("6 Original PhantomReference: " + phantomRef);
System.out.println("7 PhantomReference from Queue: " + phantomRef2);
}
}
测试输出:
1. Phantom Reference: null
2. Phantom Queued: false
3. Anything in Queue? : null
5. Anything in Queue?: true
6. Original PhantomReference: java.lang.ref.PhantomReference@2a139a55
7. PhantomReference from Queue: java.lang.ref.PhantomReference@2a139a55
和之前介绍的弱引用(WeakReference)和软引用(SoftReference)不同,包裹在虚引用(PhantomReference)中的对象实例无法通过需引用的get方法返回,因此在第一行输出我们会看到: “1. Phantom Reference: null”.
在上面示例代码中虚引用PhantomReference的构造函数里, 我传入了一个队列作为输入参数。当包裹在虚引用实例中的对象引用被Java垃圾回收器删除时,虚引用实例本身会自动被JVM插入我之前指定到虚引用构造函数输入参数的那个队列中去。
在System.runFinalization()执行之前,phantomRef.isEnqueued()返回false,phantomQueue.poll()返回空。
当phantomObj实例被JVM删除后, 虚引用PhantomReference本身被加入到队列中,并且能够通过队列提供的API所访问:phantomQueue.poll(). 打印输出的第6行和第7行也说明了这一点。
要获取更多Jerry的原创技术文章,请关注公众号"汪子熙"或者扫描下面二维码:
http://weixin.qq.com/r/LjnZwTHErmzRrXWi92w8?(二维码自动识别)
