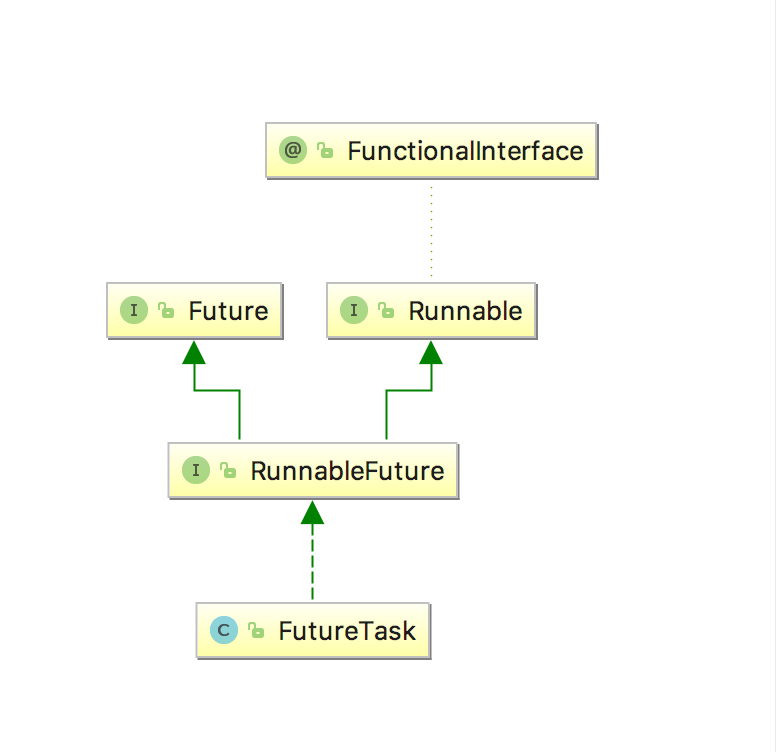
 ?FutureTask实现了RunnableFuture接口,而RunnableFuture继承了Runnable和Future,也就是说FutureTask既是Runnable,也是Future。
?主要成员变量
? ? ?
?FutureTask实现了RunnableFuture接口,而RunnableFuture继承了Runnable和Future,也就是说FutureTask既是Runnable,也是Future。
?主要成员变量
? ? ?
?
//任务运行状态
private volatile int state;
//预定义多7种状态
private static final int NEW = 0; //任务新建和执行中
private static final int COMPLETING = 1; //任务将要执行完毕中
private static final int NORMAL = 2; //任务正常执行结束
private static final int EXCEPTIONAL = 3; //任务异常
private static final int CANCELLED = 4; //任务取消
private static final int INTERRUPTING = 5; //任务线程即将被中断
private static final int INTERRUPTED = 6; //任务线程已中断
//可能的状态转换
//NEW -> COMPLETING -> NORMAL
// NEW -> COMPLETING -> EXCEPTIONAL
// NEW -> CANCELLED
//NEW -> INTERRUPTING -> INTERRUPTED
private Callable callable;//被提交的任务
private Object outcome; //任务执行结果或者任务异常
private volatile Thread runner;//执行任务的线程
private volatile WaitNode waiters;//等待节点,关联等待线程
? run
public void run() {
//如果运行状态不是NEW 或者CAS设置运行线程为当前线程失败则返回
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
//当前被提交的任务
Callable c = callable;
//如果任务不为null同时运行状态是NEW
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
//运行正常标记
boolean ran;
try {
//执行提交的任务,并将结果赋值给result,同时将运行正常标记设置为true
result = c.call();
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
//如果执行提交任务异常,则将结果设置为null,运行正常标记设置为false,同时设置异常
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);
}
//如果运行正常,则将设置结果
if (ran)
set(result);
}
} finally {
//退出前将当前运行线程设置为null
runner = null;
//重置runner后必须重新读取state防止有泄漏的中断
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
}
protected void set(V v) {
// CAS将运行状态从NEW更新为COMPLETING
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
//更新成功将结果赋值给outcome
outcome = v;
//将状态更新为NORMAL,终态
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, NORMAL);
//结束处理,删除或唤醒等待线程等
finishCompletion();
}
}
//删除或唤醒所有等待线程,待用done()同时将callable重置为null
private void finishCompletion() {
for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) {
//CAS将等待节点更新为null
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) {
for (;;) {
//获取等待节点的线程
Thread t = q.thread;
//如果等待节点电池不为null,则将其设置为null并唤醒线程
if (t != null) {
q.thread = null;
LockSupport.unpark(t);
}
//获取等待线程的直接后继节点
WaitNode next = q.next;
//如果直接后继为null则表示所有等待线程都处理完,跳出循环
if (next == null)
break;
//将节点从链表中删除
q.next = null; // unlink to help gc
//继续处理后继节点
q = next;
}
//跳出循环
break;
}
}
//调用done
done();
//将callable重置为null
callable = null;
}
protected void setException(Throwable t) {
// CAS 将运行状态从NEW 更新为 COMPLETING
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
//将异常赋值给outcome
outcome = t;
//将运行状态更新为终态 EXCEPTIONAL
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, EXCEPTIONAL);
//结束处理
finishCompletion();
}
}
//等待状态从INTERRUPTING变为终态
private void handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(int s) {
if (s == INTERRUPTING)
while (state == INTERRUPTING)
Thread.yield();
}
?get
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
//运行状态
int s = state;
//如果还没有结束
if (s <= COMPLETING)
//等待结束
s = awaitDone(false, 0L);
//返回结果
return report(s);
}
private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos)
throws InterruptedException {
//如果有超时限制,则计算deadLine
final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L;
WaitNode q = null;
//入队标记
boolean queued = false;
//循环
for (;;) {
//如果当前线程已经中断,则将该节点从等待队列中删除,并抛出异常
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
removeWaiter(q);
throw new InterruptedException();
}
//运行状态
int s = state;
if (s > COMPLETING) { //任务可能已经完成或者被取消了
if (q != null)
q.thread = null;
return s;
}
else if (s == COMPLETING) // 可能任务线程被阻塞了,主线程让出CPU
Thread.yield();
else if (q == null) // 等待线程节点为空,则初始化新节点并关联当前线程
q = new WaitNode();
else if (!queued) //如果没有入队过,等待线程入队列,成功则queued=true
queued = UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,
q.next = waiters, q);
else if (timed) {//限制超时
nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();
//如果超时移除等待节点
if (nanos <= 0L) {
removeWaiter(q);
return state;
}
//没有超时则线程挂起
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos);
}
else 线程挂起
LockSupport.park(this);
}
}
private void removeWaiter(WaitNode node) {
//如果要删除的节点不为null,则将其节点线程设置为null
if (node != null) {
node.thread = null;
retry:
for (;;) {
//q初始化为等待节点
for (WaitNode pred = null, q = waiters, s; q != null; q = s) {
//q的直接后继
s = q.next;
//如果q的线程不为null,表示q不是需要删除的节点,则将q赋值给pred
if (q.thread != null)
pred = q;
else if (pred != null) { //如果pred不为null则表示pred是有效节点,
//需要删除的后继节点作为pred的直接后继,进而将需要删除的节点从队列中删除
pred.next = s;
if (pred.thread == null) // 竞态检查
continue retry;
}//如果头节点是需要删除的节点则CAS更新
else if (!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,
q, s))
continue retry;
}
break;
}
}
}
ExecutorCompletionService
public class ExecutorCompletionService<V> implements CompletionService<V> { //具体执行任务的线程池 private final Executor executor; private final AbstractExecutorService aes; //任务执行完成的阻塞队列 private final BlockingQueue<Future<V>> completionQueue; private class QueueingFuture extends FutureTask<Void> { QueueingFuture(RunnableFuture<V> task) { super(task, null); this.task = task; } //FutureTask执行结束的时候会被调用,将task添加到阻塞队列 protected void done() { completionQueue.add(task); } private final Future<V> task; } private RunnableFuture<V> newTaskFor(Callable<V> task) { //如果aes为null则将task包装成一个新的FutureTask,否则调用aes newTaskFor方法进行包装 if (aes == null) return new FutureTask<V>(task); else return aes.newTaskFor(task); } public ExecutorCompletionService(Executor executor) { if (executor == null) throw new NullPointerException(); this.executor = executor; this.aes = (executor instanceof AbstractExecutorService) ? (AbstractExecutorService) executor : null; this.completionQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Future<V>>(); } public Future<V> submit(Callable<V> task) { //如果提交的任务为null则抛出NPE if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException(); //将当前任务包装为一个FutureTask RunnableFuture<V> f = newTaskFor(task); //再将FutureTask包装为QueueingFuture 后执行 executor.execute(new QueueingFuture(f)); return f; } public Future<V> take() throws InterruptedException { return completionQueue.take(); } public Future<V> poll() { return completionQueue.poll(); } }? ExecutorCompletionService ? AbstractExecutorService 抽象类实现了 ExecutorService 接口,然后在其基础上实现了 invokeAny 方法和 invokeAll 方法,这里的 newTaskFor 方法也比较有用,用于将任务包装成 FutureTask。 ?invokeAny
public T invokeAny(Collection> tasks)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
try {
return doInvokeAny(tasks, false, 0);
} catch (TimeoutException cannotHappen) {
assert false;
return null;
}
}
private T doInvokeAny(Collection> tasks,
boolean timed, long nanos)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
//如果提交的任务集合为null则抛NPE
if (tasks == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//提交的任务数量
int ntasks = tasks.size();
//如果提交的任务数量为0则抛一个IllegalArgumentException
if (ntasks == 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
//创建一个结果集合列表
ArrayList<future> futures = new ArrayList<future>(ntasks);
//创建一个ExecutorCompletionService
ExecutorCompletionService ecs =
new ExecutorCompletionService(this);
try {
ExecutionException ee = null;
//如果有限制超时时间则计算出deadLine
final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L;
Iterator> it = tasks.iterator();
//执行第一个任务
futures.add(ecs.submit(it.next()));
//任务数自减
--ntasks;
//活动任务数为1
int active = 1;
for (;;) {
//获取执行完成结果
Future f = ecs.poll();
//如果没有结果,则表示任务尚未执行完
if (f == null) {
//剩余任务数大于0,则继续执行
if (ntasks > 0) {
--ntasks;
futures.add(ecs.submit(it.next()));
++active;
}
else if (active == 0)//如果活动任务数为0,且没有获取到成功成功结果,则表示所有任务都失败了
break;
else if (timed) {// 如果限制超时时间
f = ecs.poll(nanos, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
if (f == null)
throw new TimeoutException();
nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();
}
else //如果没有要提交的任务,线程池中任务还没有结束阻塞等待结果
f = ecs.take();
}
//如果获取到了结果,活动任务数自减
if (f != null) {
--active;
try {
//返回结果
return f.get();
} catch (ExecutionException eex) {
ee = eex;
} catch (RuntimeException rex) {
ee = new ExecutionException(rex);
}
}
}
if (ee == null)
ee = new ExecutionException();
throw ee;
} finally {
//退出前取消所有任务
for (int i = 0, size = futures.size(); i < size; i++)
futures.get(i).cancel(true);
}
}
ThreadPoolExecutor
ThreadPoolExecutor 是 JDK 中的线程池实现,这个类实现了一个线程池需要的各个方法,它实现了任务提交、线程管理、监控等等方法
? ?首先看一下构造方法
/**
* 使用给定的初始化参数创建一个新的线程池
*
* @param corePoolSize 线程池中保持的线程数量,即使这些线程是空闲的;除非设置了allowCoreThreadTimeOut
* @param maximumPoolSize 线程池中允许的最大线程数
* @param keepAliveTime 当线程池中的线程数大于corePoolSize时,这些多余空闲线程等待新任务的最大时间
* @param unit keepAliveTime的时间单位
* @param workQueue 用来在线程执行前持有线程的队列。这个队列只持有通过executor方法提交的runnable任务
* @param threadFactory 线程池创建新线程的线程工厂
* @param handler 线程池关闭或饱和时的处理策略
*/
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
除了构造方法中的这几个初始化参数外还有一个比较重要的属性需要理解
private final AtomicInteger ctl = new AtomicInteger(ctlOf(RUNNING, 0));
// 这里 COUNT_BITS 设置为 29(32-3),为什么减去三呢?这是因为线程池有5种状态,需要用到三位,高三位用来表示线程池的状态
private static final int COUNT_BITS = Integer.SIZE - 3;
// 000 11111111111111111111111111111
// 这里得到的是 29 个 1,也就是说线程池的最大线程数是 2^29-1 大约是5亿
private static final int CAPACITY = (1 << COUNT_BITS) - 1;
// 我们说了,线程池的状态存放在高 3 位中
// 111 00000000000000000000000000000
private static final int RUNNING = -1 << COUNT_BITS;
// 000 00000000000000000000000000000
private static final int SHUTDOWN = 0 << COUNT_BITS;
// 001 00000000000000000000000000000
private static final int STOP = 1 << COUNT_BITS;
// 010 00000000000000000000000000000
private static final int TIDYING = 2 << COUNT_BITS;
// 011 00000000000000000000000000000
private static final int TERMINATED = 3 << COUNT_BITS;
// 对CAPACITY 按位去反高三位全部为1在进行按位与运算,就将地位全部变为0
private static int runStateOf(int c) { return c & ~CAPACITY; }
// 按位与允许将高三位全部变为0就得到了当前线程池中的线程数量
private static int workerCountOf(int c) { return c & CAPACITY; }
//按位或运算就得到了ctl
private static int ctlOf(int rs, int wc) { return rs | wc; }
?
在介绍完基本属性后接下来要看主要方法executor(Runnable),它处理过程分为如下三步:
public void execute(Runnable command) { //如果任务为null则抛出NPE if (command == null) throw new NullPointerException(); //获取ctl int c = ctl.get(); //如果线程池的线程数小于corePoolSize if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) { //添加新工作线程,如果添加成功则返回 if (addWorker(command, true)) return; //添加失败再次获取ctl,进行重复检查 c = ctl.get(); } //如果线程池还是运行的,则对当前任务进行排队;如果排队成功 if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) { //再次获取ctl int recheck = ctl.get(); //如果线程池已经关闭则将任务从队列中删除,如果删除成功对该任务执行饱和策略 if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command)) reject(command); else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)//如果没有运行线程,则创建一个新线程 addWorker(null, false); }//执行到此表示,线程池已经关闭或排队失败;则尝试创建新的工作线程,如果添加新的工作线程则执行饱和策略 else if (!addWorker(command, false)) reject(command); }
private final class Worker
extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
implements Runnable
{
//运行在Worker中的线程,真正执行任务的线程
final Thread thread;
//初始化的创建的第一个任务,可以为null
Runnable firstTask;
//用于存放此线程完全的任务数
volatile long completedTasks;
// 构造方法
Worker(Runnable firstTask) {
setState(-1);
this.firstTask = firstTask;
this.thread = getThreadFactory().newThread(this);
}
public void run() {
runWorker(this);
}
final void runWorker(Worker w) {
//获取当前线程
Thread wt = Thread.currentThread();
//获取worker中的firstTask
Runnable task = w.firstTask;
//将firstTask设置为null,因为这个任务是创建worker时候指定的,稍后就会执行这个任务
w.firstTask = null;
//对worker进行解锁,允许中断
w.unlock();
boolean completedAbruptly = true;
try {
//如果任务不为null或者getTask()中可以去到任务
while (task != null || (task = getTask()) != null) {
//对工作线程加锁不允许中断
w.lock();
//如果线程池状态大于等于 STOP,那么意味着该线程也要中断
if ((runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP) ||
(Thread.interrupted() &&
runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP))) &&
!wt.isInterrupted())
wt.interrupt();
try {
//执行beforeExecute,这是一个扩展点
beforeExecute(wt, task);
Throwable thrown = null;
try {
task.run();
} catch (RuntimeException x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Error x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Throwable x) {
thrown = x; throw new Error(x);
} finally {
//执行afterExecute,这里也是一个扩展点
afterExecute(task, thrown);
}
} finally {
// 置空 task,准备 getTask 获取下一个任务
task = null;
//完成的任务数自增
w.completedTasks++;
// 释放掉 worker 的独占锁
w.unlock();
}
}
completedAbruptly = false;
} finally {
// 如果到这里,需要执行线程关闭:
// 1. 说明 getTask 返回 null,没有任务要执行了
// 2. 任务执行过程中发生了异常
processWorkerExit(w, completedAbruptly);
}
}
private Runnable getTask() {
boolean timedOut = false;
for (;;) {
int c = ctl.get();
//获取运行状态
int rs = runStateOf(c);
// 如果线程池已经关闭 同时队列为空,则减少工作线程数
if (rs >= SHUTDOWN && (rs >= STOP || workQueue.isEmpty())) {
decrementWorkerCount();
return null;
}
//工作线程数
int wc = workerCountOf(c);
//是否需要计时处理,如果设置了allowCoreThreadTimeOut或当前工作线程数量大于corePoolSize 则需要计时处理
boolean timed = allowCoreThreadTimeOut || wc > corePoolSize;
//(wc > maximumPoolSize || (timed && timedOut)) 工作线程大于线程池的最大值 或需要计时且已经超时
//(wc > 1 || workQueue.isEmpty()) 工作线程数大于1或任务队列为空
if ((wc > maximumPoolSize || (timed && timedOut))
&& (wc > 1 || workQueue.isEmpty())) {
//工作线程数量减少 返回null
if (compareAndDecrementWorkerCount(c))
return null;
//如果CAS更新数量失败则继续
continue;
}
try {
//如果需要计时,则使用超时poll否则阻塞获取任务
Runnable r = timed ?
workQueue.poll(keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS) :
workQueue.take();
if (r != null)
return r;
//r 为null则是因为超时导致的
timedOut = true;
} catch (InterruptedException retry) {
timedOut = false;
}
}
}
private void processWorkerExit(Worker w, boolean completedAbruptly) {
if (completedAbruptly) // 如果是意外结束,则工作线程自减
decrementWorkerCount();
//加锁处理
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
//将当前工作线程执行的任务数加到线程池的执行的任务数上
completedTaskCount += w.completedTasks;
//将当前工作线程从工作hashSet中删除
workers.remove(w);
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
//尝试结束线程池
tryTerminate();
//获取ctl
int c = ctl.get();
//如果线程池运行状态小于STOP 即RUNNING或SHUTDOWN
if (runStateLessThan(c, STOP)) {
//如果不是意外结束
if (!completedAbruptly) {
//如果设置了allowCoreThreadTimeOut 则线程池最少持有线程则为0否则为corePoolSize
int min = allowCoreThreadTimeOut ? 0 : corePoolSize;
//如果min==0但是队列不为空则min=1
if (min == 0 && ! workQueue.isEmpty())
min = 1;
//如果工作线程大于或等于min返回
if (workerCountOf(c) >= min)
return;
}
//此时表示工作线程小于线程池最小线程数则添加一个新的工作线程,不指定firstTask
addWorker(null, false);
}
}
?