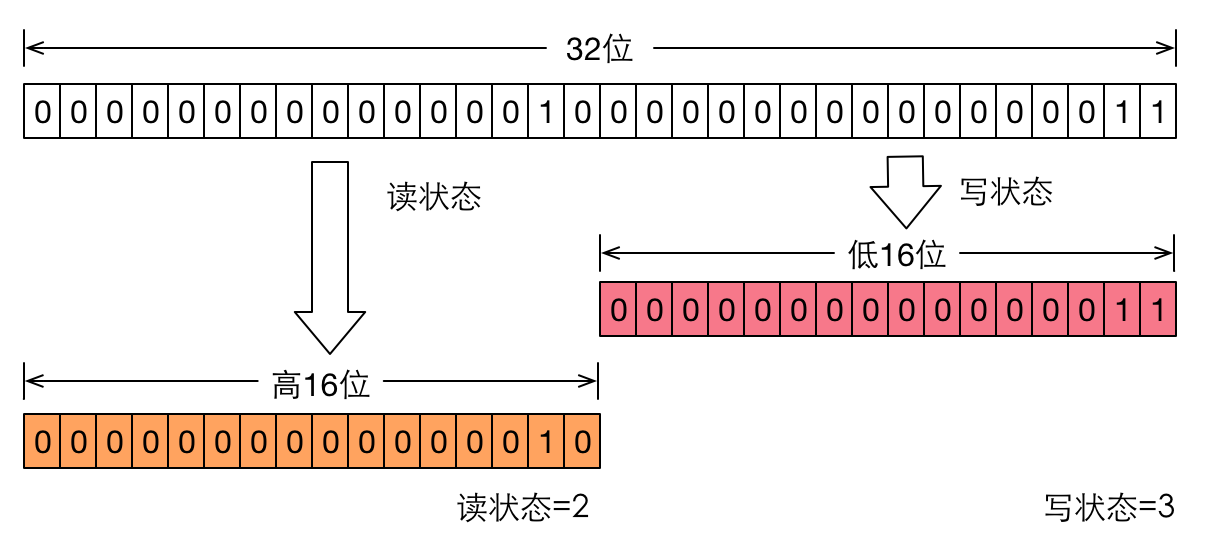
 ?
?
在本文中对AQS部分源码不在讲解,可以参考??AbstractQueuedSynchronizer源码分析? ??
首先从读锁开始看起
?readLock.lock()
? ?
?
?
在本文中对AQS部分源码不在讲解,可以参考??AbstractQueuedSynchronizer源码分析? ??
首先从读锁开始看起
?readLock.lock()
? ?
?
/** * 获取读锁 * 如果写锁没有被其他线程占有,获取读锁后立即返回 * 如果写锁被其他线程占有,则当前线程挂起直到获取到读锁 **/ public void lock() { sync.acquireShared(1); } public final void acquireShared(int arg) { if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0) doAcquireShared(arg); } /** * 如果写锁被占用则失败 * 否则该线程具有获取锁的资格,首先根据不同的队列策略判断是否需要被挂起,如果不需要 * 则通过CAS操作尝试获取锁,如果可以获取锁则需要更新计数;注意在这步操作中不进行重入处理 * 如果线程需要挂起,或达到上限或CAS操作失败都会进入完整获取读锁的循环中 **/ protected final int tryAcquireShared(int unused) { //当前线程 Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); //获取同步状态 int c = getState(); //写锁被占用,且不是当前线程;则获取读锁失败 if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0 && getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current) return -1; //获取读锁目前被占用数量 int r = sharedCount(c); //如果读取器不需要排队且读锁占用数量没有达到上限则通过CAS尝试获取读锁 if (!readerShouldBlock() && r < MAX_COUNT && compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) { //如果读区锁为0,表示还没有任何读取器占用锁,则将当前线程设置为第一个读取器,其持有锁的数量为1个 if (r == 0) { firstReader = current; firstReaderHoldCount = 1; //如果已经有线程占用读锁,且当前线程和第一个占用读锁线程相同则其持有锁的数量自增 } else if (firstReader == current) { firstReaderHoldCount++; } else { //如果已经有线程占用了读锁,但是不是当前线程 //最后一个成功获取读锁的线程占用读锁的数量计数器 HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter; //如果不为null且不是当前线程,则将其更新为当前线程的读锁计数器 if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current)) cachedHoldCounter = rh = readHolds.get(); //如果rh获取锁的数量为0则表示rh是新建对象,将其加入到readHolds中 else if (rh.count == 0) readHolds.set(rh); //持有读锁数量自增 rh.count++; } //返回1 return 1; } //如果读锁需要排队,或者达到读锁上限或者CAS失败都会进行充分获取锁重试循环 return fullTryAcquireShared(current); } /** * 获取读锁的完整版本,处理CAS遗漏以及在上一步操作中没有处理的重入问题 * **/ final int fullTryAcquireShared(Thread current) { HoldCounter rh = null; for (;;) { //获取同步状态 int c = getState(); //如果写锁被占用且不是当前线程则返回-1 if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0) { if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current) return -1; //写锁没有被占用判断当前线程是否需要挂起,如果需要挂起 } else if (readerShouldBlock()) { // Make sure we're not acquiring read lock reentrantly if (firstReader == current) { // assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0; } else { //当前第一个读取器不是当前线程,即别的线程占有了读锁 if (rh == null) { //将最后一个成功获取读锁的线程计数器赋值给rh rh = cachedHoldCounter; //如果还没有线程获取读锁,或者最后一个获取读锁的不是当前线程则获取当前线程的计数器 if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current)) { rh = readHolds.get(); //如果当前线程计数器,中获取读锁的数量为0则将其删除 if (rh.count == 0) readHolds.remove(); } } //当前线程没有获取到读锁 if (rh.count == 0) return -1; } } //如果读锁达到上限抛出异常 if (sharedCount(c) == MAX_COUNT) throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded"); //CAS操作,将写锁清0,如果成功则表示写锁没有被占用 if (compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) { if (sharedCount(c) == 0) { firstReader = current; firstReaderHoldCount = 1; } else if (firstReader == current) { firstReaderHoldCount++; } else { if (rh == null) rh = cachedHoldCounter; if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current)) rh = readHolds.get(); else if (rh.count == 0) readHolds.set(rh); rh.count++; cachedHoldCounter = rh; // cache for release } return 1; } } }readLock.unlock()
public void unlock() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int unused) {
//当前线程
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
//第一个读取器是当前线程
if (firstReader == current) {
// assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;
//如果第一个读取器持有的读锁数量为1,则将第一个读取器设置为null,否则将其持有锁的数量自减
if (firstReaderHoldCount == 1)
firstReader = null;
else
firstReaderHoldCount--;
//如果第一读取器不是当前线程
} else {
//最后一个成功获取读锁的计数器
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
//如果计数器为null或最后一个成功获取读锁的不是当前线程
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
//将当前线程的计数器赋值给rh
rh = readHolds.get();
//当前线程持有读锁的数量
int count = rh.count;
//如果持有锁的数量小于或等于1则将该线程从readHolds中删除
if (count <= 1) {
readHolds.remove();
//如果小于或等于0抛出异常,因为至少持有一把读锁
if (count <= 0)
throw unmatchedUnlockException();
}
//如果持有多把读锁则,持有锁的数量自减
--rh.count;
}
for (;;) {
//获取同步状态
int c = getState();
//计算释放一个读锁后读锁的数量
int nextc = c - SHARED_UNIT;
//CAS更新
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
//如果本次释放后,读锁没有被占用则返回成功,否则返回失败
return nextc == 0;
}
}
? writeLock.lock()public void lock() {
sync.acquire(1);
}
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
/*
*尝试获取写锁,
* 如果读锁占用数量不为0或写锁占用数量不为0且不是当前线程拥有写锁,则获取写锁失败
* 如果写锁饱和同样失败
* 否则当前线程具有获取锁的资格
*/
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
//当前线程
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
//获取同步状态
int c = getState();
//计算写锁数量
int w = exclusiveCount(c);
//如果有锁被占用(读锁或写锁)
if (c != 0) {
//如果写锁没有被占用,则表示当前有读锁被占用,获取写锁失败;如果写锁被占用且不是当前线程占用则 当前线程获取写锁失败
if (w == 0 || current != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
return false;
//如果已经占有的写锁数量加上本次占用的和超过上限则抛出异常
if (w + exclusiveCount(acquires) > MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
//写锁是当前线程占有,重入则将占用写锁的数量加上本次占用数量
setState(c + acquires);
//返回成功
return true;
}
//如果c==0表示读锁,写锁都没有被占用,判断写锁是否需要挂起,如果需要则返回获取锁失败,如果不需要则CAS竞争锁,失败返回false
if (writerShouldBlock() ||
!compareAndSetState(c, c + acquires))
return false;
//不需要挂起且竞争到了写锁则将独占锁的拥有者设置为当前线程
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
writeLock.unlock() public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
//如果当前线程没有持有写锁则抛出异常
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
//计算释放写锁后的状态
int nextc = getState() - releases;
//如果释放当前写锁后再无写锁占用,则free=true表示写锁完全释放,如果还有占用则free=false
boolean free = exclusiveCount(nextc) == 0;
//如果是完全释放则将当前线程设置为null
if (free)
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
//更新同步状态
setState(nextc);
return free;
}
//判断当前占有写锁的线程是否是当前线程,如果是返回true,否则返回false
protected final boolean isHeldExclusively() {
return getExclusiveOwnerThread() == Thread.currentThread();
}
?
?
?
?
?