曾经在做开发的过程中,编写了如下一段代码:
class="html" name="code"> map.put("dbradius","C:/temp/dbradiusx_script.xml");
map.put("radius","C:/temp/radius_script.xml");
/* * 保证脚本可用 */ public boolean isUsable(){ Iterator<String> iterator = map.keySet().iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()){ String key = iterator.next(); File f = new File(map.get(key)); if(!f.exists()){ MyTools.getLogger().error(" path " +map.get(key)+ " is unavaible!"); map.remove(key); } } return map.size()>0?true:false; }
功能非常简单,就是将map中的value值所代表的非法路径(不存在的文件)移除。执行后报错,如下:
Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException at java.util.HashMap$HashIterator.nextEntry(HashMap.java:793) at java.util.HashMap$KeyIterator.next(HashMap.java:828) at com.network.manager.nmsmanager.db.util.Bootstrap.isUsable(Bootstrap.java:68) at com.network.manager.nmsmanager.db.util.Bootstrap.executeTasks(Bootstrap.java:82) at com.network.manager.nmsmanager.db.util.Bootstrap.main(Bootstrap.java:49)
出错的根本原因在于HashMap为了保证线程安全,采取了一种策略,分析完HashMap的源代码就会知道问题出在哪里了。
如上可以这样来解决,如下:
while(iterator.hasNext()){
String key = iterator.next();
File f = new File(map.get(key));
if(!f.exists()){
MyTools.getLogger().error(" path " +map.get(key)+ " is unavaible!");
iterator.remove();// 只有在调用过next方法后才可调用iterator的remove
}
}
Iterator?支持从源集合中安全地删除对象,只需在?Iterator?上调用?remove()?即可。这样做的好处是可以避免?ConcurrentModifiedException?,这个异常顾名思意:当打开?Iterator?迭代集合时,同时又在对集合进行修改。有些集合不允许在迭代时删除或添加元素,但是调用Iterator?的?remove()?方法是个安全的做法。
通常来说,Map是一个由键值对组成的数据结构,且在集合中每个键是唯一的。下面就以K和V来代表键和值,列出一下java中关于Map的九大问题,也是面试中经常遇到的问题,如下:
在分析完源代码,读者可以回顾一下这几个问题。
Map<String, String[]> paraMap = new HashMap<String, String[]>();
for( Entry<String, String[]> entry : paraMap.entrySet() )
{
String appFieldDefId = entry.getKey();
String[] values = entry.getValue();
}
?
?
HashMap 的底层由一个散列表来实现,存储的内容是键值对(key-value),且键值不能重复,最多允许有一个null值。
?
1、Map与Set的关系
?
Set集合的特点是不能存储重复元素,不能保持元素插入时的顺序,且key值最多允许有一个null值。
由于Map中的key与Set集合特点相同,所以如果将Map中的value值当作key的附属的话,所有的key值就可以组成一个value集合。
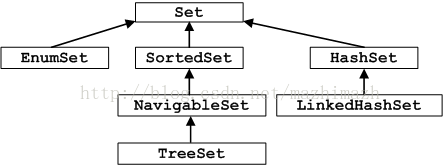
来看一下两个集合的实现类图:
?
 ? ? ?
? ? ?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?Set 集合框架图?
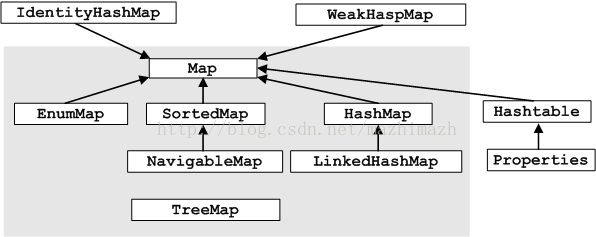
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Map集合框架图?
可以看到,两者的类图特别的相似。
?
2、Map与Set的关系
?
Map接口中定义的部分重要方法如下:
public interface Map<K,V> {
boolean containsKey(Object key);
boolean containsValue(Object value);
V get(Object key);
// Modification Operations
V put(K key, V value);
V remove(Object key);
// Bulk Operations
void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m);
void clear();
// Views
Set<K> keySet(); // 由于Map集合的key不能重复,key之间无顺序,所以Map集合中的所有key就可以组成一个Set集合
Collection<V> values(); // 获取所有的values集合
Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet(); // 获取所有的key-value键值对,由Map.Entry<K,V>来表示
interface Entry<K,V> { // 表示key-value对实体
K getKey();
V getValue();
V setValue(V value);
// 省略部分常见方法
}
// 省略部分常见的方法
}
对部分方法说明一下:
为了能够更好的表示这个key-value值,接口中还定义了一个Entry<K,V>接口,并且在这个接口中定义了一些操作key和value的方法。
?
3、Map中定义的变量及构造函数
?
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable{
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16; // 默认的初始化容量大小,必须是2的平方
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; // 最大的容量
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; // 指定负载因子
transient Entry[] table; // 存储key-value对
transient int size; // 存储的实际key-value对数量
int threshold; // 所能容纳的key-value对极限
final float loadFactor; // 负载因子
transient int modCount; // 记录修改内容的次数
}
代码中有几个变量需要说明一下:
HashMap提供了几个构造函数,如下:
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor);
// Find a power of 2 >= initialCapacity
int capacity = 1;
while (capacity < initialCapacity) // 计算出大于initialCapacity的最小的2的n次方值
capacity <<= 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = (int)(capacity * loadFactor); // 设置容量极限
table = new Entry[capacity]; // 将刚计算出的capacity当作Entry数组的大小
init();
}
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
threshold = (int)(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY * DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
table = new Entry[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];
init();
}
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this(Math.max((int) (m.size() / DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR) + 1,DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY), DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
putAllForCreate(m);
}
由第一个构造函数可以看出,其实际的capacity一般是大于我们指定的initialCapacity,除非initialCapacity正好是2的n次方值。
?
4、key-value存储实体 - Entry
?
接着就来说一下HashMap的实现原理吧。首先来看一下代表key-value对的Entry实现,如下:
private static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { // 实现Map接口中定义的Entry接口
int hash;
K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
protected Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Entry<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
protected Object clone() {
return new Entry<>(hash, key, value,(next==null ? null : (Entry<K,V>) next.clone()));
}
public K getKey() { // 获取key值
return key;
}
public V getValue() { // 获取value值
return value;
}
public V setValue(V value) { // 为value设置新的值
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
V oldValue = this.value;
this.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) { // 通过比较key和value值来确定两个Entry是否相等
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;
return (key==null ? e.getKey()==null : key.equals(e.getKey())) &&
(value==null ? e.getValue()==null : value.equals(e.getValue()));
}
public int hashCode() {
return hash ^ (value==null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
}
public String toString() {
return key.toString()+"="+value.toString();
}
}
? ? ? ?了解了key-value存储的基本结构后,就可以考虑如何存储的问题了。HashMap顾名思义就是使用哈希表来存储的,哈希表为解决冲突,采用了开放地址法和链地址法来解决问题。Java中HashMap采用了链地址法。链地址法,简单来说,就是数组加链表的结合。在每个数组元素上都一个链表结构,当数据被hash后,得到数组下标,把数据放在对应下标元素的链表上。
? ? ? ?当程序试图将多个 key-value 放入 HashMap 中时,以如下代码片段为例:
HashMap<String , Double> map = new HashMap<String , Double>();
map.put("语文" , 80.0);
map.put("数学" , 89.0);
map.put("英语" , 78.2);
? ? ? ?HashMap 采用一种所谓的“Hash 算法”来决定每个元素的存储位置。
? ? ? ?当程序执行 map.put("语文" , 80.0); 时,系统将调用"语文"的 hashCode() 方法得到其 hashCode 值——每个 Java 对象都有 hashCode() 方法,都可通过该方法获得它的 hashCode 值。得到这个对象的 hashCode 值之后,系统会根据该 hashCode 值来决定该元素的存储位置。
对于数组类型的Key值是怎么算HashCode值呢?
Map<String[], String> paraMap = new HashMap<String[], String>();
?
5、添加元素
?
?HashMap 类的 put(K key , V value) 方法的源代码:
/*
* 当向HashMap中添加mapping时,由key的hashCode值决定Entry对象的存储位置,当两个 key的hashCode相同时,
* 通过equals()方法比较,返回false产生Entry链,true时采用覆盖行为
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
/*
* 如果hash值相同且key值的索引或内容相同,则采取覆盖行为,然后返回旧值
* 这样不会对modCount进行加1操作,也就是说这样不认为是结构发生了改变
*/
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
? ? ?当key值为空时,调用putForNullKey()方法进行值的添加,如下:
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(0, null, value, 0);
return null;
}
void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) { }
? ? ?当系统决定存储 HashMap 中的 key-value 对时,完全没有考虑 Entry 中的 value,仅仅只是根据 key 来计算并决定每个 Entry 的存储位置。这也说明了前面的结论:我们完全可以把 Map 集合中的 value 当成 key 的附属,当系统决定了 key 的存储位置之后,value 随之保存在那里即可。 ? ??
? ? ?如果key为null,则hashCode值为0。所以需要遍历table[0]处的Entry链。如果已经存在null键,则覆盖并返回原始值。否则调用addEntry()方法进行添加。
接着看put(K key,V value)方法,有如下源代码:
int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); // 计算hash值
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); // 计算保存在table数组索引的位置
? ? 根据 hashCode() 返回值来计算 Hash 值的方法,并且会调用 indexFor() 方法来计算该对象应该保存在 table 数组的哪个索引,源代码如下:
static int hash(int h) {
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
? ? static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
? ? ? ? return h & (length-1);
? ? }
对两个方法的说明如下: ? ? ??
? ? ? ? 当调用put()方法向 HashMap 中添加 key-value 对,由其 key 的 hashCode() 返回值决定该 key-value 对(就是Entry 对象)的存储位置。当两个 Entry 对象的 key 的 hashCode() 返回值相同时,将由 key 通过 eqauls() 比较值决定是采用覆盖行为(返回 true),还是产生 Entry 链(返回 false),而且新添加的 Entry 位于 Entry 链的头部,这是通过调用addEntry()方法来完成的,源码如下:
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex){
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex]; // 获取指定 bucketIndex 索引处的 Entry
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e); // 将新创建的 Entry 放入 bucketIndex 索引处,并让新的 Entry 指向原来的 Entry
// 如果 Map 中的 key-value 对的数量超过了极限
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length); // 把 table 对象的长度扩充到 2 倍
}
? ? ? 将新添加的 Entry 对象放入 table数组的 bucketIndex 索引处。如果 bucketIndex 索引处已经有了一个 Entry 对象,那新添加的 Entry 对象指向原有的 Entry 对象(产生一个 Entry 链),如果 bucketIndex 索引处没有 Entry 对象, e 变量是 null,也就是新放入的 Entry 对象指向 null,也就是没有产生 Entry 链。
?
5、获取元素
?
?get()方法的源代码如下:
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
// 搜索该Entry链的下一个Entry,有多个Entry链时必须顺序遍历,降低了索引的速度
// 如果Entry链过长,说明发生“Hash”冲突比较频繁,需要采用新的算法或增大空间
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
? ? ? ? 当 HashMap 的每个 bucket 里存储的 Entry 只是单个 Entry 时的 HashMap 具有最好的性能:当程序通过 key 取出对应 value 时,只要先计算出该 key 的 hashCode() 返回值,在根据该 hashCode 返回值找出该 key 在 table 数组中的索引,然后循环遍历查找 hash值相同,key值相同的value。
? ? ? ? key为空值时调用getForNullKey()方法,源代码如下:
private V getForNullKey() {
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null)
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
key为null的Entry只可能存在于索引值为0处,遍历这个链即可。
?
6、获取key集合、values集合和Entry集合
?
分别调用如下的三个方法的进行集合的获取,其中有两个定义在AbstractMap类中,如下:
transient volatile Set<K> keySet = null;
transient volatile Collection<V> values = null;
下面一个为HashMap中,如下:
private transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet = null;
通过如果的方法来获取集合:
public Set<K> keySet() { // 所有的HashMap的key值放入到Set集合
Set<K> ks = keySet;
return (ks != null ? ks : (keySet = new KeySet()));
}
public Collection<V> values() { // 所有的HashMap的value值放入到Collection集合
Collection<V> vs = values;
return (vs != null ? vs : (values = new Values()));
}
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() { // 将Entry放到Set集合中
return entrySet0();
}
private Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet0() {
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> es = entrySet;
return es != null ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySet());
}
在每次获取对应的集合时,都会进行判断。如果变量的值来为空,则直接返回即可,否则调用静态的内部类来获取。能够看出来
?
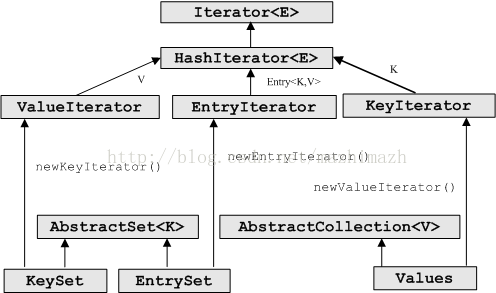
分别得获取KeySet、Values和EntrySet私有类的实例,那么他们是怎么从HashMap中取出自己需要的内容呢?其实这里会涉及到非常多的类和方法,大概框架如下所示:
?
 monospace; white-space: pre; background-color: #f0f0f0;">
monospace; white-space: pre; background-color: #f0f0f0;">
?
?
如上类中最重要的就是HashIterator类的实现,如下:
private abstract class HashIterator<E> implements Iterator<E> {
Entry<K,V> next; // next entry to return
int expectedModCount; // For fast-fail
int index; // current slot
Entry<K,V> current; // current entry
HashIterator() {
expectedModCount = modCount;
if (size > 0) { // advance to first entry
Entry[] t = table;
while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null); // 将index指向第一个table不为null的位置
}
}
public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
/*
* 这个方法是final类型的,不可以被子类覆盖,只有包访问权限,所以应用程序不可以调用
* 查找下一个Entry,下一个Entry可能与前一个Entry在不同的链表上。关于为什么这样定义还不是很清楚
*/
final Entry<K,V> nextEntry() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if ((next = e.next) == null) { // 如果遍历完一个Entry链,则继续查找下一个Entry链的索引
Entry[] t = table;
while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null);
}
current = e;
return e;
}
public void remove() {
if (current == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
Object k = current.key;
current = null;
HashMap.this.removeEntryForKey(k);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
}
和ArrayList一样,在获取到HashMap的Iterator对象后,就不可以调用HashMap中的方法添加或删除的操作了,否则会出现异常。可以使用HashIterator类进行当前的key-value对。
下面以EntrySet的实现为例,这个类是私有静态内部类,如下:
private final class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
return newEntryIterator();
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<K,V> e = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o;
Entry<K,V> candidate = getEntry(e.getKey());
return candidate != null && candidate.equals(e);
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return removeMapping(o) != null;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public void clear() {
HashMap.this.clear();
}
}
获取到EntrySet实例后就就可以调用iterator()方法进行元素的遍历了。用的是newEntryIterator()方法,这个方法定义如下:
Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> newEntryIterator() {
return new EntryIterator();
}
private final class EntryIterator extends HashIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
return nextEntry();
}
}
这个方法只实现了next()方法,这个方法中调用了HashIterator类中的final方法。定义为final,可能是一种遍历原则吧。其他都是继承HashIterator类中的方法,如hashNext()等方法。下面来举一个例子:
?
HashMap map=new HashMap();
map.put("a", "value1");
map.put("b", "value2");
map.put("c", "value3");
Set<Map.Entry<String,String>> s=map.entrySet();
Iterator iter=s.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iter.next());
}
最后运行的结果如下:b=value2
c=value3
a=value1